Purpose
A crankcase ventilation system is used to consume crankcase vapors in the combustion process instead of venting them to atmosphere.

Fresh air from the throttle body is supplied to the crankcase, mixed with blow-by gases and then passed through a crankcase ventilation valve into the supercharger inlet (L67).

Or into the intake manifold (L36).
Operation
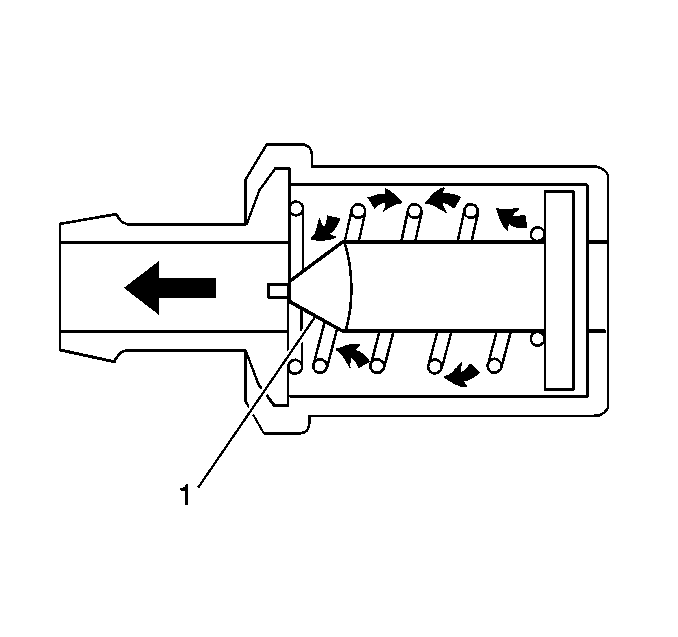
The primary control is through the crankcase ventilation valve (1) which meters the flow at a rate depending on inlet vacuum. To maintain idle quality, the crankcase ventilation valve restricts the flow when inlet vacuum is high. If abnormal operating conditions arise, the system is designed to allow excessive amounts of blow-by gases to back flow through the crankcase vent into the throttle body to be consumed by normal combustion.
