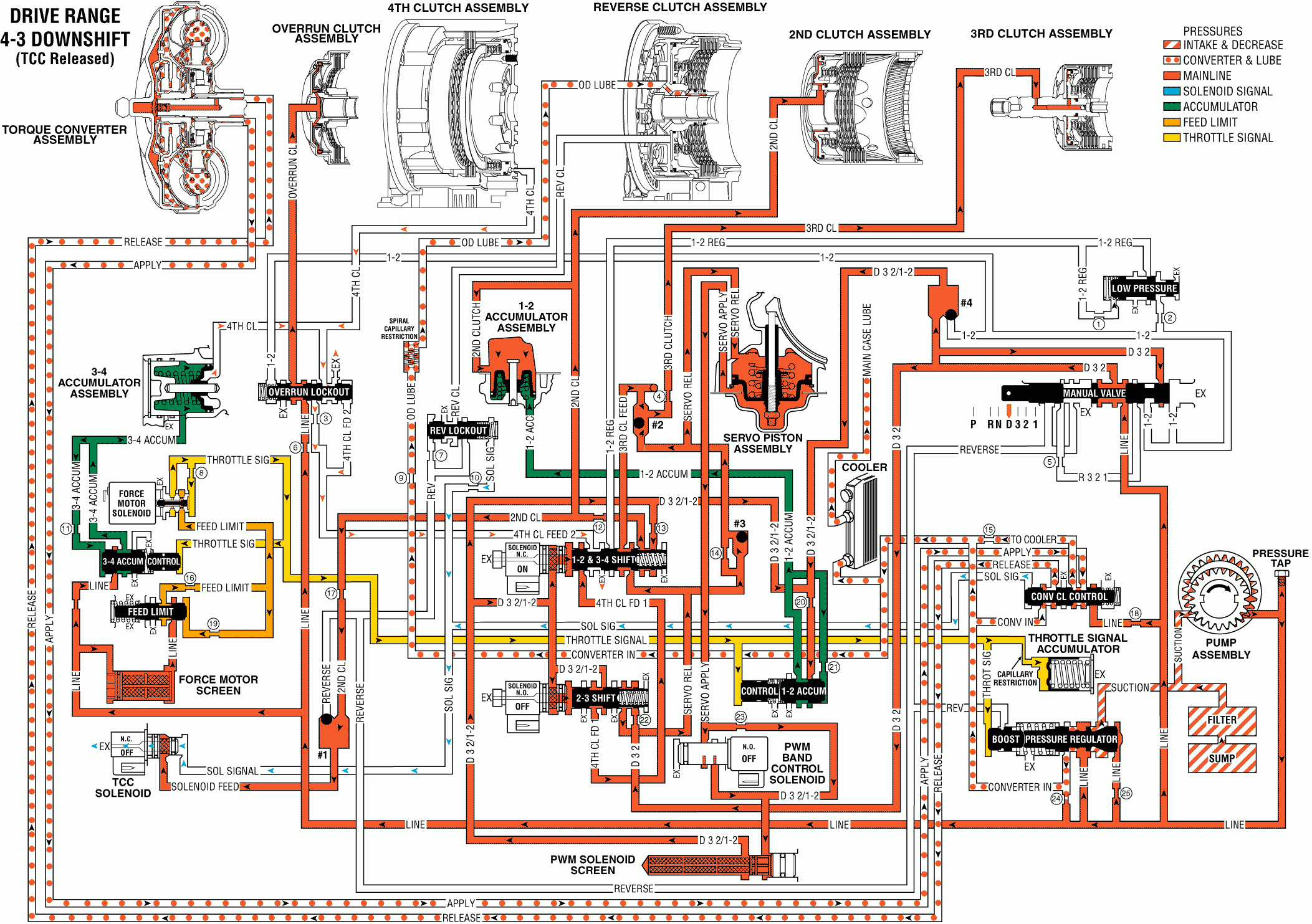
For 1990-2009 cars only
With the transmission operating in Fourth gear, a 4-3 downshift can occur due to coastdown or heavy throttle conditions. Also, increased engine load will cause a 4-3 downshift. During a 4-3 downshift the following changes occur to the transmissions hydraulic and electrical systems:
4th Clutch Releases & Overrun Clutch Applies
1-2/3-4 Shift Solenoid: Energized (turned ON) by the TCM, the solenoid opens and D32/1-2 fluid flows through the solenoid, acting on the 1-2/3-4 shift valve.1-2/3-4 Shift Valve: D32/1-2 fluid pressure from the solenoid moves the valve against spring force and into the Second and Third gear position, thereby causing the following:
| • | 4th clutch feed 1 fluid is blocked by the valve and the 4th clutch feed 2 fluid circuit is open to an exhaust port. |
| • | Servo release fluid is blocked from entering the 2nd clutch fluid circuit and fills the 3rd clutch feed fluid circuit. |
| • | Orificed D32/1-2 fluid at the spring end of the valve feeds the 2nd clutch fluid circuit. |
4th Clutch Piston: 4th clutch fluid pressure exhausts from the piston, thereby releasing the 4th clutch plates.
3-4 Accumulator Piston: With 4th clutch fluid exhausting, 3-4 accumulator fluid pressure and spring force move the piston to a Third gear position.
3-4 Accumulator Valve Train: Regulates line pressure into the 3-4 accumulator fluid circuit in relation to throttle signal fluid pressure.
Overrun Clutch Piston: Overrun clutch fluid pressure moves the piston to apply the overrun clutch and obtain Third gear.
Checkball #2: 3rd clutch feed fluid pressure unseats the checkball and, in addition to servo release fluid, feeds the 3rd clutch fluid circuit.
Force Motor Solenoid: Remember that the force motor solenoid continually adjusts throttle signal fluid pressure, and line pressure, in relation to TCM input signals.
Converter Clutch
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Solenoid: During the downshifting from Fourth gear to Third gear the TCM releases the converter clutch by de-energizing the TCC solenoid. When de-energized, the solenoid blocks solenoid feed fluid from entering the solenoid signal fluid circuit. The solenoid signal fluid circuit is open to an exhaust through the solenoid.TCC Control Valve: With solenoid signal fluid pressure exhausted, spring force moves the valve into the release position. This blocks line pressure from entering the apply fluid circuit and apply fluid returning from the converter enters the cooler fluid circuit. Also, 'converter in' fluid fills the release fluid circuit with the valve in the release position.
TCC Apply Checkball: This retainer & ball assembly, located in the turbine shaft, is unseated by release fluid pressure. This allows release fluid to quickly fill the converter.
Torque Converter: Release fluid is routed between the converter cover and pressure plate to keep the converter clutch released and fill the converter with fluid. Fluid exits the converter in the apply fluid circuit, flows through the TCC control valve and into the cooler fluid circuit.
Important: The converter clutch will re-apply in Third gear under normal operating conditions.
4-3 Downshift - Valves in Third Gear Position