For 1990-2009 cars only
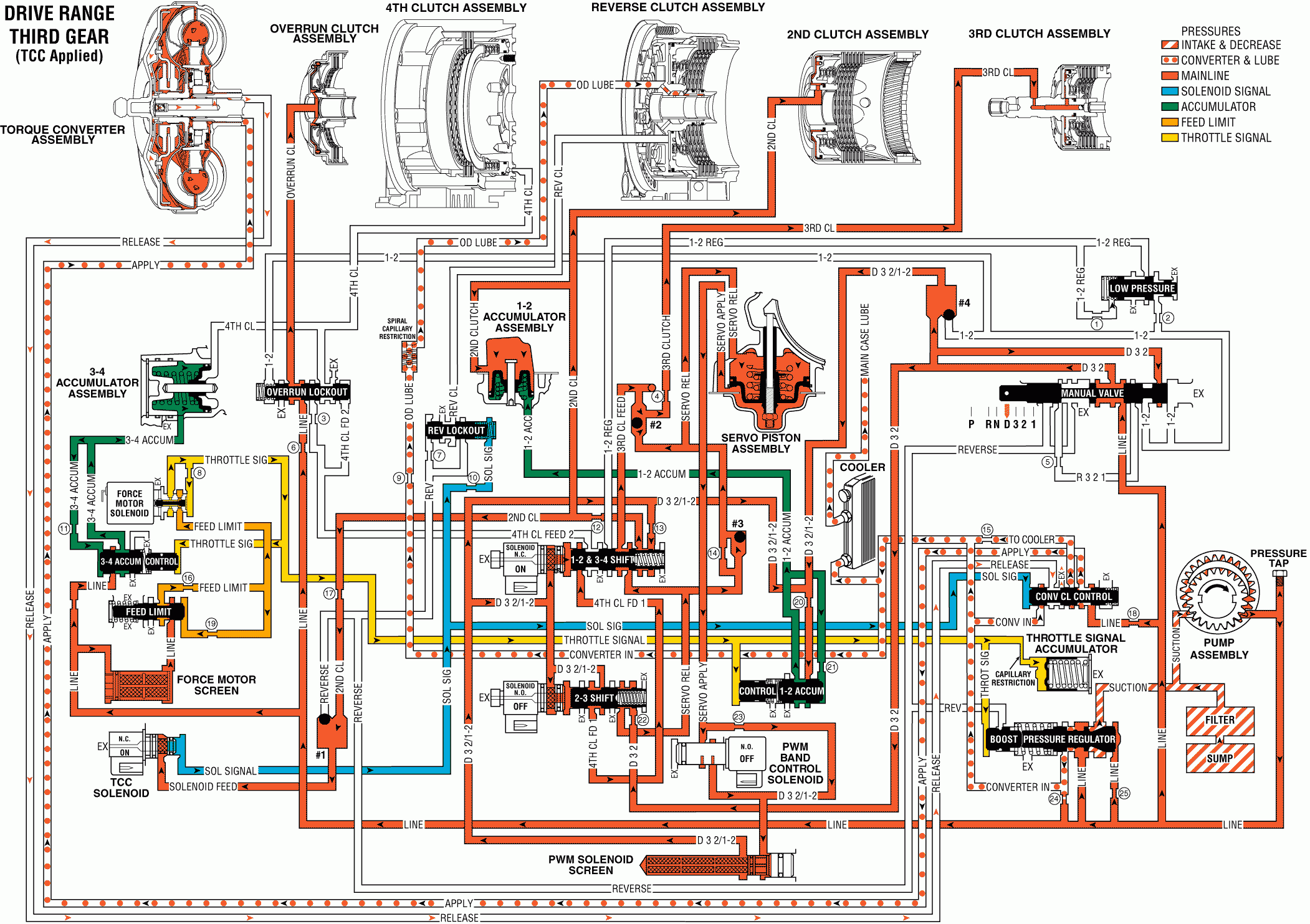
As vehicle speed increases further, and when other input signals to the TCM are appropriate, the TCM de-energizes the 2-3 shift solenoid to shift the transmission into Third gear.
2-3 Shift Solenoid: De-energized (turned OFF) by the TCM, the solenoid opens. D32/1-2 fluid pressure flows through the solenoid and acts on the end of the 2-3 shift valve.2-3 Shift Valve: D32/1-2 fluid pressure from the 2-3 shift solenoid moves the valve against spring force and into the Third and Fourth gear position. With the valve in this position, D32/1-2 fluid at the middle of the valve fills the 4th clutch feed 1 fluid circuit. Also, orificed D32 fluid is routed into the servo release fluid circuit.
Brake Band Releases
Checkball #3: Servo release fluid pressure unseats and flows past the checkball, thereby bypassing orifice #22d.Servo Piston: Servo release fluid pressure assists servo cushion and servo return spring forces acting on the servo piston. These forces overcome servo apply fluid pressure and move the piston and apply pin into the released position, thereby releasing the brake band. As the piston moves, some servo apply fluid is forced out of the servo.
PWM Band Apply Solenoid (323)
Low Speed Upshift (Below approximately 20 km/h, 13 mph): The TCM energizes the normally open solenoid to a maximum duty cycle (100%). This blocks D32/1-2 fluid from feeding the servo apply fluid circuit through the solenoid. In this position the solenoid also blocks exhausting excess servo apply fluid pressure. This excess servo apply fluid pressure exhausts through orifice #17, into the D32/1-2 fluid circuit and regulated at the pressure regulator valve.High Speed Upshift (Above approximately 20 km/h, 13 mph: The TCM keeps the solenoid de-energized and at 0% duty cycle. In the position the solenoid is open and exhausting excess servo apply fluid pressure flows through the solenoid and into the D32/1-2 fluid circuit. Exhausting through the solenoid and bypassing orifice #17 creates a faster release of the band as needed at higher speeds.
Important:: When the band is released and the transmission is operating in Third gear, the PWM solenoid is de-energized (normally open) and D32/1-2 fluid pressure passes through the solenoid.
1-2/3-4 Shift Solenoid: Energized (ON) as in Second gear, the solenoid is open and D32/1-2 fluid pressure acts on the solenoid end of the 1-2/3-4 shift valve.1-2/3-4 Shift Valve: As in Second gear, D32/1-2 fluid pressure from the 1-2/3-4 shift solenoid holds the valve against spring force and in the Second and Third gear position. In this position the following occurs:
| • | 4th clutch feed 1 fluid is blocked in preparation for a 3-4 upshift. |
| • | Servo release fluid flows through the valve and feeds the 3rd clutch feed fluid circuit. |
| • | D32/1-2 fluid at the spring end of the valve continues to feed the 2nd clutch fluid circuit. |
3RD Cutch Applies
Checkball #3: Both servo release fluid and 3rd clutch feed fluid are routed to the checkball. The ball remains unseated as both of these fluids feed the 3rd clutch fluid circuit.3rd Clutch Piston: Orificed 3rd clutch fluid pressure moves the piston to apply the 3rd clutch plates. The 3rd clutch fluid circuit orifice (#23b) helps control the apply feel of the 3rd clutch. Also, remember that the servo assembly acts as an accumulator to help cushion 3rd clutch apply by absorbing initial servo release fluid pressure.
Converter Clutch Applies
TCC Solenoid: Under normal operating conditions the TCC can either be applied or released in Third gear. To apply the TCC the TCM energizes the normally closed TCC solenoid, thereby opening the solenoid. This allows solenoid feed fluid to fill the solenoid signal fluid circuit.TCC Control Valve: Solenoid signal fluid pressure moves the valve against spring force and into the apply position. In this position release fluid is open to an exhaust port and line pressure feeds the apply fluid circuit.
Torque Converter: Apply fluid flows between the converter hub and stator shaft and fills the converter with fluid. This fluid pressure in the converter forces the converter clutch pressure plate against the converter cover. As the pressure plate applies, fluid from the release side of the pressure plate is forced back through the turbine shaft (506).
TCC Apply Checkball: Located in the end of the turbine shaft, this checkball is seated by exhausting release fluid pressure. This forces release fluid to exhaust through the orifice around the checkball. Orificing exhausting release fluid controls the apply feel of the converter clutch.
Cooler and Main Case Lubrication Fluid Circuits: With the TCC control valve in the apply position, these fluid circuits are fed by 'converter in' fluid through orifice #3.
Overdrive Range, Third Gear - TCC Applied