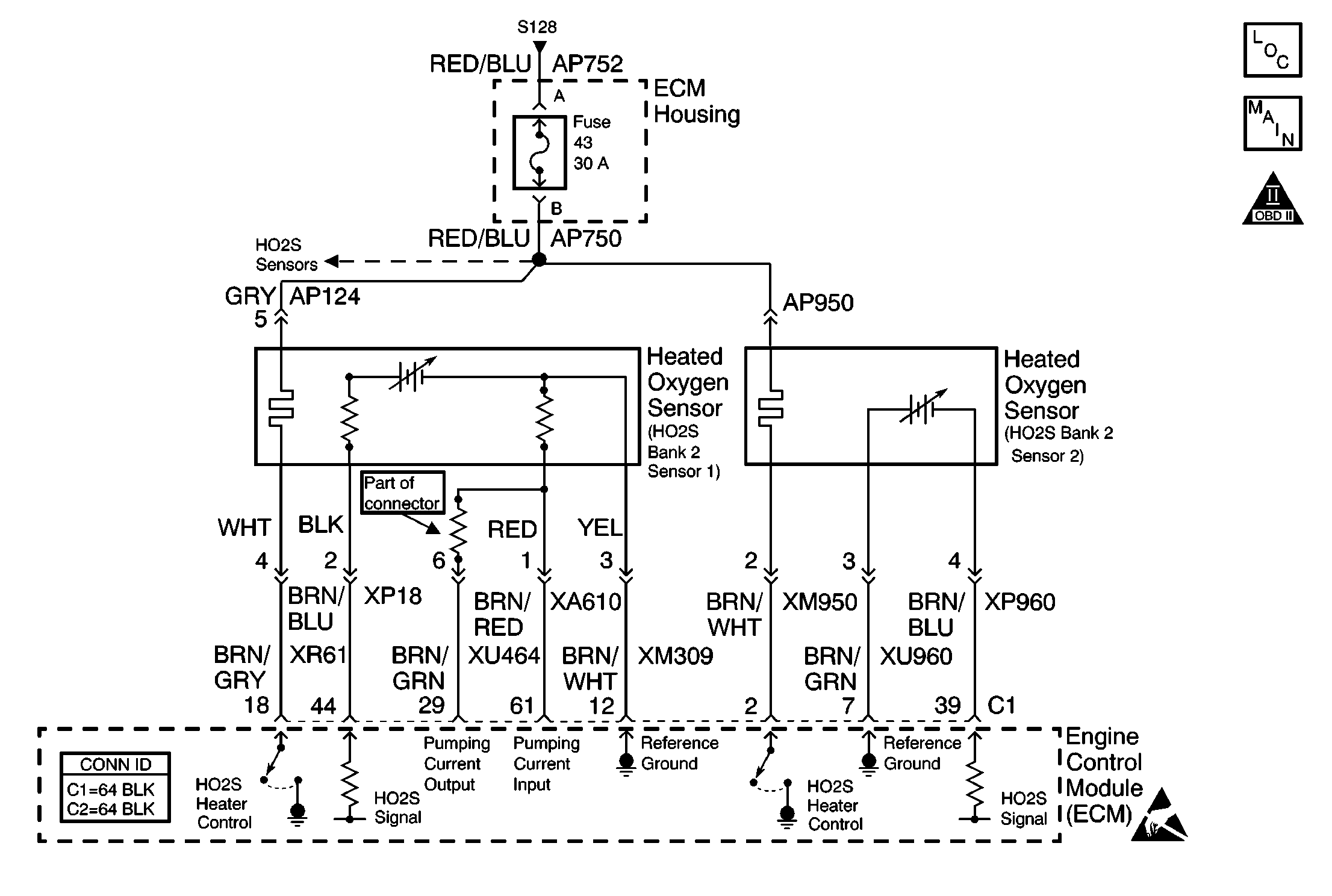
Circuit Description
The wide band heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust stream more quickly and accurately than the switching style HO2S. The wide range HO2S sensor functions more like an air fuel sensor. The wide band sensor consists of an oxygen sensing cell, an oxygen pumping cell, and a heater. The exhaust gas sample passes through a diffusion gap between the sensing cell and the pumping cell. The engine control module (ECM) supplies a signal voltage to the HO2S and uses this voltage as a reference to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system. An electronic circuit within the ECM controls the pump current through the oxygen pumping cell in order to maintain a constant signal voltage. The ECM monitors the voltage variation on the signal circuit and attempts to keep the voltage constant by increasing or decreasing the amount of current flow or reversing the direction of the current flow to the pumping cell. By measuring the direction and amount of current required to maintain the signal voltage, the ECM can determine the concentration of oxygen in the exhaust. The signal voltage is displayed as a lambda value. A lambda value of 1 is equal to a stoichiometric air fuel ratio of 14.7:1. Under normal operating conditions, the lambda value will remain around 1. When the system is lean, the oxygen level will be high and the lambda signal will be high (greater than 1). When the oxygen level is low, the lambda signal will be low (less than 1). The ECM uses this information to maintain the proper air/fuel ratio.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The following DTCs are not set: P0300-P0306, P0171, P0172, P0174, P0175, P0440, P0442, P0443, P0446, P0455, and P0460. |
| • | Engine at operating temperature |
| • | The engine speed must be between 1400 and 2400 RPM. |
| • | Engine load 8-12 percent |
| • | Mass air flow 18-22 g/s |
| • | Throttle position 6-10 percent |
| • | The secondary air diagnosis is not running. |
| • | Closed loop fuel control has not reached maximum or minimum. |
| • | There is no EVAP high loading indicated. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM has determined that the HO2S sensor does not respond as expected.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) and records the operating conditions in the Freeze Frame on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The ECM turns OFF the MIL after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles in which no failures are reported by this diagnostic or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | The ECM battery voltage is interrupted. |
| • | The scan tool clears the MIL/DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Notice: Using the J 35616-A Connector Test Adapter Kit will prevent damage to the harness connector terminals.
Use theJ 35616 connector test adapter kit for any test that requires probing the ECM harness connector or a component harness connector. Using this kit will prevent damage to the harness connector terminals.
This DTC is most likely to set by a blocked passage that does not allow the exhaust gas to pass through the sensor. Check for any sign of contamination and the source of the contamination.
Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Inspect the HO2S 1 harness for any signs of high resistance or shorts to ground. Use J 39200 DMM if necessary.
An open fuse in the HO2S heater circuit may be caused by the heater element in one of the sensors. The condition may not be present until the heater operates for a period of time. If no fault is present in the heater circuit, monitor the amperage of each heater using the DMM to determine if one of the heater elements is the cause of the open fuse.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
Multiple DTCs will set if the supply voltage to the sensor heaters is open.
-
Any exhaust leak, even a small one, can affect the operation of the HO2S. The ECM compares the reading of sensor 1 with the reading of sensor 2 as part of the diagnosis. A leak between sensor 1 and sensor 2 may set a DTC.
-
The test lamp may illuminate or flash depending on the operating conditions. This indicates the ECM and the control circuit are functioning. The engine must be running for the ECM to operate the control circuit.
-
A short between the signal circuit and the reference ground circuit or the pump current input and output circuits may not appear on the voltage tests. The ECM must be disconnected and each circuit tested for continuity with the other HO2S circuits.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||
Using the scan tool, observe the DTC information. Are all of the HO2S heater DTCs set? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 | |||||||
3 |
Is fuse 43 open? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 20 | ||||||
Did you find and repair an exhaust leak? | -- | Go to Step 27 | Go to Step 5 | |||||||
5 |
Important: The ignition must be OFF when disconnecting or connecting the HO2S electrical connector.
Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 6 | ||||||
6 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 23 | ||||||
7 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 9 | ||||||
8 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 26 | ||||||
Does the test lamp illuminate or flash? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 18 | |||||||
10 |
Is the voltage within the specified value? | 2-4 V | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 15 | ||||||
11 | Measure the voltage of the HO2S reference ground circuit at the ECM side of the connector to battery ground. s the voltage within the specified value? | 2-4 V | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 15 | ||||||
12 | Measure the voltage of the HO2S pump current input circuit at the ECM side of the connector to battery ground. s the voltage within the specified value? | 0.2-0.4 V | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 15 | ||||||
13 | Measure the voltage of the HO2S pump current output circuit at the ECM side of the connector to battery ground. s the voltage within the specified value? | 0.2-0.4 V | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 15 | ||||||
Did you find and correct a problem? | -- | Go to Step 27 | Go to Step 24 | |||||||
15 | Was the voltage above the specified value? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 16 | ||||||
16 |
Did you find and correct a problem? | -- | Go to Step 27 | Go to Step 25 | ||||||
17 |
Did you find and correct a problem? | -- | Go to Step 27 | Go to Step 25 | ||||||
18 |
Did you find and correct a problem? | -- | Go to Step 27 | Go to Step 25 | ||||||
19 |
Did you find and correct a problem? | -- | Go to Step 27 | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||
20 | Locate and repair the open in the switched B+ circuit from the Engine Controls Power Relay to the splice for the oxygen sensors. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 27 | -- | ||||||
21 | Repair or replace the terminal as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 27 | -- | ||||||
22 | Repair the short to ground in the heater control circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 27 | -- | ||||||
23 | Repair the open in the B+ circuit from the splice to the oxygen sensor. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 27 | -- | ||||||
24 | Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Step 27 | -- | ||||||
25 |
Did you find and correct a problem? | -- | Go to Step 27 | Go to Step 26 | ||||||
26 |
Important:
Replace the ECM. Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 27 | -- | ||||||
27 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the diagnostic Passed? | -- | Go to Step 28 | Go to Step 2 | ||||||
28 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
