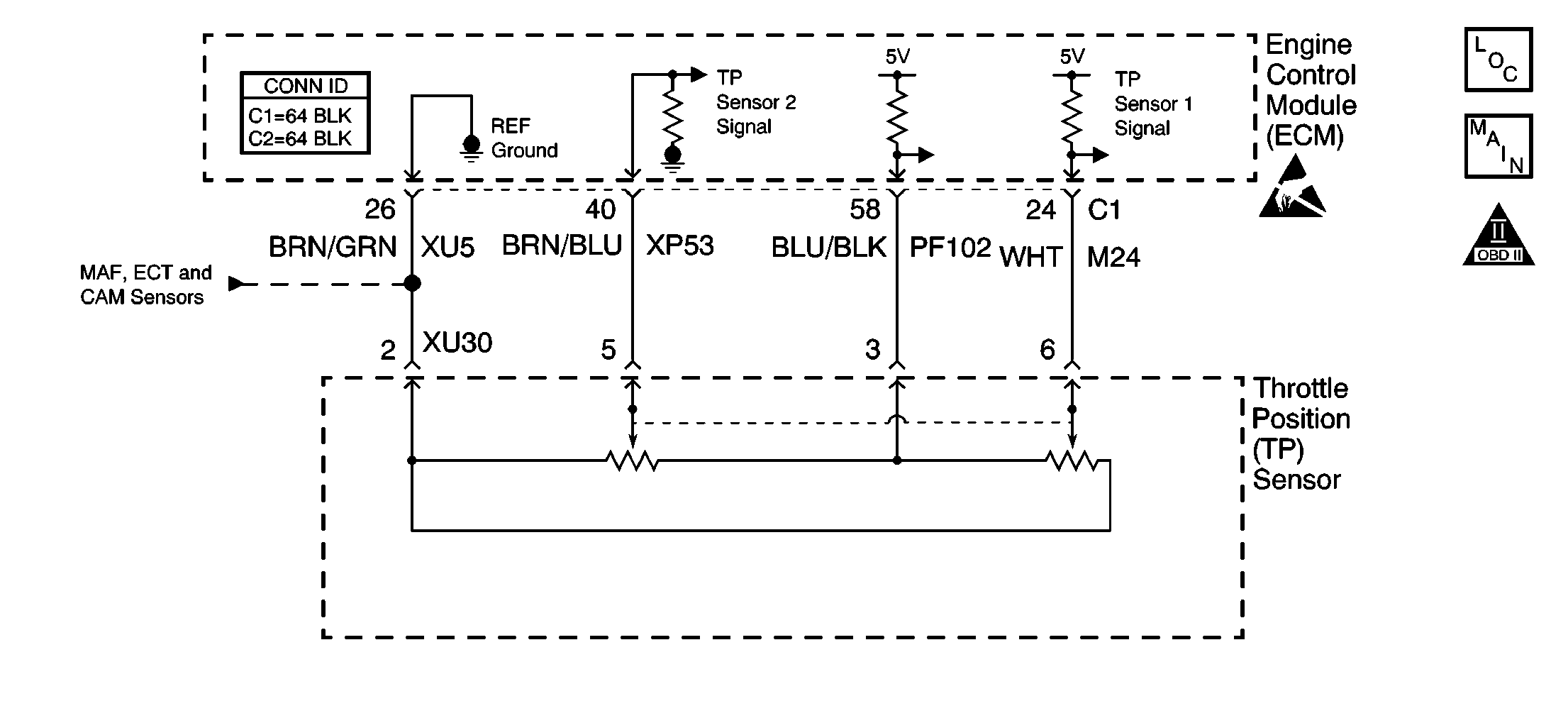
Circuit Description
The TP sensor 2 is part of the electronic throttle control (ETC). The TP sensor 2 is used in order to compare to the TP sensor 1. The ECM supplies a 5 volt reference and a ground to the sensor. The TP sensor then sends a voltage signal back to the ECM. The ECM then compares this voltage to the TP sensor 1. If the voltage goes above or below the calibrated value then this DTC will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The battery voltage is more than 7.0 volts.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The throttle position (TP) sensor 2 voltage is less than 0.156 volt, or more than 4.8 volt. |
| • | The difference between TP sensor 1 and TP sensor 2 is more than 13 percent. |
| • | One of the above conditions is met for 140 ms (0.140 seconds). |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The engine control module (ECM) illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the first drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The ECM attempts to record the operating conditions in the Freeze Frame. |
| • | The vehicle will default to the limp home mode. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The ECM turns off the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles in which no failures are reported by this diagnostic or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | The ECM battery voltage is interrupted. |
| • | The scan tool clears the MIL/DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
With the ignition ON and the engine OFF, view the TP sensor 1 and the TP sensor 2 with a scan tool. Slowly depress the accelerator pedal, the voltage on TP sensor 1 should increase steadily from 0.2 volt to about 4.6 volt. TP sensor 2 should move opposite from above 4.0 to about 0.2 volt. If one sensor value changes and the other does not, inspect the sensor circuits for high resistance or shorts. If the circuits are OK, replace the TP sensor.
Notice: Using the J 35616-A Connector Test Adapter Kit will prevent damage to the harness connector terminals.
Use the J 35616 connector test adapter kit for any test that requires probing the ECM harness connector or a component harness connector.
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connections at the ECM or at the component--Inspect the harness connectors for a poor terminal to wire connection. Refer to Engine Control Module Diagnosis , Checking Terminal Contact, for the proper procedure. |
| • | Damaged harness--Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the scan tool while moving the related connectors and the wiring harnesses. A change in the display may help locate the fault. |
Refer to Symptoms for the Intermittents.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step tests for the proper operation of the circuit in the low voltage range.
-
This step tests for the proper operation of the circuit in the high voltage range. If the fuse in the jumper opens when you perform this test, the signal circuit is shorted to ground.
-
This step tests for a short to voltage in the 5 volt reference circuit.
-
This step tests for a high resistance or an open in the ground circuit.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
2 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the TP sensor 2 parameter is within the specified range? | 0.2 V to 4.8 V | Go to Diagnostic Aids | Go to Step 3 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the TP sensor 2 parameter is less than the specified value? | 0.2 V | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 10 | |
Does the scan tool indicate that the TP sensor 2 parameter is more than the specified value? | 4.8 V | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 8 | |
Does the voltage measure less than the specified value? | 5.2 V | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 7 | |
Does the resistance measure less than the specified value? | 5 ohms | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 11 | |
7 | Test the 5 volt reference circuit of the TP sensor 2 for a short to voltage. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 13 |
8 | Test the 5 volt reference circuit of the TP sensor 2 for a short to ground, a high resistance, or an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 9 |
9 | Test the signal circuit of the TP sensor 2 for a short to ground, a high resistance, or an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 13 |
10 | Test the signal circuit of the TP sensor 2 for a short to voltage. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 13 |
11 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 13 |
12 | Inspect for connections at the harness connector of the TP sensor 2. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the problem? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 14 |
13 | Inspect for poor connections at the harness connector of the engine control module. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 15 |
14 | Replace the throttle body assembly . Refer to Throttle Body/Throttle Position Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 16 | -- |
15 |
Important: Perform the set up procedure for the engine control module. Replace the engine control module. Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement/Programming . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 16 | -- |
16 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 2 |
17 | Does the scan tool display any additional, undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
