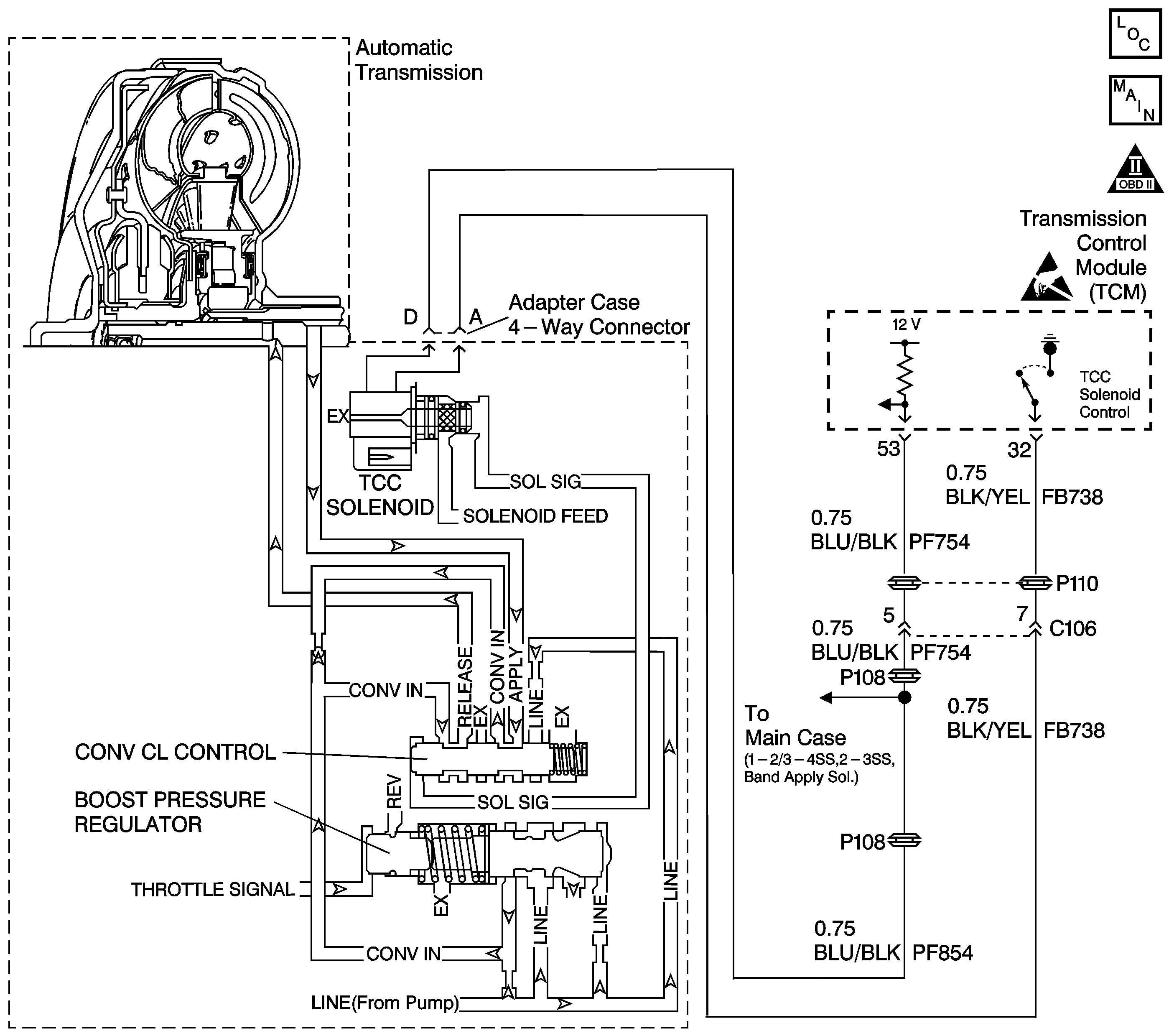
Circuit Description
The torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve is a normally-closed exhaust valve that is used to control solenoid signal fluid acting on the converter clutch control valve. The TCC solenoid valve attaches to the adapter case valve body. When grounded (energized) by the transmission control module (TCM), the TCC solenoid valve stops solenoid feed oil from exhausting. This causes solenoid signal oil pressure to increase and move the converter clutch control valve against spring force and into the apply position. In this position, release fluid is open to an exhaust port and apply fluid fills the fluid circuit. The converter apply fluid applies the TCC. When the TCM no longer provides a ground path, the TCC solenoid valve de-energizes and apply fluid exhausts, releasing the TCC.
When the TCM detects low torque converter slip when the TCC is commanded OFF, then DTC P0742 sets. DTC P0742 is a type B DTC.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No engine speed DTCs P0725 or P0727. |
| • | No APP sensor DTCs P0120, P0121, P0122 or P0123. |
| • | No VSS DTC P0722. |
| • | No TCC enable solenoid valve DTC P0743. |
| • | The TP angle is 18-100%. |
| • | The engine speed is 1000-3488 RPM. |
| • | The vehicle speed is 25-120 km/h (15-74 mph). |
| • | The engine torque is 50-200 N·m (68-271 lb-ft). |
| • | The commanded gear is not 1st. |
| • | The gear range is D4. |
| • | The TCC is commanded OFF. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0742 sets during the second consecutive trip in which the following condition occurs. This condition must occur twice per trip.
The TCC slip speed is -20 to +64 RPM for 3 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | Early production - The TCM illuminates the service transmission lamp (STL) and sends a MIL request to the ECM on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails. The ECM then illuminates the MIL. |
| • | Late production - The TCM flashes the Sport Mode Lamp and sends a MIL request on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails. The TCM then illuminates the MIL. |
| • | The ECM records the operating conditions in the Freeze Frame at the time of the MIL request from the TCM. |
| • | The transmission operates in the default mode (maximum line pressure, command 4th gear, inhibit TCC, freeze shift adapts). |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | Early production - The TCM turns off the STL as soon as the fault is no longer present. |
| • | Late production - The TCM stops flashing the sport mode lamp as soon as the fault is no longer present. |
| • | The ECM turns off the MIL after three consecutive drive trips during which the TCM sends no MIL request. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are present by this diagnostic or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | The scan tool clears the MIL/DTC. |
| • | The TCM cancels the DTC default mode actions when the fault no longer exists and the ignition switch is Off long enough in order to power down the TCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Vehicles equipped with Fuel Cap Lamps utilize the Sport Mode lamp to indicate a transmission malfunction. In these vehicles, the Sport Mode Lamp flashes at 200 millisecond intervals when the TCM commands the lamp ON. |
| • | Vehicles not equipped with Fuel Cap Lamps are equipped with a dedicated Service Transmission Lamp (STL) on the Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC). The STL illuminates steadily when the TCM commands the lamp ON. |
| • | If the TCC is mechanically stuck ON with the parking brake applied and any gear range selected, the TCC fluid mechanically applies the TCC. TCC fluid mechanically applying the TCC can cause an engine stall. |
| • | First diagnose and clear any engine DTCs or TP sensor codes that are present. Then inspect for any transmission DTCs that may have reset. |
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the diagnostic table.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the Scan Tool in order to record the Freeze Frame and Failure Records. Using the Clear Info function erases the Freeze Frame and Failure Records from the ECM/TCM. Does the Scan Tool display a TCC Slip Speed within the specified range while the TCC Solenoid is off? | -20 to +64 RPM | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
3 | The TCC is hydraulically stuck on. Perform the following inspections:
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | -- | |
4 | Perform the following procedure in order to verify the repair:
Is the TCC slip speed within the specified RPM for 2 seconds? | 200-1200 RPM | System OK |
