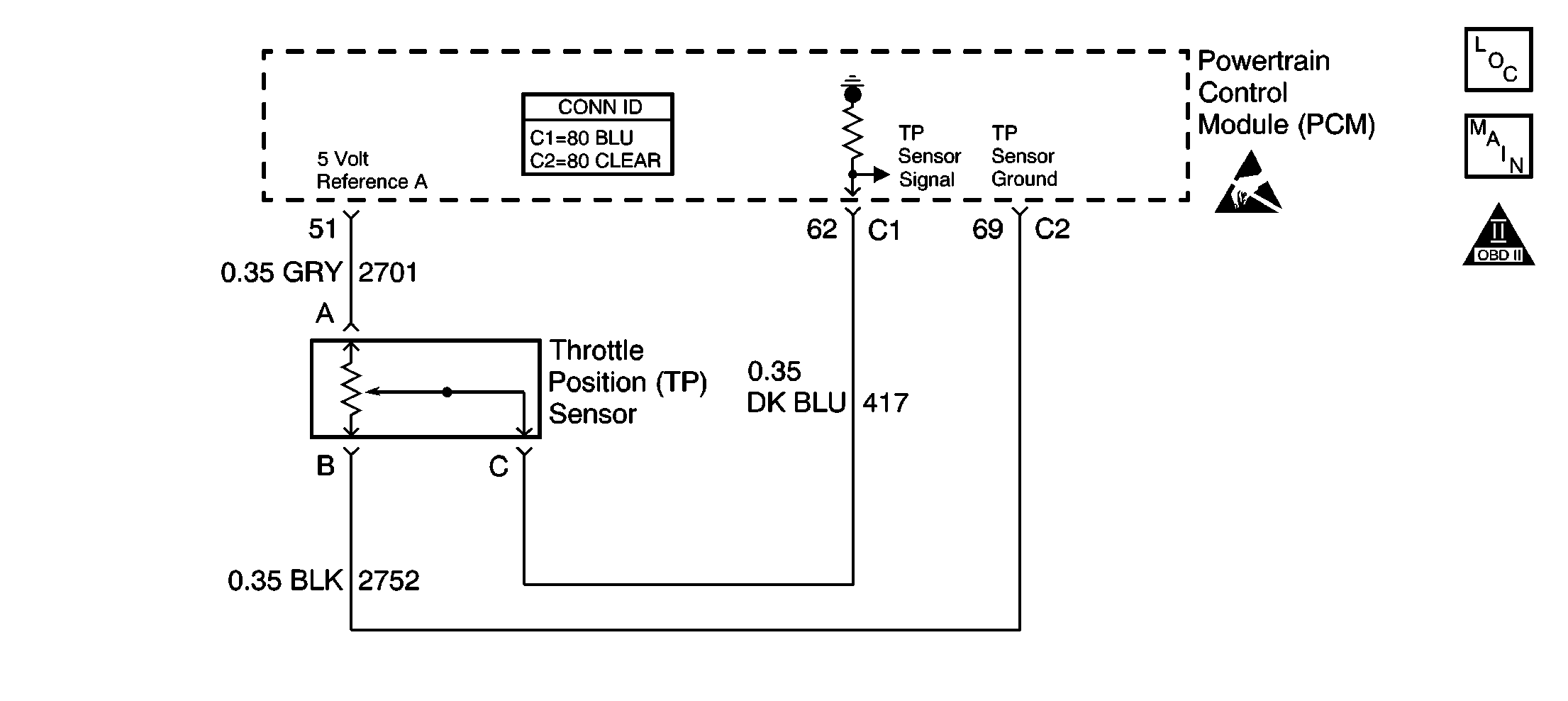
Circuit Description
The throttle position (TP) sensor is potentiometer used to indicate the amount of throttle opening. The PCM supplies the TP sensor with a voltage reference and a ground. The TP sensor provides a signal voltage to the PCM relative to throttle blade angle. With the throttle closed, the PCM should detect a low signal voltage. At wide open throttle, the PCM should detect a high signal voltage. The PCM checks the TP sensor to ensure that the sensor is functioning properly. The PCM predicts a TP sensor value based on MAP, and engine speed. The PCM compares the predicted value to the actual TP sensor input. DTC P0121 will set if the actual TP sensor input does not closely match the predicted value.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | MAP, IAC or TP sensor DTCs are not failing. |
| • | The engine is running. |
| • | ECT is more than 0°C (32°F). |
| • | IAC valve position is between 10 and 160 counts. |
| • | MAP is less than 55 kPa to check for a stuck high TP signal. |
| • | MAP is more than 63 kPa to check for a stuck low TP signal. |
| • | Traction control inactive |
| • | Engine over-temp inactive |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The actual TP sensor input does not match the predicted value.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) the first time the malfunction is detected. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame and Fail Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF after the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has been run and passed. |
| • | The History DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool Clear DTC Information function. |
Diagnostic Aids
If the conditions is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
If DTC P1635 sets at the same time, this indicates that the 5 volt reference circuit is either shorted to a ground or shorted to a voltage. The 5 volt reference circuit is internally connected within the PCM.
-
The MAP value should change with the engine speed. If a MAP sensor voltage changes, there is no malfunction with the MAP sensor.
-
This step tests for an intermittent connection at the sensor.
-
If the TP sensor voltage changes, there is no malfunction with the TP sensor wiring or the PCM.
-
This tests the 5 volt reference circuit, signal circuit, and the PCM. If the scan tool displayed 5 volts, the TP sensor circuits are OK.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||
Did P1404 or P1635 or any MAP sensor DTCs also set? | -- | |||||||||||
Does the MAP sensor voltage change when the engine speed changed? | 2000 RPM | |||||||||||
Is the MAP value affected by moving the harness or connectors? | -- | |||||||||||
5 |
Did the MAP value change smoothly through the entire range of the test without any erratic readings? | -- | ||||||||||
6 | Apply 20 inches Hg vacuum to the MAP sensor. Is the MAP sensor reading the same or less than the specified value? | 34 kPa | ||||||||||
7 | Disconnect the vacuum source from the MAP sensor. Does the MAP sensor reading return to the original value that you observed in step 5? | -- | ||||||||||
Does the TP sensor voltage go from below the specified value to above the specified value? | Below 1.0V to above 4.0V | |||||||||||
9 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic failed this ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||
10 |
Is the TP sensor voltage near the specified value? | 0.0V | ||||||||||
Jumper the TP sensor 5 volt reference circuit to the TP sensor signal circuit using a fused jumper wire. Is the TP sensor voltage near the specified value? | 5V | |||||||||||
12 | Replace the TP sensor. Refer to Throttle Position Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
13 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||
14 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||
15 |
Important: Program the replacement PCM. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
16 | Locate and repair the affected circuits. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
17 | Replace the MAP sensor. Refer to Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
18 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||||||||||
19 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info using the scan tool. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | System OK |
