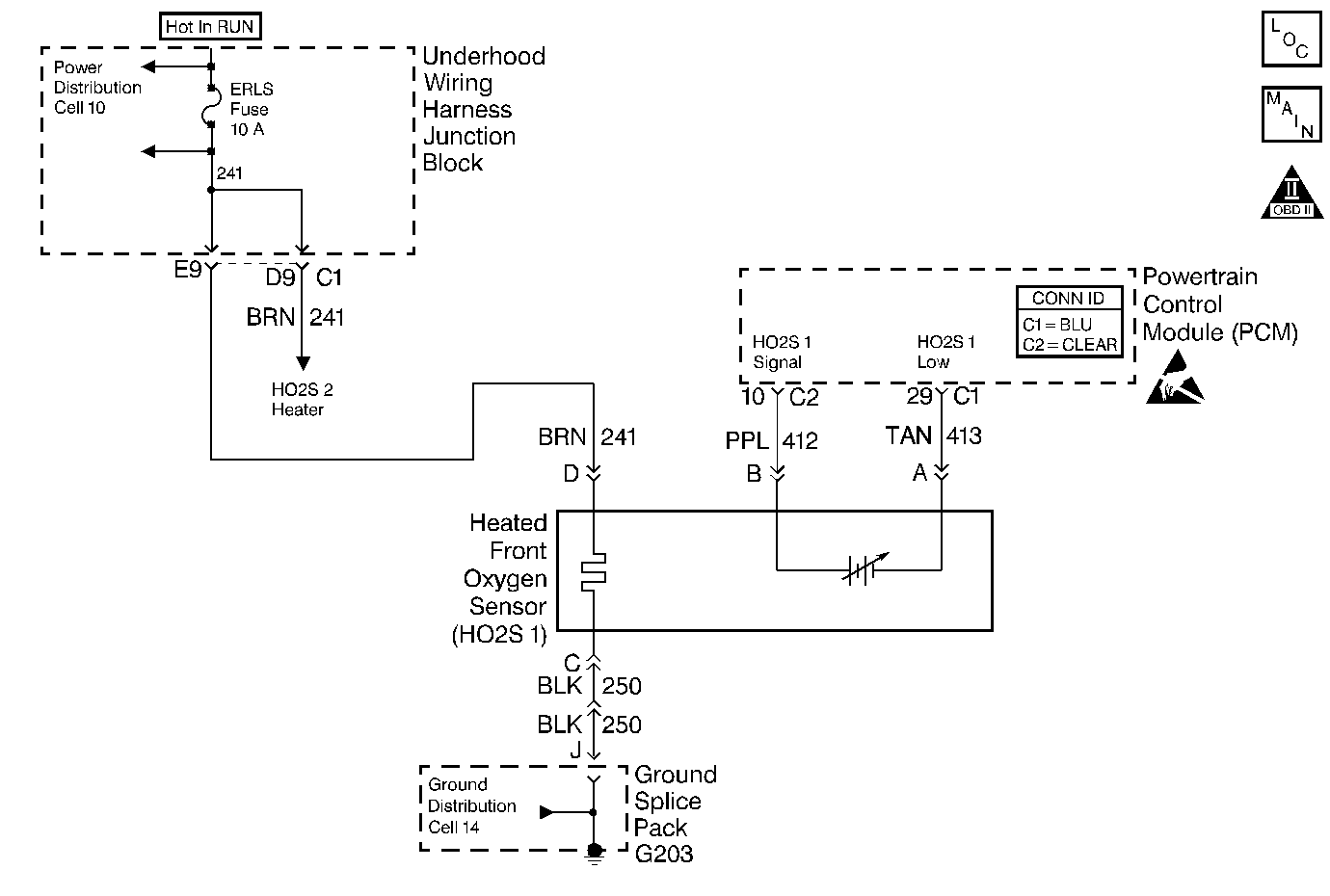
Circuit Description
The PCM monitors the Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) activity for 100 seconds. During this test period the PCM counts the number of times that the HO2S signal voltage crosses the rich to lean and lean to rich thresholds. If the PCM determines that the HO2S did not switch enough times, DTC P1133 will be set.
A lean to rich switch is determined when the HO2S voltage changes from less than 300 mV to greater than 600 mV. A rich to lean switch is determined when the HO2S voltage changes from more than 600 mV to less than 300 mV.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | No active injector circuit, MAF sensor, TP sensor, EVAP, IAT sensor, MAP sensor, fuel trim, EGR, ECT sensor or HO2S heater DTCs. |
| • | Above conditions present for a 100 second monitoring period after closed loop. |
| • | The PCM monitors fewer than 40 rich to lean and 40 lean to rich switches for HO2S 1. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame/Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
A malfunction in the HO2S heater ignition feed or ground circuit may cause a DTC P1133 to set. Check HO2S heater circuitry for intermittent faults or poor connections. If connections and wiring are OK and DTC P1133 continues to set, replace the HO2S 1. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor 1 Replacement .
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain ON Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||||||||||
2 |
Important: : If any DTCs are set (except P1133 or P1134), go to those DTCs before proceeding with this diagnostic table.
Does the scan tool indicate DTC failed this ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||
3 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||||||
Visually, physically inspect the following items:
Was a problem found in any of the above areas? | -- | |||||||||||
5 |
Does the scan tool indicate voltage near the specified value? | 450 mV | ||||||||||
6 |
Does the scan tool indicate voltage less than the specified value? | 300 mV | ||||||||||
7 |
Notice: Contamination of the oxygen sensor can result from the use of an inappropriate RTV sealant (not oxygen sensor safe) or excessive engine coolant or oil consumption. Remove the HO2S and visually inspect the portion of the sensor exposed to the exhaust stream in order to check for contamination. If contaminated, the portion of the sensor exposed to the exhaust stream will have a white powdery coating. Silicon contamination causes a high but false HO2S signal voltage (rich exhaust indication). The control module will then reduce the amount of fuel delivered to the engine, causing a severe driveability problem. Eliminate the source of contamination before replacing the oxygen sensor. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
8 | Repair the condition as necessary. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
9 | Repair open HO2S low signal circuit or grounded HO2S 1 high signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
10 | Repair open HO2S 1 high signal circuit or faulty PCM connections. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
11 |
Does the scan tool indicate DTC failed this ignition? | -- | System OK |
