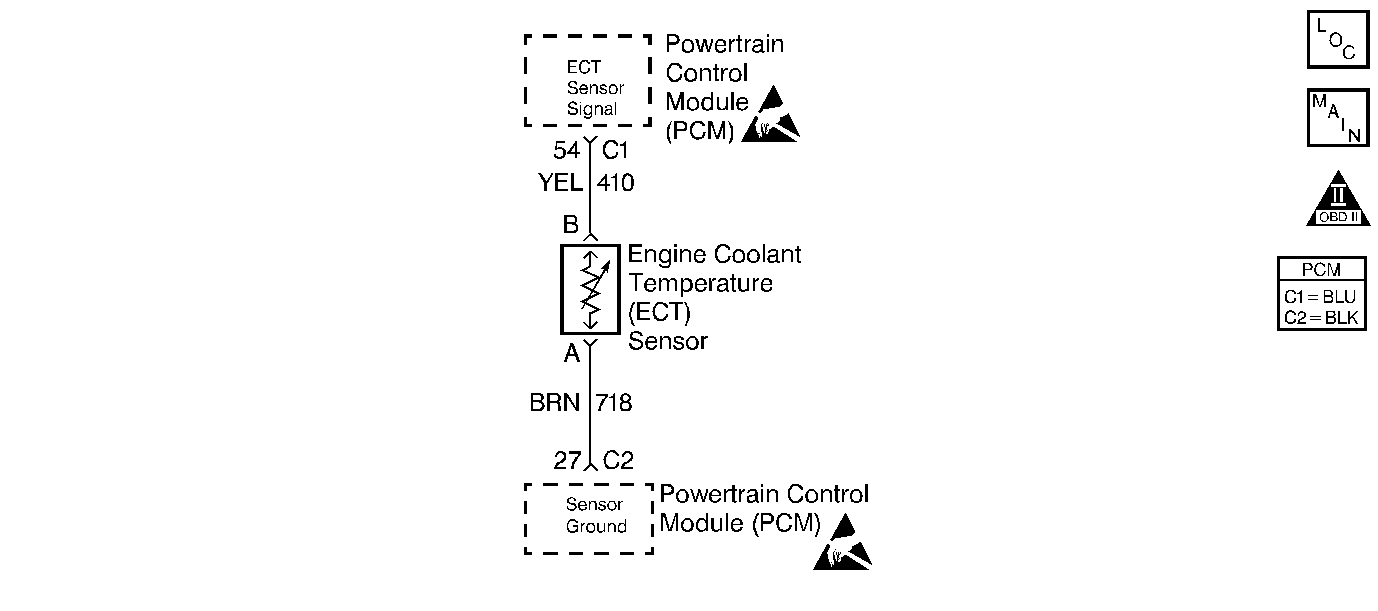
Circuit Description
When the vehicle is first started, the engine operates in an Open Loop operation, ignoring the oxygen sensor signal and calculating the air/fuel ratio based on inputs from the engine coolant temperature (ECT), the throttle position, and the manifold absolute pressure sensors only. The powertrain control module (PCM) will begin by using the oxygen sensor signal for controlling the fuel delivery (Closed Loop) when the following conditions are met:
| • | The engine has run a minimum amount of time based on ECT at engine start up. |
| • | The oxygen sensor (O2S 1) has a varying voltage output showing that it is hot enough to operate properly. |
| • | The ECT has increased a minimum amount based on the ECT at engine start up. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Region 1 - Ambient Temperature Above 10°C (50°F)
| • | The IAT is greater than 10°C (50°F). |
| • | The ECT is greater than 10°C (50°F). |
| • | The engine run time is greater than 120 seconds. |
| • | The maximum idle time is less than 90 seconds. |
OR
Region 2 - Ambient Temperature Above -7°C (19°F)
| • | The IAT is greater than -7°C (19°F). |
| • | The ECT is greater than -7°C (19°F). |
| • | The engine run time is greater than 300 seconds. |
| • | The maximum idle time is less than 225 seconds. |
OR
Region 3 - Ambient Temperature Below -7°C (19°F)
| • | The IAT is greater than -7°C (19°F). |
| • | The ECT is less than -7°C (19°F). |
| • | The engine run time is greater than 1350 seconds |
| • | The maximum idle time is less than 1013 seconds |
The conditions below are present for all three regions.
| • | The minimum calculated airflow is less than 10 gps to be considered at idle for all three temperature regions. |
| • | The ECT is less than 40°C (113°F). |
| • | The vehicle is in an Open Loop operation. |
| • | No DTCs P0112, P0113, P0117 or P0118. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will illuminate after two consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the malfunction present. |
| • | The PCM will record the operating conditions at the time that the diagnostic fails. This information will store in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers. |
| • | A history DTC stores. |
| • | The coolant fan turns ON. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | The MIL/DTCs can be cleared by using the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the insulation.
| • | Check for a poor connection or a damaged PCM harness. Inspect the ECT sensor signal circuit and the ground circuit terminals for the following conditions: |
| - | Improper mating |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Improperly formed connectors |
| - | Damaged terminals |
| - | A poor terminal to wire connection |
| - | Damaged harness |
| • | Perform an intermittent test. If the connections and the harness check OK, monitor a digital voltmeter connected between ECT sensor signal circuit and ground circuit terminals while moving the related connectors and the wiring harness. If a fault is induced, the resistance reading will change. This may help in order to isolate the location of the malfunction. |
| • | Use the Temperature vs. Resistance table below in order to evaluate the possibility of a skewed sensor. Refer to Temperature vs Resistance . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts you to complete some of the basic checks and to store the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data captured when the malfunction occurred. The scan tool stores this data for later reference.
-
Allow the engine to fully cool. The ECT sensor and the IAT sensor will read close to the ambient temperature in order to check for a possible skewed ECT sensor.
-
Measure the engine coolant temperature with a thermometer in order to determine what the actual value the ECT sensor should be. Take into consideration if the engine has been operating and if the engine coolant has been warmed.
-
This step simulates a DTC P0118. The PCM and wiring are OK if the PCM senses a change.
-
Reprogram the replacement PCM and perform the crankshaft position system variation learn procedure. Refer to PCM Replacement/Programming for PCM programming and CKP System Variation Learn Procedure for the crankshaft position system variation learn procedure.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check for 2.4L or Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check for 2.2L | ||||||
Are the temperature readings close? | -- | |||||||
Does the ECT sensor accurately reflect the actual engine coolant temperature? | -- | |||||||
4 | Is the ECT sensor value close to the IAT sensor reading on the scan tool? | -- | ||||||
Is the ECT sensor value less than the specified value? | -30°C (-22°F) | |||||||
6 | Connect a jumper wire between the following circuits at the ECT sensor electrical connector.
Is the ECT sensor value greater than the specified value? | 130°C (266°F) | ||||||
7 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||
8 |
Is the ECT sensor value greater than the specified value? | 130°C (266°F) | ||||||
9 |
Does the temperature rise more than the specified temperature? | 5°C (9°F) | ||||||
10 |
Does the DMM read a voltage greater than the specified value? | 0.5 volt | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||
11 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||
12 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||
13 | Repair the ECT sensor ground circuit for a short to voltage. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
Replace the PCM. Refer to PCM Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||
15 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
16 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | -- | ||||||
17 | Check to see if any additional DTCs are set. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
