Circuit Description
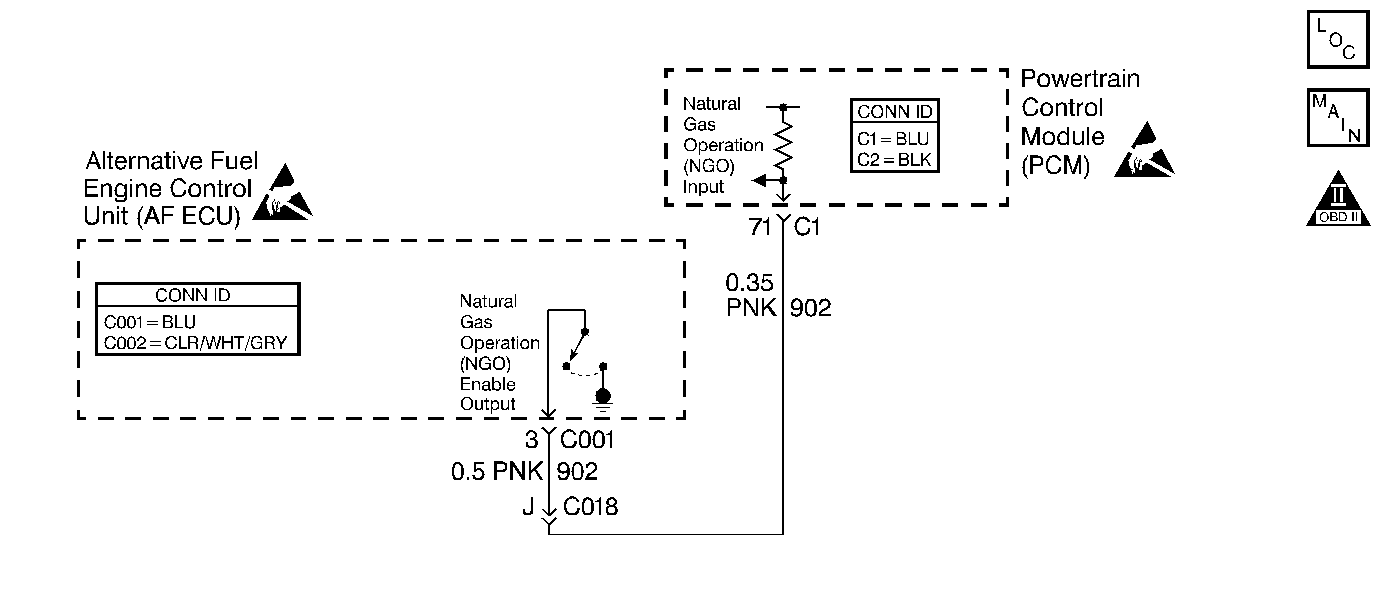
The AF ECU and the gasoline control module (VCM/PCM or ECM) are connected by the natural gas operation (NGO) Enable circuit. In order for the engine to switch-over to CNG operation the gasoline control module must be commanded to disable the gasoline fuel injectors, switch to a different ignition spark calibration and disable some of the gasoline control module DTCs. The AF ECU performs the switch-over command by grounding the NGO Enable circuit when CNG operation is desired.
This vehicles primary fuel source is compressed natural gas (CNG). The vehicle will only switch-over to gasoline operation if one of the following conditions is present:
| • | The fuel pressure sensor (FPS) indicates the CNG tank is empty. |
| • | A wide-open mixture control valve (MCV) is detected. |
| • | A system fault is detected by a control module (AFECU, VCM / PCM or ECM). |
| • | The manual shut-off valve is closed. |
| • | Engine crank time exceeds about 8 seconds. |
| • | Every 100th start and also when the coolant temperature is below 10°F (-12°C) the vehicle will start and run briefly on gasoline. A switch-over to CNG will occur only during a decel condition. |
Diagnostic Aids
This diagnostic information should be utilized only if the concern of the vehicle operator can be duplicated. An unwanted switch may occur only during specific vehicle operation. An example follows:
- The vehicle has an intermittently leaking low pressure lock-off (LPL) solenoid.
- After turning the engine OFF and waiting several minutes all of the CNG purges from the lines.
- During the next ignition ON key cycle the high pressure lock-off (HPL) is opened for about 1 second.
- The vehicle may start and run on CNG during any ignition cycle in which the LPL does not leak.
At the same moment that the HPL is opened the AF ECU monitors the fuel pressure sensor.
If the LPL is still leaking, the CNG pressure cannot build within the system and low fuel pressure is observed by the AF ECU.
Detecting the low fuel pressure in the system the AF ECU performs a switch-over to gasoline.
The customer concern would be an intermittent unwanted switch to gasoline with no DTCs stored and possibly a no-start flooded condition.
If an unwanted switch only occurs during certain driving conditions perform the Fuel System Diagnosis and verify that fuel pressure can be maintained during all driving conditions.
Fault Not Present
Fault Not Present indicates the condition that caused the concern is intermittent and not currently present. Refer to the Intermittent Conditions diagnostic information located in Symptoms - Engine Controls. If any additional concerns were observed return to Diagnostic System Check - Alternative Fuels (Engine Controls) .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
The System Check MUST be performed before proceeding with this diagnostic table. Failure to perform the System Check will result in mis-diagnosis.
-
This step inspects if the AF ECU has commanded the gasoline control module (using the NGO Enable circuit) to start on CNG.
The NGO Signal Command parameter is the commanded state of the NGO Enable circuit from the AF ECU. The NGO Signal parameter is the monitored state of the NGO Enable circuit from the GASOLINE control module (VCM/PCM or ECM).
-
This step inspects if the FIL is illuminated during CNG operation. The FIL should illuminate only during gasoline operation.
-
This step inspects if the FPS is monitoring adequate fuel tank pressure for the vehicle to start on CNG.
-
This step tests the ability of the AF ECU to command Natural Gas Operation (NGO) and the gasoline control modules ability to monitor the command.
-
This step indicates all the possibilities that cause a switch-over to gasoline operation.
-
This step inspects the ignition system of the vehicle for proper operation. A vehicle that operates correctly on gasoline but not on CNG may have a faulty ignition system.
-
Performing the Fuel System Diagnosis checks the basic AF fuel system for proper pressures and lock-off solenoid operation.
-
A fuel system that is unable to retain fuel pressure after the ignition is turned OFF may cause an Unwanted Switch to Gasoline. The AF ECU commands the HPL open for about 1 second every time the ignition is turned ON. If the fuel line system leaks during ignition OFF the next ignition ON prime pulse will usually recharge the fuel lines and the FPS. A 'sluggish' HPL may not open enough during the 1 second prime pulse but will open when commanded with the scan tool.
-
This step tests for proper fuel pressure sensor operation.
-
This step tests for an inoperative HPL. After connecting to a CNG dispensing station the CNG fuel lines, the FPS and the fuel tank will be charged by the station. The CNG fuel pressure in the lines and the FPS will quickly drop if the engine is operating on CNG but the HPL fails to open.
-
This step tests for proper operation of the NGO Enable circuit and the gasoline control module.
-
This step tests for a leaking fuel system with a 'sluggish' HPL.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Diagnostic System Check - Alternative Fuels (Engine Controls) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Do BOTH the data parameters indicate that Natural Gas Operation is enabled? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Observe the fuel indicator lamp (FIL) located in the fuel gauge select switch button with the vehicle running. Is the FIL illuminated? | -- | Go to Fuel Indicator Lamp Always On - Alternative Fuels in Instrument Panel, Gauges, and Console | Go to Step 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
4 | The fault is not present. Refer to Diagnostic Aids. Is their a system operation concern? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check - Alternative Fuels (Engine Controls) | Go to Intermittent Conditions | ||||||||||||||||||||
Using the scan tool communicate with the AF ECU and observe the Fuel Pressure Sensor data parameter. Does the Fuel Pressure Sensor indicate pressure greater than the value specified? | 8274 kPa (1200 psi) | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 10 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Does the parameter indicate that Natural Gas Operation is enabled? | -- | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Was a problem found and repaired? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Important: A higher secondary ignition voltage is required to operate the engine on CNG than on gasoline. A vehicle that operates normally on gasoline does not indicate a fully functional ignition system. Important: Accurate CKP operation is required for CNG operation. Check the CKP sensor on any vehicle that starts and immediately stalls.
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Perform the Fuel System Diagnosis procedure and return to this step. Was a repair required in the Fuel System Diagnosis? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 21 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Does the FPS fuel pressure increase greater than the value specified when the HPL is opened? | 8274 kPa (1200 psi) | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 11 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Important: Before proceeding with FPS diagnosis ensure that the manual lock-down screw of the HPL manual shut-off fitting is open by rotating the allen screw counter-clockwise until fully seated.
Is the FPS accurately indicating fuel pressure? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Fuel Gauge Inaccurate or Inoperative - Alternative Fuels in Instrument Panel, Gauges, and Console | |||||||||||||||||||||
Review the Test Description. Does the FPS data parameter ever drop below the pressure value specified? | 8274 kPa (1200 psi) | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 22 | |||||||||||||||||||||
If the jumper fuse opens repair the short to voltage on the NGO Enable circuit. Does the data parameter indicate that Natural Gas Operation is enabled? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 14 | |||||||||||||||||||||
14 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 17 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||
16 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||
17 |
Important: The following control module replacement procedures must all be completed before attempting to operate the vehicle.
Important: In order to perform the variation learn procedure a switch-over to gasoline operation is necessary. Remove the CNG 20 amp fuse in order to perform the switch-over. All of the above procedures are located in the gasoline service manual. Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
18 |
Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
19 |
Did the test lamp illuminate when commanded? | -- | Go to Step 20 | Go to DTC P1215 | ||||||||||||||||||||
20 | Replace the high pressure lock-off (HPL solenoid. Refer to High Pressure Lock-Off Solenoid Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
21 | Replace the GMS/MCV. Refer to Gas Mass Sensor/Mixture Control Valve Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Step 22 | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
22 |
Does the vehicle operate on CNG with normal driveability, no FIL/MIL illumination and no stored DTCs? | -- | System OK | Go to Diagnostic System Check - Alternative Fuels (Engine Controls) |
