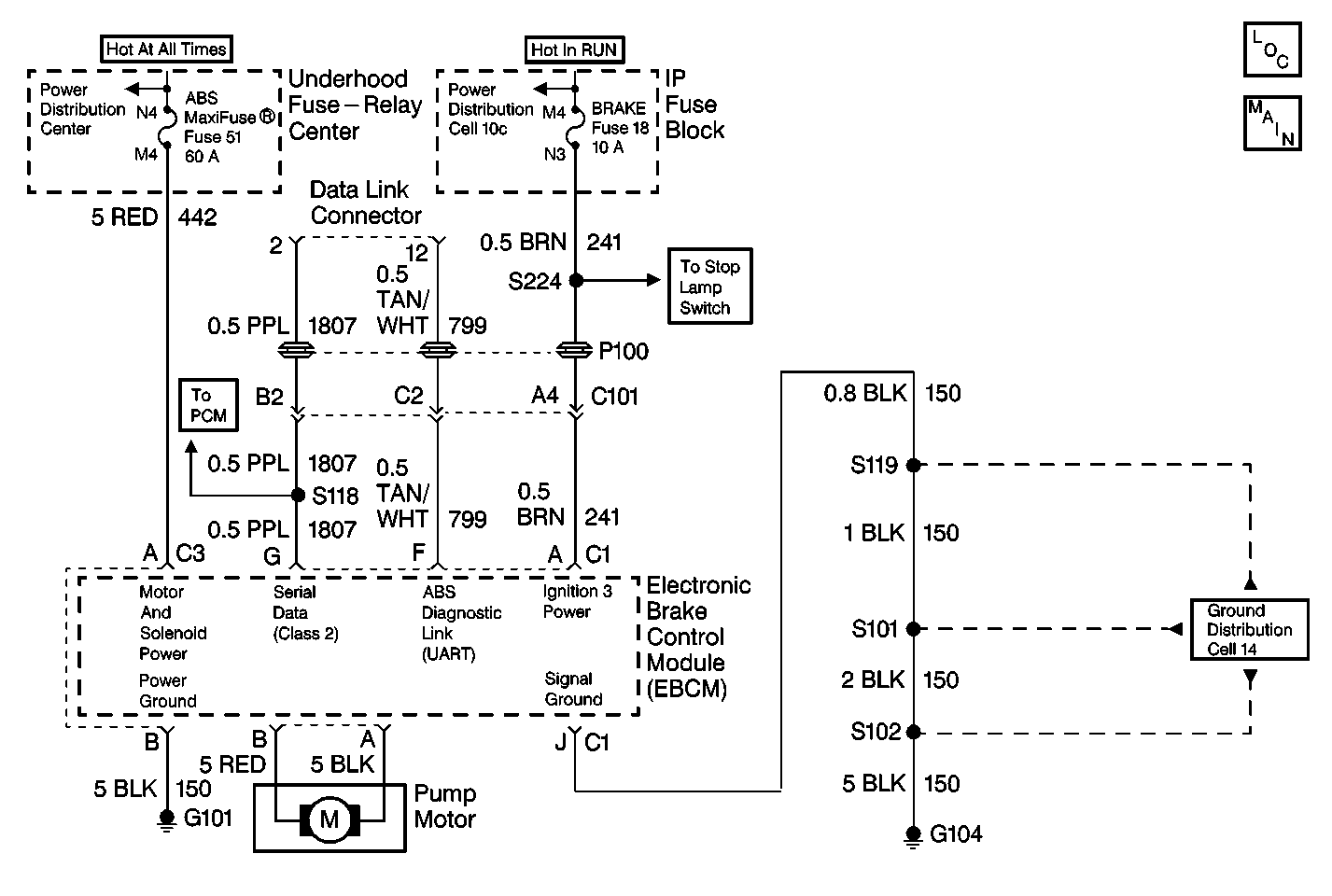
Circuit Description (DTCs C0265/C0266)
The pump motor relay supplies power to all six solenoid coils (three isolation solenoid coils and three dump solenoid coils) and the pump motor when the ABS is required. The relay and the six solenoid coils are located within the EBCM.
Conditions for Setting the DTC (DTC C0265)
| • | The EBCM microprocessor commands the relay on |
| • | Low voltage exists on all six solenoid driver circuits when high voltage is expected (the solenoid is not energized) |
Conditions for Setting the DTC (DTC C0266)
| • | The ABS bulb check is complete |
| • | High voltage exists on the pump motor driver circuit when all are expected to be low (the relay is not commanded on) |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The ABS indicator lamp turns on |
| • | The ABS disables |
DTCs C0265 and C0266 are Ignition Latched DTCs, which indicates that the above actions remain true until the ignition is turned to OFF (even if the cause of the DTC is intermittent).
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | Repair the conditions responsible for setting the DTC |
| • | Use the Scan Tool Clear DTCs function |
Diagnostic Aids (DTC C0265)
DTC C0265 usually sets because of an open relay coil or non-closable relay contacts. The relay is located within the EBCM. The relay is not serviceable. If the test does not repair the DTC, then replace the EBCM.
If DTC C0265 appears with other DTCs repair the other DTCs first. Clear all DTCs. Then run three function tests with the Scan Tool . Refer to this diagnostic chart if DTC C0265 resets.
Diagnostic Aids (DTC C0266)
DTC C0266 usually sets when the relay contacts are stuck closed. The relay is located within the EBCM. The relay is not serviceable. If the test does not repair the DTC, then replace the EBCM.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the steps in the diagnostic table:
-
This step determines the resistance of the power ground circuit.
-
This step determines the battery voltage available to the EBCM.
-
This step determines the resistance of the signal ground circuit.
-
This step determines the ignition voltage available to the EBCM.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | |
2 |
Is the connector in good condition? | -- | ||
Measure the resistance between terminal B of the 2-way EBCM harness connector and the ground using a J 39200 . Is the resistance measurement within the specified range? | 0-2ohms | |||
Measure the voltage between terminal A of the 2-way EBCM harness connector and the ground using a J 39200 . Is the voltage equal to or greater than the specified value? | 10.0 V | |||
5 | Inspect the 60-amp ABS maxi-fuse. Is the maxi-fuse open? | -- | ||
6 |
Is the connector in good condition? | -- | ||
Measure the resistance between terminal J of the 10-way EBCM harness connector and the ground using a J 39200 . Is the resistance measurement within the specified range? | 0-2ohms | |||
Is the voltage equal to or greater than the specified value? | 10.0 V | |||
9 | Inspect the 10-amp BRAKE fuse. Is the fuse open? | -- | ||
10 |
Does the DTC set as a current DTC? | -- | Malfunction is intermittent. Refer to Diagnostic Aids | |
11 | Repair the 2-way EBCM harness connector. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
12 | Repair the open or the high resistance in the CKT 150. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
13 | Repair the short to ground in the CKT 442. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
14 | Repair the open or the high resistance in the CKT 442. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
15 | Repair the 10-way EBCM harness connector. Is the repair complete? | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- | |
16 | Repair the open or the high resistance in the CKT 150. Is the repair complete? | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- | |
17 | Repair the short to ground in the CKT 241. Is the repair complete? | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- | |
18 | Repair the open or the high resistance in the CKT 241. Is the repair complete? | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- | |
19 | Replace the EBCM. Is the repair complete? | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
