For 1990-2009 cars only
- Raise and support the vehicle. Refer to Lifting and Jacking the Vehicle in General Information.
- Ensure that the following conditions exist:
- Position a dial indicator against the top of the idler arm grease cap.
- Place a spring scale near the relay rod end of the idler arm.
- Apply a 110 N·m (25 lb) force.
- Measure the total distance the idler arm moves under the specified force.
- For commercial vehicles: replace the idler arm if the idler arm fails the above test. Refer to Idler Arm Replacement .
- For motorhomes: adjust the idler arm if the idler arm fails the above test. Refer to Idler Arm Adjustment-Motorhome. If replacement is necessary, refer to Idler Arm Replacement .
| • | The front wheels rotate freely. |
| • | The steering mechanism turns freely. |
| • | The wheels are positioned straight ahead. |
Important:
• Do not jerk the right wheel and tire assembly back and forth in
order to cause an up and down movement of the idler arm. This is not an acceptable
testing procedure because you cannot control the amount of force that you
apply to the idler arm. • Loose idler arms or other suspension or steering system faults
may create a shimmy condition. Shimmy conditions may also originate at the
wheel and tire assembly from the following conditions: - Dynamic imbalance - Runout or force variations - Road surface irregularities • Consider all possible causes of a shimmy complaint. Refer to
Wheel Mounting Surface Check
in Tires
and Wheels.
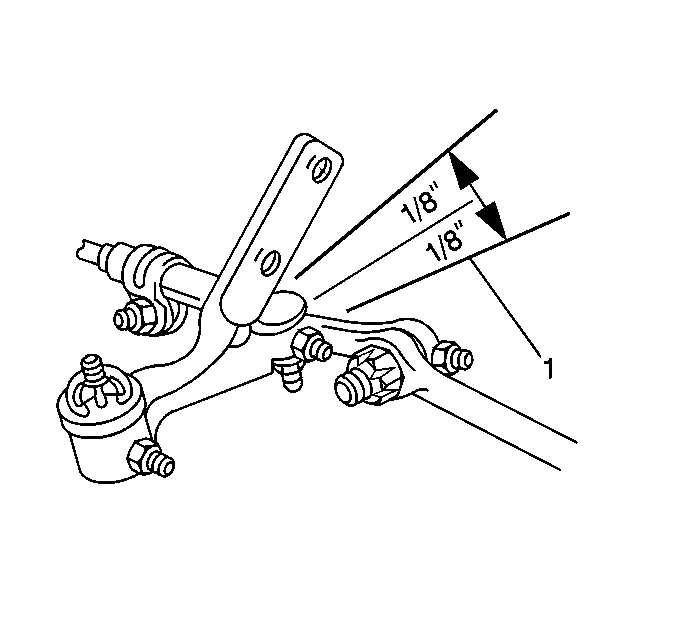
Allow no more than 6.36 mm (¼ in) (1) of deflection.
