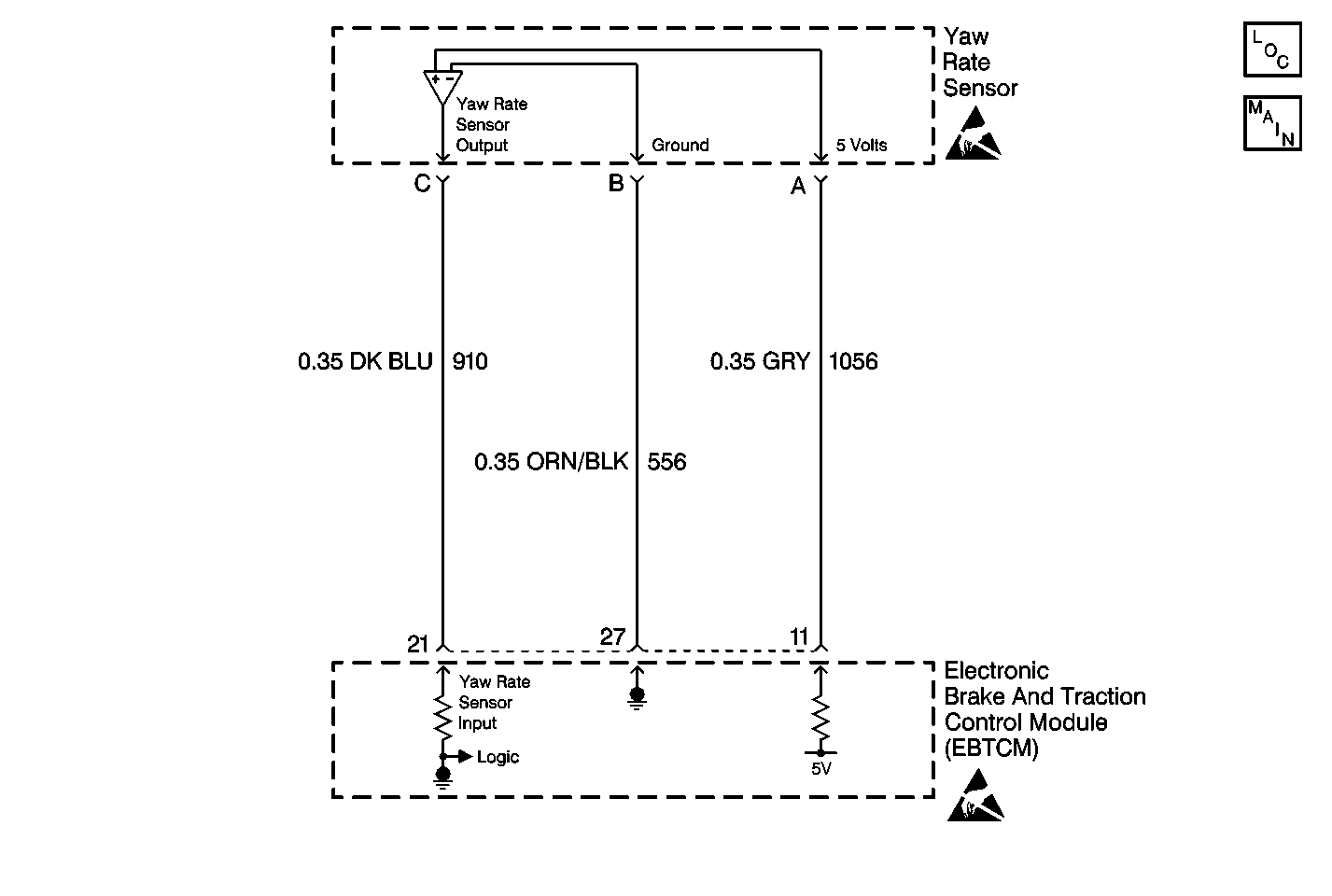
Circuit Description
The yaw rate bias is calculated by the EBTCM any time ignition is present. This value is used to compensate for offsets in the yaw rate sensor output due to temperature changes and manufacturing differences.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | DTC C1282 can be set any time ignition is present and the yaw rate bias exceeds 7 degrees/seconds. |
| • | DTC C1282 can be set if the measured yaw rate changes by more than 390 degrees/second within one second. |
| • | DTC C1282 can be set if the signal voltage is less than 0.15 volts or greater than 4.85 volts. |
| • | DTC C1282 can be set during an Active Handling event. the EBTCM does a comparison between the actual yaw rate and a yaw rate derived from the difference in output from the front wheel speed sensors during an understeer condition or the rear wheel speed sensors during an oversteer condition. If this yaw rate difference is greater than 10 degrees/seconds for more than 60 seconds DTC C1282 will be set. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
ABS and TCS remain enabled, Active Handling™ is disabled.
| • | Indicators that turn on: |
| Car Icon (TCS indicator) |
| • | Messages displayed on the DIC: |
| Service Active HNDLG |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | Condition for DTC is no longer present and scan tool clear DTC function is used. |
| • | Fifty ignition cycles have passed with no DTCs detected. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | It is very important to check the vehicle for proper alignment. The car should not pull in either direction while driving straight on a flat surface. |
| • | When performing the following diagnostic procedure, insure that the vehicle is parked on a level surface. |
| • | It is very important to find out from the driver when the code was set, (when the SERVICE ACTIVE HNDLG message was activated). This information may help to duplicate the failure. |
| • | It is very important that a thorough inspection of the wiring and connectors be performed. Failure to carefully and fully inspect wiring and connectors may result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with reappearance of the malfunction. Check connector C102 RH side rear of engine compart for water intrusion or missing plugs, and that the connector is oriented horizontal to prevent water intrusion. |
| • | It is very important to properly check the 5 volt power supply to the Yaw Rate Sensor. The Yaw Rate Sensor must have at least 4.75 volts, if the Yaw Rate Sensor does not have a stable (not drifting) supply voltage of at least 4.75 volts then DTC C1282 will set. |
| • | An intermittent malfunction is most likely caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a wire that is broken inside the insulation. Refer to Testing for Electrical Intermittents in Wiring Systems. |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
This step checks for the EBTCM pull up voltage.
-
This step checks for the proper Yaw Rate Sensor signal being sent to the EBTCM.
-
This step checks if the EBTCM can properly interpret the Yaw Rate Sensor signal.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 |
Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
3 | Repair CKT 910 for a short to ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
4 | Using J 39200 DMM, measure the resistance between J 39700 terminals 11 and B. Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
5 | Repair CKT 1056 for a short to ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
6 |
Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
7 | Repair short between CKT(s) 556 and 1056. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
8 | Using J 39200 DMM, measure the resistance between J 39700 terminals 11 and 21. Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
9 | Repair short between CKT(s) 910 and 1056. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
10 | Using J 39200 DMM, measure the resistance between J 39700 terminals 27 and 21. Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
11 | Repair short between CKT(s) 556 and 910. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
12 |
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Greater than 1V | ||
13 | Repair CKT 910 for a short to voltage. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
14 | Using J 39200 DMM, measure the voltage between J 39700 terminals 11 and B. Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Greater than 1V | ||
15 | Repair CKT 1056 for a short to voltage. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
16 | Using J 39200 DMM, measure the voltage between J 39700 terminals 27 and B. Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Greater than 1V | ||
17 | Repair CKT 556 for a short to voltage. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
18 |
Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 0-5ohms | ||
19 | Repair CKT 910 for an open or high resistance. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
20 |
Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 0-5ohms | ||
21 | Repair CKT 556 for an open or high resistance. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
22 |
Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 0-5ohms | ||
23 | Repair CKT 1056 for an open or high resistance. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 4.75-5.25V | |||
Using J 39200 DMM, measure the voltage between J 39700 terminals 21 and 27. Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 2.35-2.65V | |||
Using a scan tool read the Yaw Rate Sensor value in volts. Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 2.0-3.0V | |||
27 | Replace the Yaw Rate Sensor. Refer to Vehicle Yaw Sensor Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
28 |
Did DTC C1282 set as a current DTC while the vehicle was being driven? | -- | ||
29 | Replace the EBTCM. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- |
