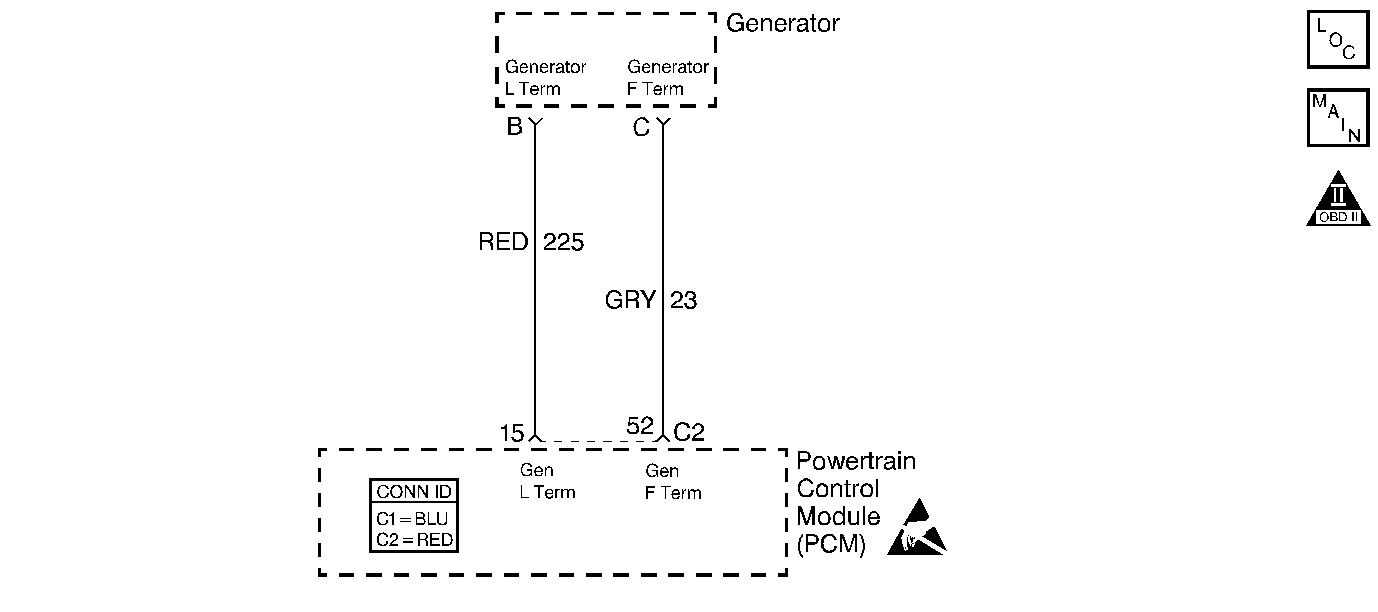
Circuit Description
The L-terminal circuit from the generator is a discrete circuit (a discrete circuit has no splices and only one source and destination) into the PCM. The PCM applies ignition voltage to the generator L-terminal circuit. A small amount of current flows from this circuit through the generator windings to ground to create a magnetic field which starts the generator process. When the generator is at operating speed and producing voltage, a solid state switch for the L-terminal circuit in the generator opens and the PCM detects that the initial startup current flow has stopped.
The PCM expects to detect low voltage on the L-terminal circuit prior to the generator rotating at operating speed and conversely expects the circuit to be at ignition voltage potential when the generator is operational. When the PCM detects a fault (circuit shorted to ground, or circuit shorted to voltage), the Driver Information Center will display Charging System Fault.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The ignition switch in the ON position or the engine is operating.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The PCM detects the L terminal as Active with the key ON and the engine not running or the PCM detects the L-terminal as Inactive with the engine running. |
| • | All conditions met for 6 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM stores the DTC information into memory when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illuminate. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. |
| • | A message is displayed on the Drivers Information Center. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | A last test failed, or current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other non-emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important:
• Remove any debris from the PCM\TAC module connector surfaces before servicing
the PCM\TAC module. Inspect the PCM\TAC module connector gaskets when diagnosing/replacing
the modules. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent
contaminate intrusion into the PCM\TAC modules. • For any test that requires probing the PCM or a component harness
connector, use the Connector Test Adapter Kit J 35616
. Using this kit prevents damage to the harness/component terminals.
Refer to
Using Connector Test Adapters
in Wiring Systems.
| • | The following may cause an intermittent: |
| - | Poor Connections; Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. |
| - | A mis-routed harness |
| - | A rubbed through wire insulation |
| - | A broken wire inside the insulation |
| • | DTCs P1637 and P1638 may set at the same time depending on the failure. Also, the L-terminal circuit can cause a DTC P1638 to set. This diagnostic table diagnoses both DTCs P1637 and P1638. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to diagnosis the generator circuits. The scan tool should display Inactive for the L terminal and 10-40 percent for the F terminal when the ignition is ON. When the engine is operating, the display should indicate that the L terminal is Active and the F terminal is greater than 5 percent. |
| • | A generator fault, such as a shorted output diode, malfunctioning regulator, open or shorted rotor, or open sense lead or battery feed may cause a low battery charge. Refer to Generator Not Operating Properly in Engine Electrical for further information and generator diagnosis. |
| • | Using the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If you cannot duplicate the DTC, the information included in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data can help determine how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also help determine how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass and/or a fail. Operate the vehicle within the same freeze frame conditions (RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature etc.) that you observed. This isolates when the DTC failed. |
| • | For an intermittent condition, refer to Symptoms . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table.
-
This step verifies the fault is current.
-
Inspect the circuit for an open or a short to ground if the test lamp did not illuminate.
-
If the scan tool displays Active, this indicates the circuit is open.
-
This step tests the F terminal for being shorted to a voltage. With the ignition ON, the F terminal should display between 10-40 percent. If the F terminal displays greater than 40 percent, inspect the circuit for a short to voltage.
-
When the engine is started the L terminal should be active.
-
This step is testing the L terminal for an open. If the L terminal displays Active when the circuit is grounded, this indicates the circuit is open.
-
This step is testing the F terminal circuit for an open or a short to ground. If the F terminal parameter goes to 99 percent the condition is within the generator.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
|
Important: The following tests assumes that the generator belt is installed correctly and in good condition. The battery is adequately charged.
Did DTC P1637 and/or P1638 fail this ignition? | -- | |||
3 |
Did DTC P1637 and/or P1638 fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
Does the test lamp illuminate for both circuits? | -- | |||
Does the scan tool display L terminal as inactive? | -- | |||
Monitor the F terminal parameter using a scan tool in the Engine 3 Data list. Is the F terminal percentage less than the specified value? | 40% | |||
Does the scan tool display L terminal as inactive? | -- | |||
Does the scan tool display L terminal as inactive? | -- | |||
9 |
Does the DMM indicate continuity within the specified range? | 0-2ohms | ||
Did the Generator F terminal parameter change from 0% to 99%? | -- | |||
11 | Test the continuity of the F terminal circuit from the generator harness connector to battery ground using the DMM J 39200 . Refer to Testing for Continuity in Wiring Systems. Does the DMM indicate continuity within the specified range? | 0-10ohms | ||
12 |
Does the DMM indicate continuity within the specified range? | 0-2ohms | ||
13 | Disconnect the generator 4-way electrical connector. Is the F terminal percentage at the specified value? | 0% | ||
14 |
Does the scan tool display L terminal as inactive? | -- | ||
15 | Repair the open, high resistance, or grounded generator circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
16 | Repair the short to ground in the generator circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
17 | Repair the short to voltage on the F terminal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
18 |
Is the action complete? | -- | ||
19 |
Important: Program the replacement PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module/Throttle Actuator Control Module Replacement Replace the PCM. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
20 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
21 | Replace the generator. Refer to Generator Replacement in Engine Electrical. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
22 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | -- | ||
23 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
