Refer to
Cell 20: TP and APP Sensors
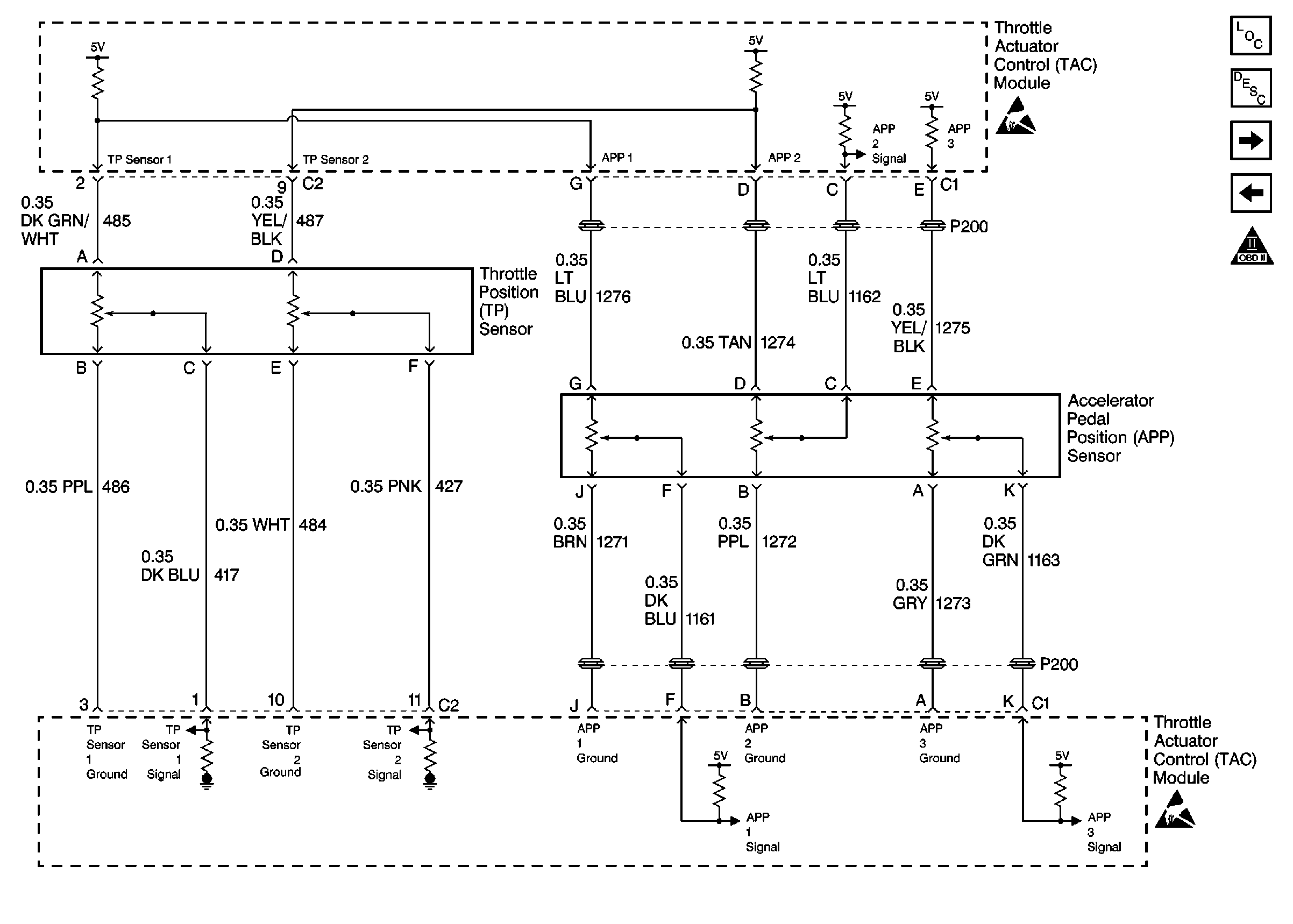
for complete circuit details.
Circuit Description
The Throttle Position (TP) sensor is mounted on the throttle body assembly. The sensor is actually two individual Throttle Position sensors within one housing. Two separate signal, ground and 5 volt reference circuits are used to connect the TP sensor assembly and the Throttle Actuator Control (TAC) Module. The two sensors have opposite functionality. The TP sensor 1 signal voltage increases as the throttle opens, from below 1.0 volt at 0% throttle to above 3.5 volts at 100% throttle. The TP sensor 2 signal voltage decreases from around 3.8 volt at 0% throttle to below 1.0 volt at 100% throttle. Observe also that the signal circuit for TP Sensor 1 is pulled up to 5 volts and that the signal circuit for TP Sensor 2 is referenced to ground within the TAC Module.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0606, P1517, P1518 are not set. |
| • | The ignition switch in the crank or run position. |
| • | The ignition voltage is greater than 5.23 volts. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The TP sensor 2 voltage is less than 0.13 volts or greater than 4.87 volts. |
| • | All above conditions met for less than 1 second. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM stores the DTC information into memory when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The PCM stores this information in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records. |
| • | The TAC system operates in reduced engine power mode. If certain TAC system DTCs are set at the same time, the TAC system may command the engine to shut down. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A last test failed, or current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL and the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important:
• Remove any debris from the PCM\TAC module connector surfaces before
servicing the PCM\TAC module. Inspect the PCM\TAC module connector gaskets
when diagnosing/replacing the modules. Ensure that the gaskets are installed
correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminate intrusion into the PCM\TAC
modules. • For any test that requires probing the PCM or a component
harness connector, use the Connector Test Adapter Kit J 35616
. Using this kit prevents damage
to the harness/component terminals. Refer to
Using Connector Test Adapters
in Wiring Systems.
| • | The following may cause an intermittent: |
| - | Poor connections; Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. |
| - | Corrosion |
| - | Mis-routed harness. |
| - | Rubbed through wire insulation. |
| - | Broken wire inside the insulation. |
| - | Inspect the TAC module connectors for signs of water intrusion. When this occurs, multiple DTCs should be set and no circuit or component conditions can be located. |
| • | The APP sensor 1 and the TP sensor 1 5.0 volt reference circuits are internally connected within the TAC module. |
| • | The APP sensor 2 and the TP sensor 2 5.0 volt reference circuits are internally connected within the TAC module. |
| • | When the TAC module detects a condition within the TAC System, more than one TAC System related DTC may set. This is due to the many redundant tests run continuously on this system. Locating and repairing one individual condition may correct more than one DTC. Keep this in mind when reviewing captured DTC info. |
| • | For an intermittent, refer to Symptoms . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
Disconnect the Throttle Actuator connector before inserting fingers into the throttle bore. Re-install the air inlet duct after repairs are completed.
-
The sensor voltage should drop to zero when you disconnect the sensor.
-
Using a test lamp reduces the amount of current fed into the signal circuit. The scan tool should display the maximum value for this parameter (5 volts) even though the actual voltage is higher.
-
This step is testing for a short to voltage on the TP 2 sensor signal circuit.
-
This step is testing for a short to voltage on the APP sensor 2 signal circuit.
The TP sensor 2 and the APP sensor 2 share a common 5 volt reference. A short to voltage on the APP sensor 2 signal circuit will affect the 5 volt reference circuit.
-
This step is testing for a short to voltage on the TP sensor 2 5.0 volt reference circuit.
The TP 2 sensor and the APP 2 sensor share a common 5 volt reference. The 5 volt reference circuits are connected internally within the TAC module. Disconnecting the TAC module will isolate the 5 volt reference circuits.
-
This step is testing for a short to voltage on the APP sensor 2 5.0 volt reference circuit.
The TP sensor 2 and the APP sensor 2 share a common 5 volt reference. A short to voltage on the APP sensor 2 5 volt reference circuit will affect the TP sensor 2 5 volt reference circuit.
-
This step is testing for an open TP sensor 2 5 volt reference circuit.
-
The TP sensor 2 5 volt reference circuit is shorted to ground if the DMM indicates continuity.
-
The APP sensor 2 5 volt reference circuit is shorted to ground if the DMM indicates continuity.
-
When the TAC module detects a problem within the TAC System, more than one TAC System related DTC may set. This is due to the many redundant tests run continuously on this system. Locating and repairing one individual problem may correct more than one DTC. Keep this in mind when reviewing captured DTC info.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
2 | Is DTC P1515, P1516, or P1518 also set? | -- | Go to Applicable DTC | |
Important: Disconnecting the throttle actuator motor connector causes additional DTCs to set. Is the voltage within the specified range? | 4.3-4.8V | |||
4 | Open the throttle blade to Wide Open Throttle (WOT) by hand while observing the TP sensor 2 voltage on the scan tool. Is the voltage within the specified range? | 0.13-1V | ||
5 |
Does the harness movement cause this DTC to set? | -- | ||
6 |
Did this DTC set? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
7 | Monitor the TP sensor 2 voltage using a scan tool. Is the voltage near the specified value? | 5V | ||
Disconnect the TP sensor harness connector. Does the scan tool indicate the specified voltage for TP sensor 2? | 0V | |||
9 |
Is the resistance within the specified range? | 0-5ohms | ||
10 |
Is the voltage near the specified value? | 5V | ||
Does the scan tool indicate the specified voltage? | 5V | |||
Is any voltage present? | -- | |||
Is any voltage present? | -- | |||
14 |
Does the DMM indicate continuity? | -- | ||
15 | Test the harness for continuity between the TP sensor 2 signal circuit and the battery ground using the DMM J 39200 . Does the DMM indicate continuity? | -- | ||
16 | Test the TAC harness for continuity between the TP sensor 2 signal circuit and all other circuits in both TAC module connectors using the DMM J 39200 . Does the DMM indicate continuity? | -- | ||
Is any voltage present? | -- | |||
Is any voltage present? | -- | |||
Is the resistance within the specified range? | 0-2ohms | |||
Test the harness for continuity between the TP sensor 2 5 volt reference circuit and the battery ground using the DMM J 39200 . Does the DMM indicate continuity? | -- | |||
Does the DMM indicate continuity? | 0-2ohms | |||
22 | Test the TAC harness for continuity between the TP sensor 2 5 volt reference circuit and all other circuits in both TAC module connectors using the DMM J 39200 . Does the DMM indicate continuity? | -- | ||
23 | Test the TAC harness for continuity between the APP sensor 2 5 volt reference circuit and all other circuits in both TAC module connectors using the DMM J 39200 . Does the DMM indicate continuity? | -- | ||
24 | Repair the short to voltage in the APP signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
25 | Repair the harness/connections as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
26 | Repair the short to voltage in the TP sensor 2 5 volt reference circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
27 | Repair the short to voltage in the APP sensor 5 volt reference circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
28 | Repair the open/high resistance in the 5 volt reference circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
29 | Repair the short to ground in the 5.0 volt reference circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
30 | Repair the signal circuit shorted to voltage. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
31 | Repair the open/high resistance in the signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
32 | Repair the short to ground in the signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
33 | Repair the open/high resistance in the ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | -- | |
34 | Repair the circuits that are shorted together. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
35 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
36 | Replace the throttle body assembly. Refer to Throttle Body Assembly Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
37 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
38 | Replace the TAC Module. Refer to Powertrain Control Module/Throttle Actuator Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
39 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | -- | ||
Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
