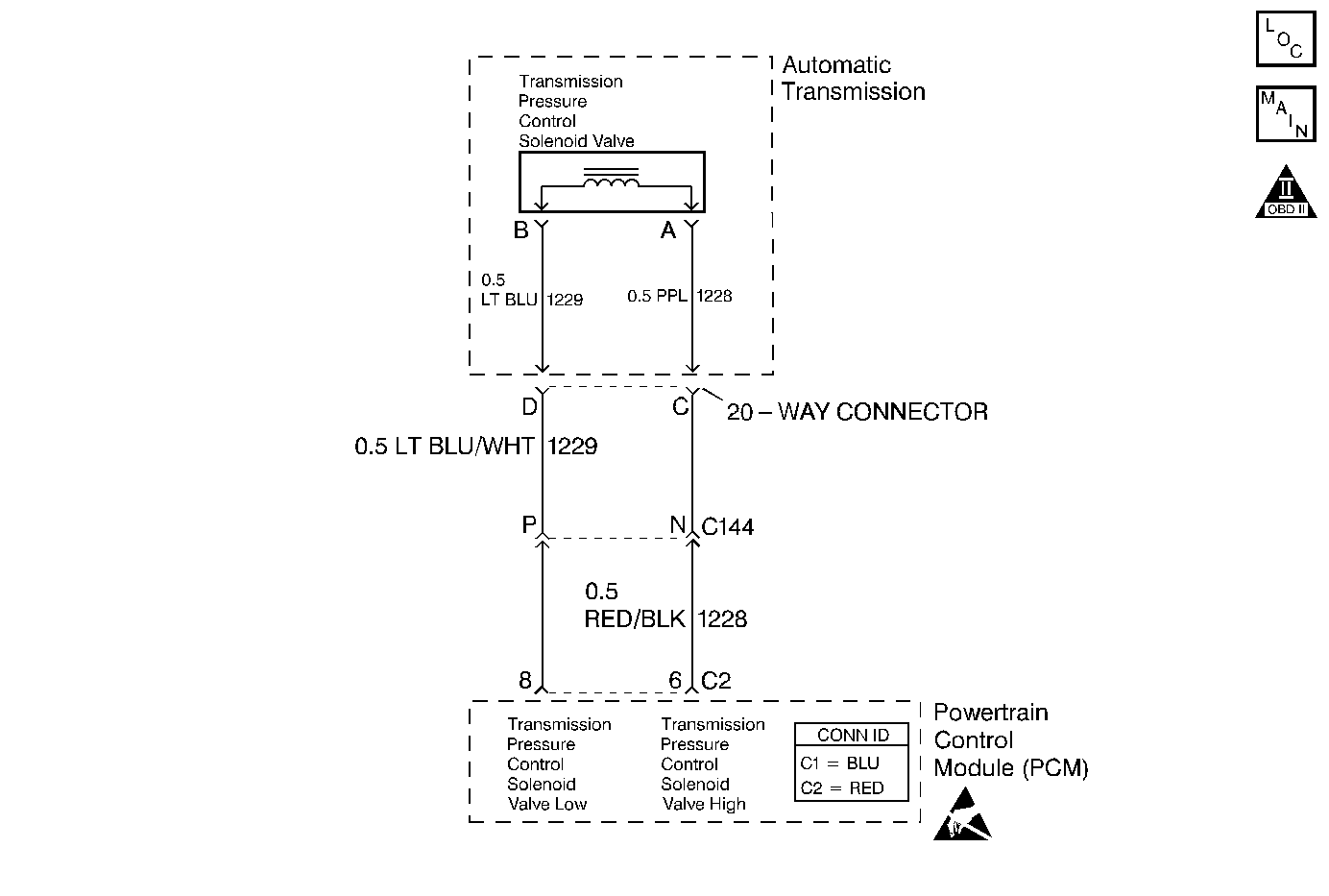
Circuit Description
The pressure control (PC) solenoid valve is an electronic device that regulates transmission line pressure based on the current flow through its coil winding. The magnetic field produced by the coil moves the solenoid's internal valve which varies pressure to the pressure regulator valve. The powertrain control module (PCM) controls the PC solenoid valve by applying a varying amount of amperage to the solenoid. The applied amperage can vary from 0.1 to 1.1 amps. Low amperage (0.1 amp) indicates high line pressure. High amperage (1.1 amps) indicates low line pressure. The duty cycle of the PC solenoid valve is expressed as a percentage of energized ON time. Zero percent indicates zero ON time (non-energized) or no current flow. Approximately 60% at idle indicates maximum ON time (energized) or high current flow. The PCM determines the appropriate line pressure for a given load by comparing the throttle position (TP) voltage, the engine speed and other inputs.
When the PCM detects a continuous open or short to ground in the PC solenoid valve circuit or the PC solenoid valve, then DTC P0748 sets. DTC P0748 is a type D DTC.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The system voltage is 8-18 volts. |
| • | The engine is running. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PC solenoid valve duty cycle reaches its high limit (approximately 95%) or low limit (approximately 0%) for 200 milliseconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM does not illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). |
| • | The PC solenoid valve is OFF. |
| • | The PCM freezes shift adapts from being updated. |
| • | The PCM stores DTC P0748 in PCM history. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | A scan tool clears the DTC from PCM history. |
| • | The PCM clears the DTC from PCM history if the vehicle completes 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a non-emission-related diagnostic fault occurring. |
| • | The PCM cancels the DTC default actions when the fault no longer exists and the ignition switch is OFF long enough in order to power down the PCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Inspect the wiring at the PCM, the transmission connector and all other circuit connecting points for the following conditions: |
| - | A backed out terminal |
| - | A damaged terminal |
| - | Reduced terminal tension |
| - | A chafed wire |
| - | A broken wire inside the insulation |
| - | Moisture intrusion |
| - | Corrosion |
| • | When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test equipment for a change. |
| • | DTC P0748 may set under low voltage conditions caused by high electrical system demands. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step tests the ability of the PCM to command the PC solenoid valve.
-
This step tests the PC solenoid valve and automatic transmission (A/T) wiring harness assembly for incorrect resistance.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
Important: Before clearing the DTC, use the scan tool in order to record the Failure Records. Using the Clear Info function erases the Failure Records from the PCM. Is the PC Solenoid Actual Current always within the specified value of the PC Solenoid Ref. Current? | 0.16 amp | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
Is the resistance within the specified range? | 3-7 ohms | |||
4 | Is the resistance greater than the specified value? | 7 ohms | ||
5 | Inspect circuit 1228 (PPL) and circuit 1229 (LT BLU) of the A/T wiring harness assembly for an open condition. Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Was an open condition found? | -- | ||
6 | Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 3 ohms | -- | |
7 | Inspect circuit 1228 (PPL) and circuit 1229 (LT BLU) of the A/T wiring harness assembly for a shorted together condition. Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Was a shorted together condition found? | -- | ||
8 | Measure the resistance from terminal C to the transmission case. Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 9 ohms | ||
9 | Inspect circuit 1228 (PPL) and circuit 1229 (LT BLU) of the A/T wiring harness assembly for a short to ground condition. Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Was a short to ground condition found? | -- | ||
10 | Replace the PC solenoid valve. Refer to Control and Shift Solenoids Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
11 |
Is the resistance within the specified range? | 3-7 ohms | ||
12 | Is the resistance greater than the specified value? | 7 ohms | ||
13 |
Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Was an open condition corrected? | -- | -- | |
14 | Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 3 ohms | -- | |
15 |
Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Was a shorted condition corrected? | -- | -- | |
16 | Using the J 39200 DMM and the J 35616-A , measure the resistance between terminal C2-6 to ground. Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 9 ohms | ||
17 |
Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Was a short to ground condition corrected? | -- | -- | |
18 | Replace the A/T wiring harness assembly. Refer to Torque Converter Clutch Pulse Width Modulation Solenoid, Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid, and Wiring Harness Replacement. Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
19 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module/Throttle Actuator Control Module Replacement in Engine Controls. Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
20 | Perform the following procedure in order to verify the repair:
The difference between the scan tool PC Solenoid Actual Current and the PC Solenoid Ref. Current is less than 0.16 amp. Has the test run and passed? | -- | System OK |
