DTC C1281 Steering Sensor Uncorrelated Malfunction RPO JL4
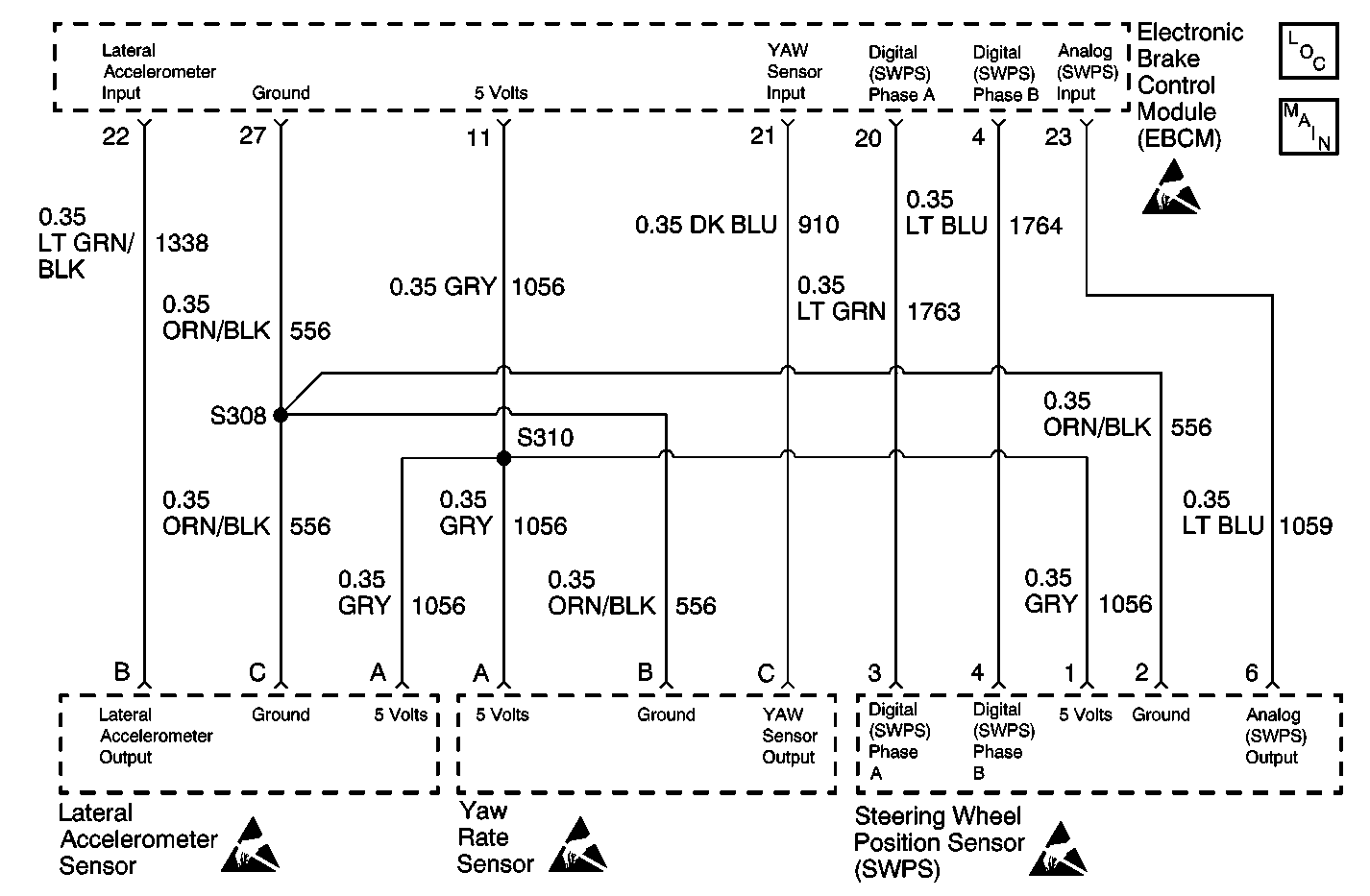
Circuit Description
Active Handling™ is activated by calculating the driver's desired yaw rate (based on wheel speed sensor inputs, lateral acceleration and steering wheel position information) and compares it to the actual yaw rate as measured by the yaw rate sensor. The difference between these two is the yaw rate error, which is then used to determine the amount of oversteer or understeer. If the yaw rate error becomes too large the system attempts to correct the vehicle's yaw motion by using differential braking on the left or right front and rear wheel brakes. To correct for oversteer differential braking is used on the left or right front outer wheel brake. To correct for understeer differential braking is used on the left or right rear inner wheel brake.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The analog and digital steering sensor do not agree for one second while in an Active Handling™ event. |
| • | DTC C1281 can be set any time after the steering angle has been centered and Active Handling™ is activated. If the Active Handling event occurs for 10 seconds without a sign of the yaw rate error ever changing, this code will be set. This is the only condition that will set DTC C1281 by itself. |
| • | DTC C1281 can be set along with DTC C1287. During an Active Handling event the EBCM does a comparison between the SWPS digital value and the SWPS analog value. If the difference is greater than 20 degrees for 1 second both DTC C1281 and DTC C1287 will be set. |
| • | DTC C1281 can be set along with DTC C1282. During an Active Handling event the EBCM does a comparison between the actual yaw rate and a yaw rate derived from the difference in output from the front wheel speed sensors during an oversteer condition or the rear wheel speed sensors during an understeer condition. If this yaw rate difference is greater than 10 degrees/seconds for more than 5 seconds DTC C1281 and DTC C1282 will be set. The use of DTC C1281 with DTC C1282 indicates that the road surface (typically ice) may have created an unusually long period where the wheel speed estimate of yaw rate may have been inaccurate due to vehicle sideslip. This means the DTCs may have been falsely set. |
| • | Normal conditions which could cause code C1281 to set include Active Handling™ activation's brought on by aggressive driving on extremely slippery road surfaces for example, spinning the car in one direction for greater than 10 seconds. This means the DTC may have been falsely set due to aggressive driving. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
ABS and TCS remain enabled, Active Handling™ is disabled.
| • | Indicators that turn on: |
| Car Icon (TCS indicator) |
| • | Messages displayed on the DIC: |
| Service Active HNDLG |
| • | Service Vehicle Soon. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | Condition for DTC is no longer present and scan tool clear DTC function is used. |
| • | Fifty ignition cycles have passed with no DTCs detected. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | It is very important to check the vehicle for proper alignment. The car should not pull in either direction while driving straight on a flat surface. |
| • | It is very important to find out from the driver when the code was set (when the SERVICE ACTIVE HNDLG message was activated). This information may help to duplicate the failure. |
| • | It is very important that a thorough inspection of the wiring and connectors be performed. Failure to carefully and fully inspect wiring and connectors may result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with reappearance of the malfunction. Check connector C102 RH side rear of engine compartment for water intrusion or missing plugs, and that the connector is oriented horizontal to prevent water intrusion. |
| • | An intermittent malfunction is most likely caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a wire that is broken inside the insulation. Refer to Testing for Electrical Intermittents in Wiring Systems. |
| • | The Snapshot function on the scan tool may help in finding an intermittent DTC C1281. |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
This step checks the accuracy of the analog and digital inputs from the SWPS.
-
This step checks for inaccurate yaw rate sensor input.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 | Is this vehicle equipped with Active Handling (RPO JL4)? | -- | ||
3 |
Are any of the following DTC(s) present, C1221-C1235, C1282 or C1287? | -- | Go to Applicable DTC table. Go to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List/Type | |
Using the scan tool perform the Steering Wheel Position Sensor Test. Refer to Scan Tool Diagnostics . Is the analog and digital display on the scan tool within plus or minus 5 degrees of each other at the center (zero) position? | -- | |||
5 | Replace the Steering Wheel Position Sensor. Refer to Steering Shaft, Lower Bearing, and Jacket - Disassemble - Off Vehicle in Steering Wheel and Column - Tilt. Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
Carefully drive vehicle above 24 km/h (15 mph) for 45 seconds in a straight line, while monitoring the Yaw Rate sensor with a scan tool. Is the degrees/second displayed on the scan tool within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 0-5 degrees/second | |||
7 | Replace the Yaw Rate Sensor. Refer to Vehicle Yaw Sensor Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
8 | Perform the Diagnostic Test Drive. Refer to Diagnostic Test Drive . Did DTC C1281 set as a current DTC? | -- | ||
9 | Replace the EBCM Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- |
DTC C1281 Steering Sensor Uncorrelated Malfunction Without RPO JL4
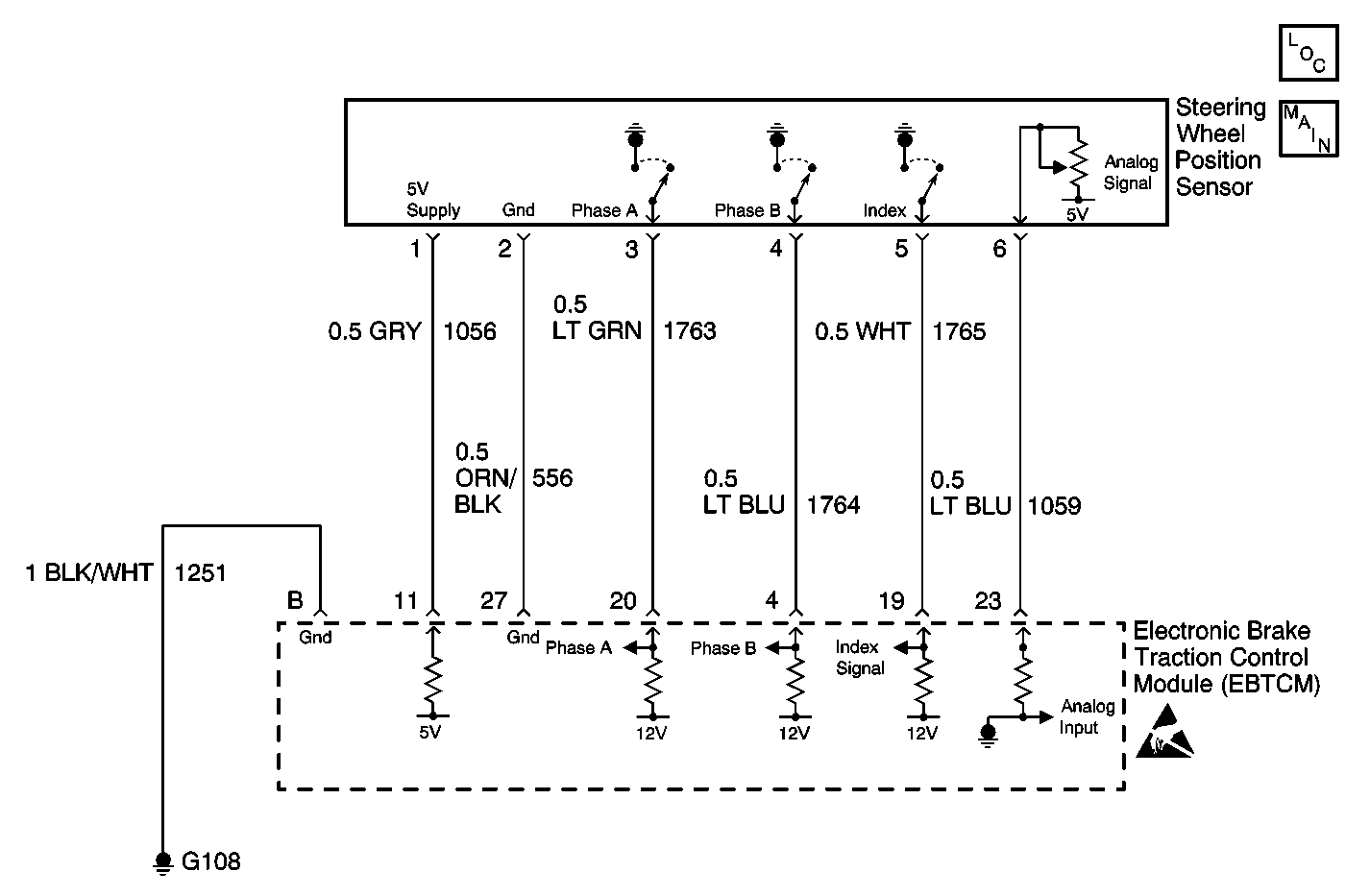
Circuit Description
The EBCM uses four inputs from the Steering Wheel Position sensor:
| • | Phase A digital input |
| • | Phase B digital input |
| • | Index pulse |
| • | Analog input |
This information is used to calculate three things:
| • | The front wheels position when centered. |
| • | The front wheels position when turning. |
| • | The vehicles lateral acceleration. |
The EBCM runs a centering routine when the vehicle speed goes above 30 km/h (18 mph). When the vehicle reaches 30 km/h (18 mph), the EBCM monitors the Steering Wheel Position Sensor inputs (Phase A, Phase B and Analog voltage) to see if the steering wheel is moving. If the steering wheel is not moving for a set period of time then the EBCM assumes the vehicle is going in a straight line. At this point, the EBCM looks at the analog voltage signal and reads the voltage. This voltage normally around 2.5 V, is then considered the center position and the digital degrees also become zero at the same time. This centering routine is necessary to compensate for wear in the steering and suspension. Wear in the steering and suspension can result in a change in the relationship between the steering wheel and the front wheels. By running the centering routine the EBCM can compensate for these changes by changing the digital and analog center position.
The EBCM uses the digital input (Phase A and Phase B) from the Steering Wheel Position Sensor to calculate the direction the driver of the vehicle is trying to steer during an ABS event. This information is also used to calculate the vehicles lateral acceleration for Magnasteer®2.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | DTC C1281 will set when the digitally derived centered angle differs from the analog derived angle by 27 degrees or more for a period of 5 seconds. |
| • | DTC C1281 will set if the index pulse is not seen between ± 37 degrees or is seen between -185 degrees and -37 degrees or 37 degrees and 185 degrees of steering wheel travel. |
| • | DTC C1281 will set if phase A and or phase B are shorted. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
Magnasteer®2 is disabled, ABS/TCS remains active.
Messages displayed on the DIC:
Service Vehicle Soon
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | Condition for DTC is no longer present and scan tool clear DTC function is used. |
| • | Fifty ignition cycles have passed with no DTCs detected. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | If the analog Steering Wheel Position Sensor input is missing then DTC C1288 will set. |
| • | If the Steering Wheel Position Sensor 5 volt supply or the Steering Wheel Position ground is missing DTC C1288 will set. |
| • | It is very important that a thorough inspection of the wiring and connectors be performed. Failure to carefully and fully inspect wiring and connectors may result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with reappearance of the malfunction. Check connector C102 RH side rear of engine compartment for water intrusion or missing plugs, and that the connector is oriented horizontal to prevent water intrusion. |
| • | An intermittent malfunction can be caused by poor connections, broken insulation, or a wire that is broken inside the insulation. |
| • | If an intermittent malfunction exists refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
Checks for the analog voltage to change, if the analog voltage does not change DTC C1281 will set.
-
Checks if the digital Phase A and Phase B are changing state from high to low.
-
checks to see if the analog and digital readings are ± 27 degrees of each other.
-
Checks to see if the EBCM is supplying the pull up voltage for Phase A.
-
Checks to see if the EBCM is supplying the pull up voltage for Phase B.
-
Checks to see if the EBCM is supplying the pull up voltage for the Index pulse.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 | Is this vehicle equipped with Active Handling (RPO JL4)? | -- | ||
3 |
Are any of the following DTC(s) present, C1286 or C1288? | -- | Go to Applicable DTC table. Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List/Type | |
Does the Analog Steer Sensor Voltage change as the steering wheel is rotated? | -- | |||
Using a scan tool in the Data List monitor the Digital SWPS Input as you rotate the steering wheel from left to right. Does the Digital SWPS Input change as the steering wheel is rotated? | -- | |||
6 |
Does the Analog Steer Sensor Voltage read within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 2.7-3.3 V | ||
7 |
Does the voltage change as the steering wheel is rotated? | -- | ||
8 | Rotate the steering wheel in either direction while monitoring the Digital SWPS Index Pulse with a scan in Data List. Does the Digital SWPS Index Pulse go HIGH within ± 37 degrees of steering center while rotating the steering wheel? | -- | ||
9 | Replace the Steering Wheel Position Sensor. Refer to Steering Shaft, Lower Bearing, and Jacket - Disassemble - Off Vehicle in Steering Wheel and Column. Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
10 | Replace the EBCM. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
11 |
Does the voltage toggle between 0 and Battery volts as the steering wheel is rotated? | -- | ||
12 | Using J 39200 DMM, measure the voltage at terminal 4 of J 39700 as an assistant rotates the steering wheel. Does the voltage toggle between 0 and Battery volts as the steering wheel is rotated? | -- | ||
13 |
Does the voltage toggle between 0 and Battery volts one time as the steering wheel is rotated to the right? | -- | ||
14 |
Is the resistance within the range specified within the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
15 | Repair short to ground in CKT 1765. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
16 |
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Above 1 V | ||
17 | Repair short to voltage in CKT 1765. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
18 |
Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 0-5 ohms | ||
19 | Repair open or high resistance in CKT 1765. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
20 |
Is the resistance within the range specified within the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
21 | Repair short to ground in CKT 1763. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
22 |
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Above 1 V | ||
23 | Repair short to voltage in CKT 1763. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
24 |
Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 0-5 ohms | ||
25 | Repair open or high resistance in CKT 1763. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
26 |
Is the resistance within the range specified within the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
27 | Repair short to ground in CKT 1764. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
28 |
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Above 1 V | ||
29 | Repair short to voltage in CKT 1764. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
30 |
Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 0-5 ohms | ||
31 | Repair open or high resistance in CKT 1764. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Battery volts | |||
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Battery volts | |||
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Battery volts |
