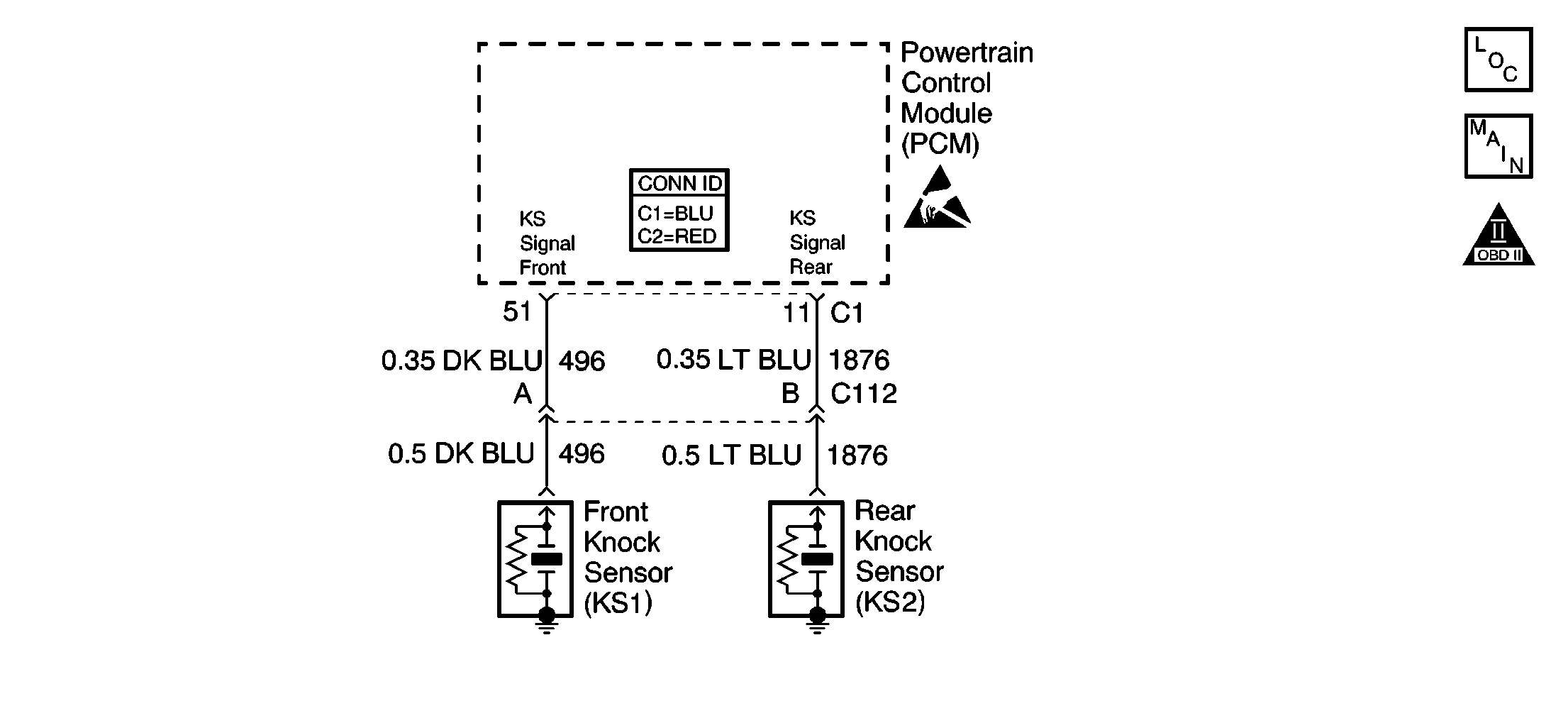
Circuit Description
The knock sensor (KS) system detects engine detonation. The PCM retards the spark timing based on the signals from the knock sensors. The knock sensors produce an AC voltage. The knock sensor voltages are an input to the PCM. The amount of AC voltage produced is proportional to the amount of knock.
An operating engine produces a normal amount of engine mechanical vibration (noise). The knock sensors produce an AC voltage signal from this noise. When an engine operates, the PCM learns the minimum and maximum frequency of the noise the engine produces. When the PCM determines that this frequency is less than or greater than the expected amount, a knock sensor DTC sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine speed is between 1650 RPM and 3000 RPM. |
| • | The MAP is less than 49 kPa (7.1 psi). |
| • | The engine coolant temperature is greater than 60°C (140°F). |
| • | The throttle angle is greater than the idle throttle angle. |
| • | The engine has been operating for longer than 20 seconds. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM determines that this frequency is less than or greater than the expected amount for less than 3.0 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A last test failed, or current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL and the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important:
• Remove any debris from the PCM\TAC module connector surfaces before
servicing the PCM\TAC module. Inspect the PCM\TAC module connector gaskets
when diagnosing/replacing the modules. Ensure that the gaskets are
installed correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminate intrusion into
the PCM\TAC modules. • For any test that requires probing the PCM or a component
harness connector, use the Connector Test Adapter Kit J 35616
. Using this kit prevents damage
to the harness/component terminals. Refer to
Using Connector Test Adapters
in Wiring Systems.
| • | Inspect the knock sensor for proper installation. A knock sensor that is loose or over torqued may cause DTC P0327 to set. |
| • | The knock sensor jumper harness is located at the left rear of the intake manifold near the crankcase vent. |
| • | For an intermittent, refer to Symptoms . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This verifies the malfunction is present. The scan tool will display DTC Ran=Yes and Pass=Int if the failure is intermittent. This indicates the diagnostic passed this ignition cycle and failed this ignition cycle. At this point the resistance of the knock sensors should be verified to be in the correct range. If the knock sensor resistances are correct, inspect the KS system wiring connections. When inspecting the KS system connections, start at the KS system jumper harness connector located behind the intake manifold. Then inspect the connections at the PCM. Refer to the wiring schematic for the correct connector and terminal. Then inspect the connections at the appropriate knock sensor. Failure Records data does not include the parameter KS Activity, however other parameters may aid in locating the conditions under which an intermittent occurred.
-
This test isolates the Knock Sensor from the rest of the circuit.
-
Tap on the engine block in the location of the appropriate knock sensor.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||
|
Important: If an engine knock can be heard, repair the engine mechanical condition before proceeding with this diagnostic.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic failed this ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
Is the resistance of the knock sensor within the specified range? | 93-107Kohms | |||||||||
Important: Do not tap on plastic engine components. Is any signal indicated on the DMM while tapping on the engine near the Knock Sensor? | -- | |||||||||
5 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
6 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
7 | Replace the Knock Sensor. Refer to Knock Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
8 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
9 |
Important: Program the replacement PCM. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
10 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||||||||
11 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option with the scan tool. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
