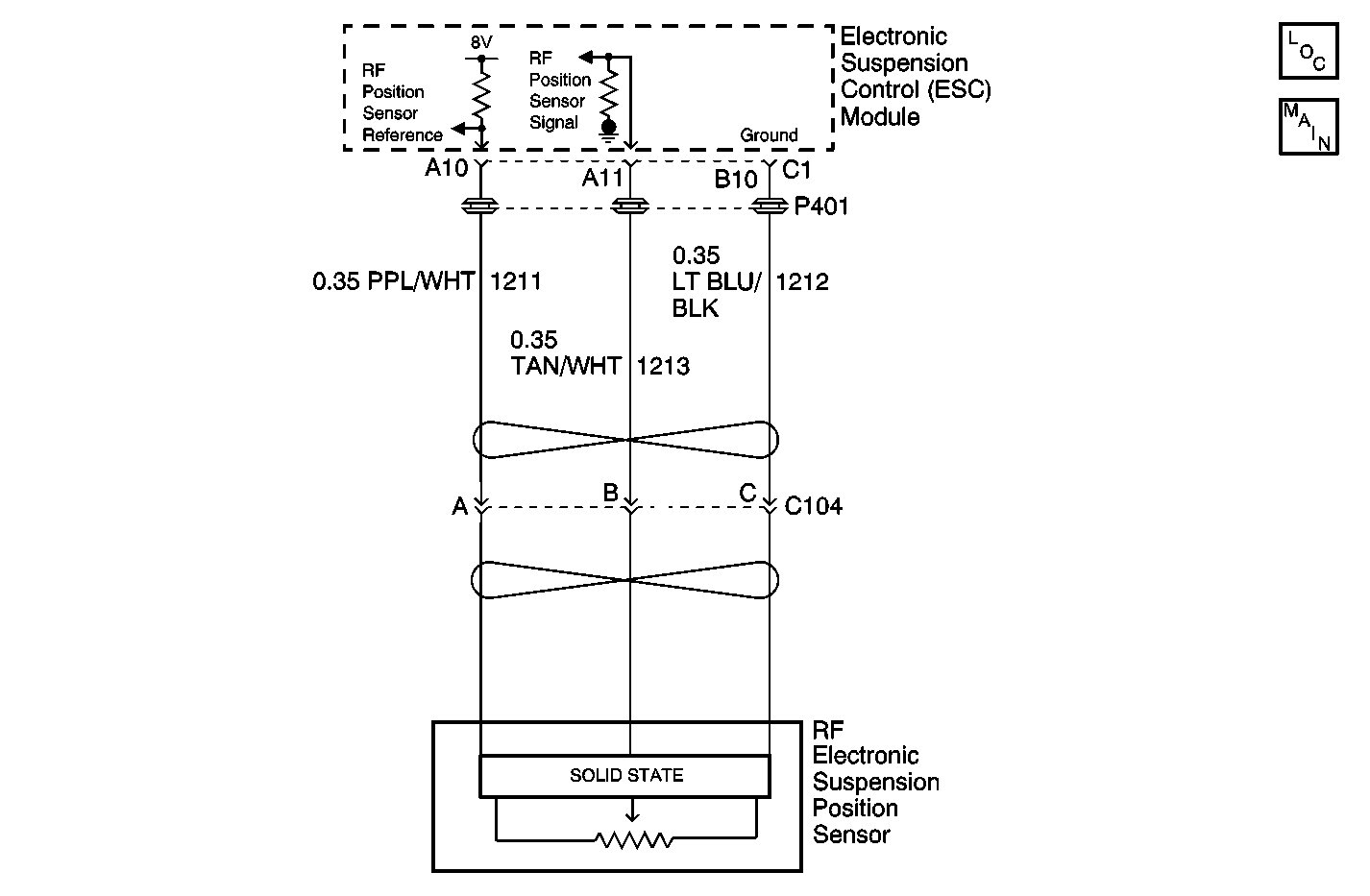
Circuit Description
The ESC module supplies 8 volts to the position sensors. The position sensors use the supplied 8 volts to produce an analog output range of 0-5 volts. The ESC module calculates vehicle suspension settings based upon the voltage levels received back from the position sensors. The ESC model monitors for an out of range condition.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The ESC module senses position sensor output voltage under 0.35 volts or over 4.75 volts. |
| • | The condition must be detected for 1 second in 4 consecutive ignition cycles. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | Stores a DTC C0620 in the ESC memory. |
| • | Provides shocks absorber solenoid control based on the vehicle speed only. |
| • | Sends a message to the IPC to display the SERVICE RIDE CONTROL message. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | A history DTC will clear after 100 consecutive ignition cycles if the condition for the malfunction is no longer present. |
| • | The ESC module senses the correct position sensor output voltage between 0.35-4.75 volts. |
| • | Use the IPC clearing DTC feature. |
| • | Using a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | The following conditions may cause an intermittent malfunction to occur: |
| - | An intermittent open or short in the RF position sensor circuit. |
| - | Bent, disconnected, or damaged position sensor linkage. |
| • | When using a scan tool in order to read position sensor voltage, always make sure the vehicle is sitting with the full vehicle weight on its wheels. Measuring position sensor voltage with the vehicle raised and the wheels hanging may lead to incorrect diagnosis. |
| • | An intermittent DTC C0620 may produce a random firm/soft ride condition. |
| • | The ESC module uses an ignition cycle counter diagnostic approach to set this DTC. This requires the ESC module to detect the malfunction 4 times before setting the DTC. To disable this feature, use a scan tool to clear all DTCs before preforming diagnostic procedures. |
| • | If the DTC is a history DTC, the problem may be intermittent. Using a scan tool, monitor the position sensor voltage while test driving the vehicle or moving the wiring and the connectors. This can often cause the malfunction to occur. |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
This tests the RF position sensor signal voltage range using a scan tool. Normal signal voltage range is between 0.35-4.75 volts.
-
This tests the RF position sensor signal voltage range using a scan tool with the sensor disconnected. Normal signal voltage range with the sensor disconnected is approximately 0 volts.
-
Tests for the proper operation of the circuit in the high voltage range. If the fuse in the jumper opens when you perform this test, the signal circuit is shorted to ground.
-
Tests for a short to voltage in the 8 volt reference circuit.
-
Tests for a high resistance or an open in the ground circuit.
-
Tests for an open or high residence in the position sensor ground circuit.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the RTD Diagnostic System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Diagnostic System Check |
Does the scan tool indicate that the RF Position Sensor data parameter is within the specified range? | 0.35 - 4.75 V | Go to Diagnostic Aids | Go to Step 3 | |
Does the scan tool indicate that the RF Position Sensor data parameter is less than the specified value? | 0.35 V | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 10 | |
Does the scan tool indicate that the RF Position Sensor data parameter is greater than the specified value? | 4.75 V | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 8 | |
Does the voltage measure less than the specified value? | 8 V | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 7 | |
Does the resistance measure less than the specified value? | 5 ohms | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 11 | |
7 | Test the 8 volt reference circuit of the RF Position Sensor for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 13 |
8 | Test the 8 volt reference circuit of the RF Position Sensor for a short to ground, a high resistance, or an open. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 9 |
9 | Test the signal circuit of the RF Position Sensor for a short to ground, a high resistance, or an open. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 13 |
10 | Test the signal circuit of the RF Position Sensor for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 13 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 13 | |
12 | Inspect for poor connections at the harness connector of the RF Position Sensor. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 14 |
13 | Inspect for poor connections at the harness connector of the ESC module. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 15 |
14 | Replace the RF Position Sensor. Refer to Electronic Suspension Front Position Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 16 | -- |
15 | Replace the ESC module. Refer to Electronic Suspension Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 16 | -- |
16 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | Go to Step 2 | System OK |
