Circuit Description
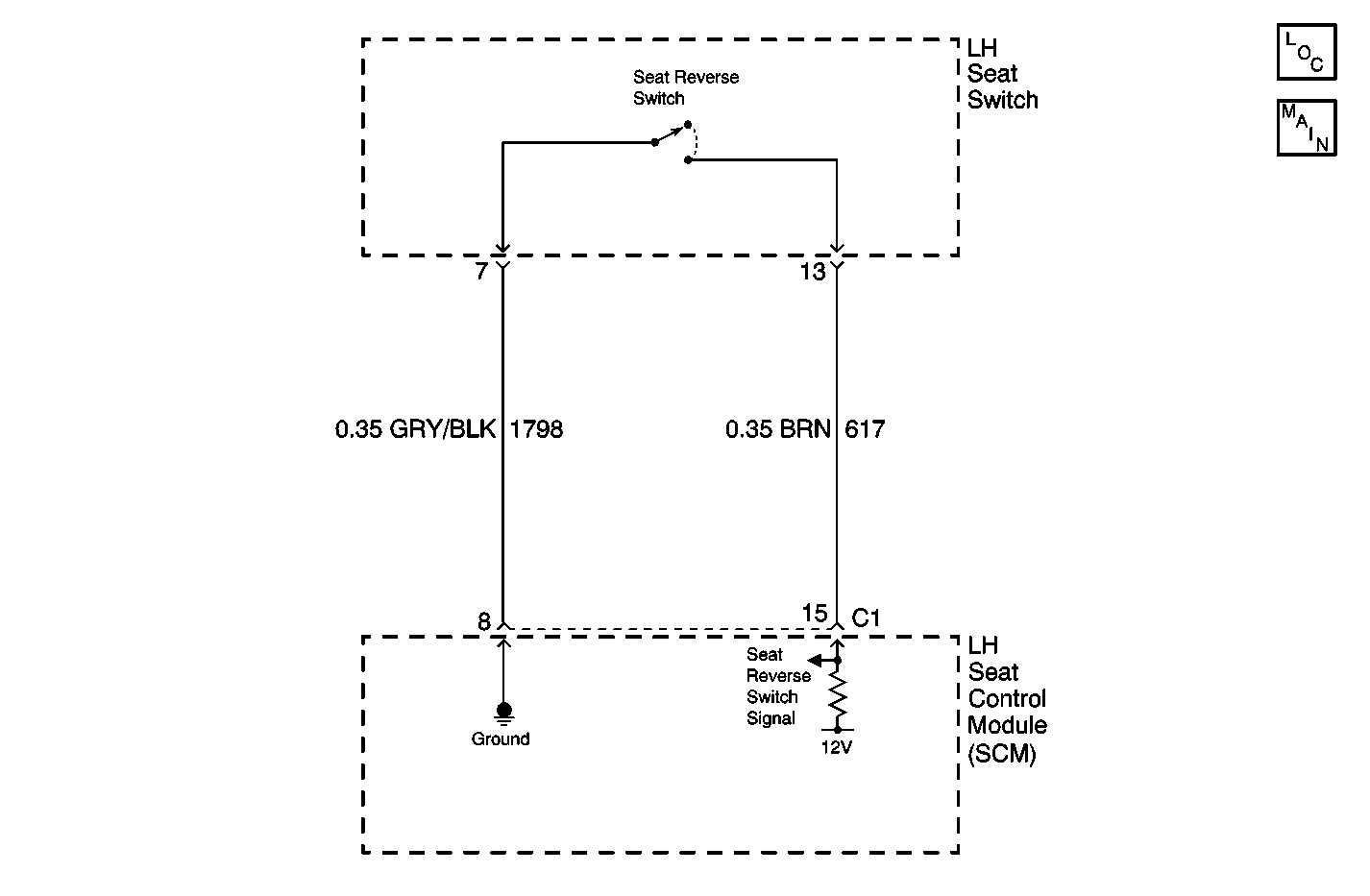
The LH seat switch circuit provides an input to the LH Seat Control Module (SCM) when the seat reverse switch is pressed in REVERSE. This input allows the SCM to detect a seat REVERSE request. The SCM provides a signal, which is pulled up to system battery voltage through a pull-up resistor, and a ground to the seat reverse switch. When the seat reverse switch is pressed the signal is pulled low within the SCM. When the SCM detects the transition from high to low it will command the seat to move in the REVERSE direction. When the switch is released it will command the seat to stop.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The seat reverse switch input, to the SCM, is active (low) for more than 20 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | Stores a history DTC B2197 in the SCM memory. |
| • | This DTC can only be set as a history code even if the malfunction is current. |
| • | No driver warning message will be displayed for this DTC. |
| • | The operation/function of the seat reverse switch is disabled. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The seat reverse switch input, to the SCM, is inactive (high) for less than 20 seconds. |
| • | Using a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | The following conditions may cause an intermittent malfunction: |
| - | There is an intermittent short to ground in CKT 617. |
| - | The seat reverse switch is shorted to ground internally or is sticking. |
| - | The seat reverse switch was pressed for longer than 20 seconds. |
| • | If CKT 617 is shorted to ground or the seat reverse switch is stuck closed, the seat will remain in the reverse position at all times. |
| • | Using a scan tool, select SCM inputs and monitor the seat reverse switch status. If the scan tool displays ACTIVE, disconnect the seat reverse switch and check if the seat status changes to INACTIVE. If the status changed, then replace the LH seat switch. If the status did not change, then check CKT 617 for a short to ground. |
| • | If the DTC does not reset after the code is cleared, then the problem may be intermittent. Perform the tests shown while moving related wiring and connectors. This can often cause the malfunction to occur. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Activate the seat reverse switch numerous times while monitoring the status on the scan tool to see if it sticks intermittently. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
This test determines the status of the seat reverse switch using a scan tool. The scan tool will display the seat reverse switch status as ACTIVE (button pressed) and INACTIVE (button released).
-
This test checks if the seat reverse switch is shorted to ground or stuck. If the seat reverse switch status changes from ACTIVE to INACTIVE when the seat reverse switch is disconnected, then the switch assembly must be replaced.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Were you sent here from the Power Seat Diagnostic System Check? | -- | ||
Using a scan tool, select SCM input display and monitor the seat reverse switch status. Does the scan tool display seat reverse switch status as ACTIVE? | -- | |||
Does the scan tool display seat reverse switch status as ACTIVE? | -- | |||
4 | Inspect and repair circuit 617 for a short to ground. Was a problem found and repaired? | -- | ||
5 | Replace the power seat switch assembly. Refer to Power Seat Switch Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
6 | Replace the SCM. Refer to Memory Seat Control Module Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
7 | Inspect and repair the seat reverse switch circuit for an intermittent malfunction. Refer to Testing for Electrical Intermittents . Was a problem found and repaired? | -- | ||
8 |
Does DTC B2197 set as history? | -- | System OK | |
9 |
Did you correct the condition? | -- | System OK |
