To diagnose valve or piston faults and poor engine operation,
a compression test must be performed to determine the cylinder compression
pressure. When checking the cylinder compression, the following conditions
must be met:
| • | The throttle must be wide-open. |
| • | All of the spark plugs must be removed. |
| • | The battery must be at or near full charge. |
Test each cylinder four times.
Tool Required
J 22794 Spark Plug
Port Adapter
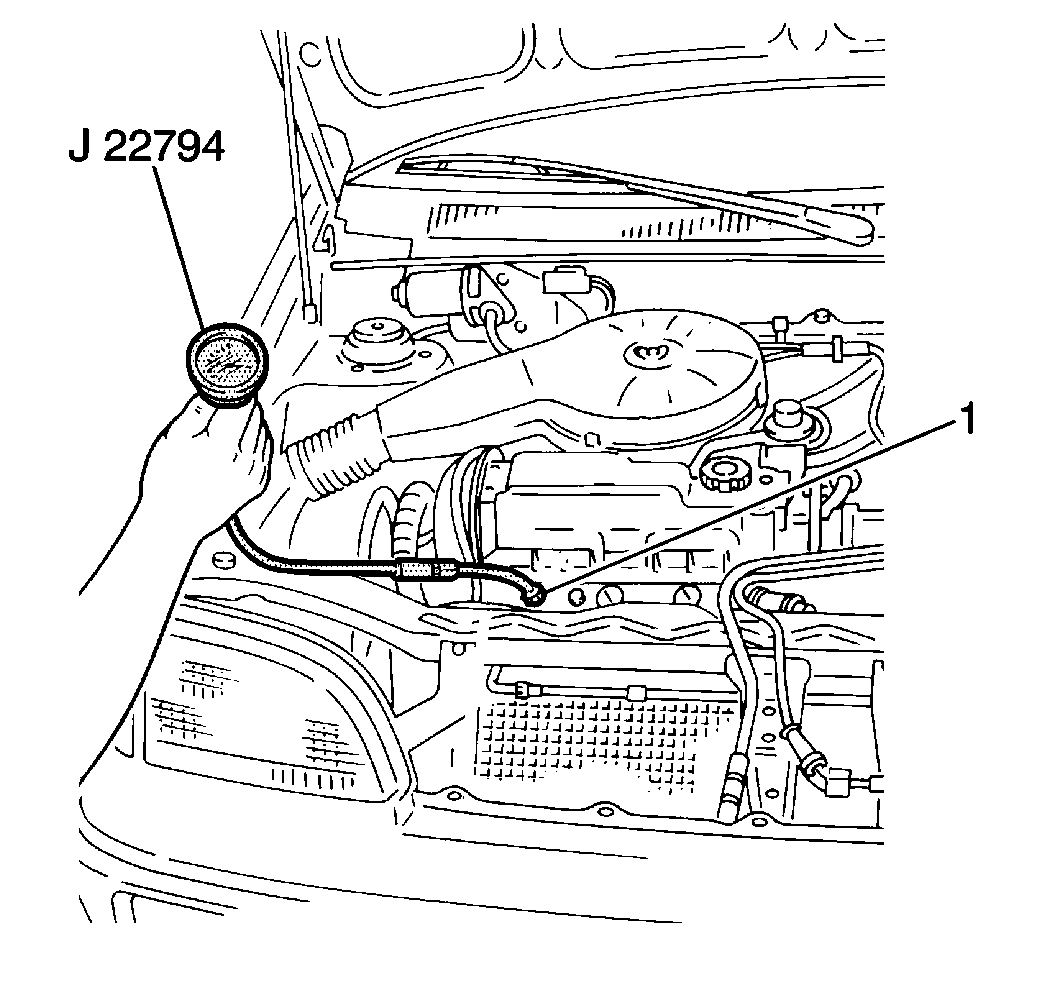
- Turn the ignition switch
to LOCK.
Important: Be certain to clean any debris from around the spark plug holes prior
to removing the spark plugs.
- Remove all of the spark plugs and disconnect the distributor electrical
connector. Refer to
Spark Plug Replacement
in Engine Electrical.
- Remove the FI fuse (1) from the fuse and relay box.

- Install a J 22794
and a compression gage into a spark
plug hole (1).
- Disengage the clutch (manual transaxle equipped vehicles) to lighten
the starting load on the engine. Depress the accelerator pedal to the floor
(wide-open throttle).
- Crank the engine (with a fully charged battery) to take four pressure
readings.
- Measure the highest pressure reading on the compression gage.
| • | Standard compression pressure is 1,400 kPa (199 psi)
at 250 RPM. |
| • | Minimum allowable compression pressure is 1,100 kPa (156.4 psi)
at 250 RPM. |
Important: The maximum allowable compression pressure difference between any two
cylinders is 100 kPa (14.2 psi) at 250 RPM.
- Repeat the compression test procedures for the remaining two cylinders.
- Remove the J 22794
and compression gage from the engine.
- Install all three spark plugs and connect the distributor electrical
connector. Refer to
Spark Plug Replacement
in Engine Electrical.
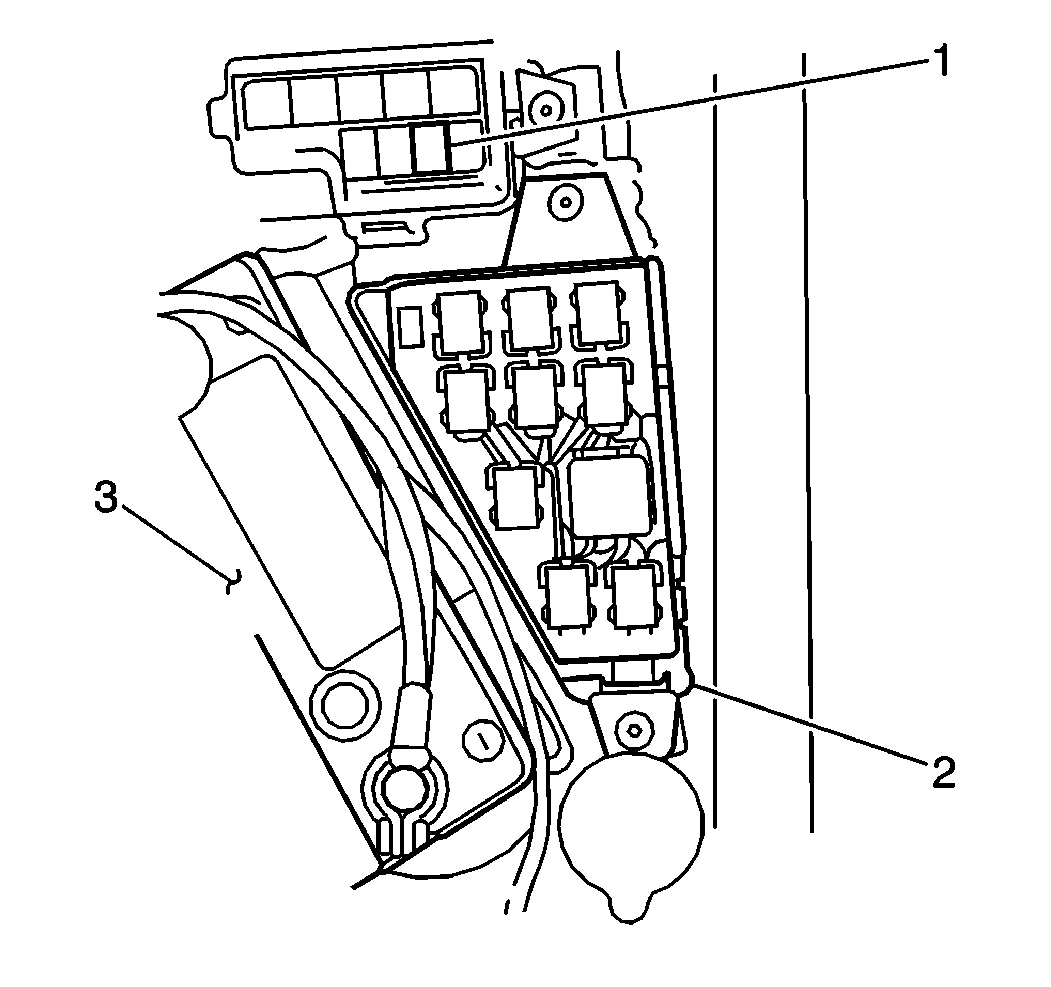
- Install the FI fuse (1)
to the fuse and relay box (2).
- Evaluate the compression tests:
| • | Normal operation--If the cylinder compression pressure increases
quickly and evenly to the compression standard [1,400 kPa (199 psi)
at 250 RPM], the pistons, piston rings and the valves are operating
normally. |
| • | Piston rings faulty--If the cylinder compression is low on
the first stroke and tends to increase on the following strokes (but does
not reach the compression standard), the probable cause is that the piston
rings are faulty. The addition of oil should improve the compression pressure
considerably. |
| • | Valves faulty--If the cylinder compression is low on the
first stroke and does not increase on following strokes, the probable cause
is that the valves are faulty. The addition of oil does not significantly
improve the compression pressure. |



