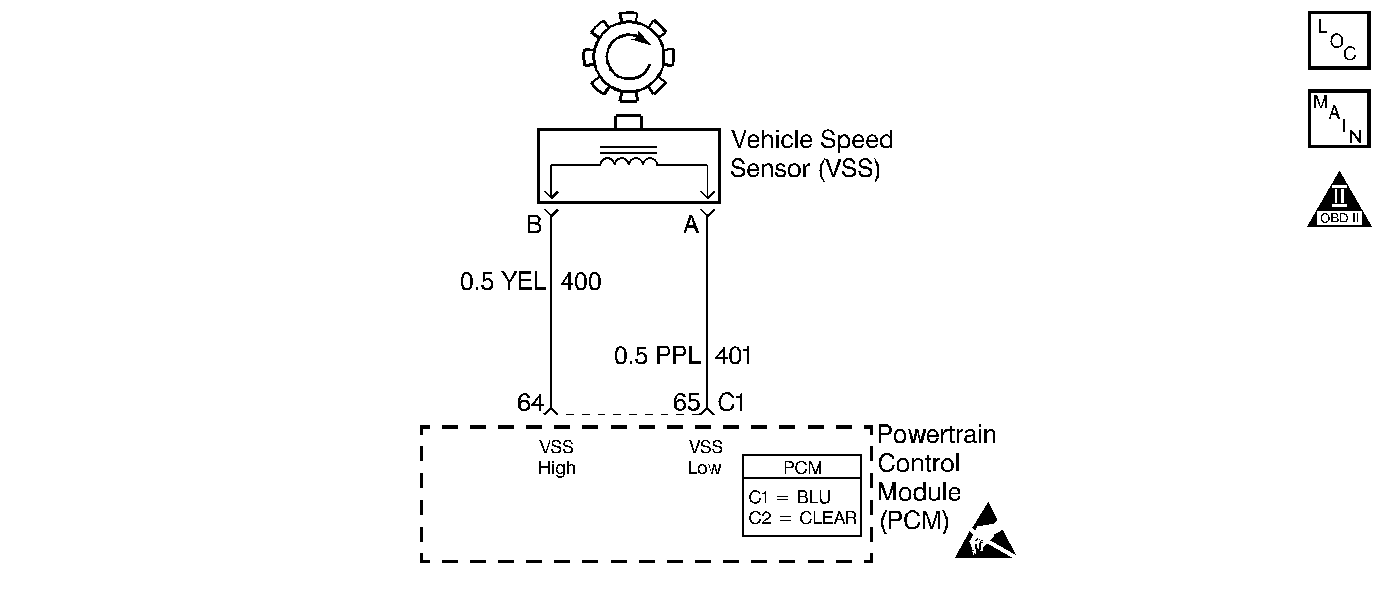
Circuit Description
The vehicle speed sensor (VSS) system is a pulse generator consisting of a speed sensor assembly, located in the case, and a toothed speed sensor rotor, which is pressed onto the final drive assembly. As the vehicle drives forward, the speed sensor rotor also rotates. This rotation produces a variable voltage signal in the pickup coil that is proportional to vehicle speed.
The VSS generates AC voltage varying from 0.5 volts at 100 RPM to more than 100 volts at 6000 RPM.
The PCM uses this signal to determine vehicle speed, and to develop the shift pattern for the transmission. Other systems also use VSS information:
| • | TCC apply and release |
| • | Cruise control system |
| • | Fuel delivery systems |
When the PCM detects an unrealistic, large, rapid drop in vehicle speed, with a high engine speed while in a drive range, then DTC P0503 sets. DTC P0503 is a type A DTC.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine speed is more than 500 RPM for 5 seconds. |
| • | The engine is not in fuel shut off. |
| • | More than 6 seconds has elapsed since the last range selector position change. |
| • | The output speed does not rise more than 500 RPM within 2 seconds. |
| • | The transmission is not in Park or Neutral. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0503 sets when the output speed drops more than 1,500 RPM within 2 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). |
| • | The transmission defaults to 3rd gear. |
| • | The PCM inhibits TCC operation. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns OFF the MIL during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test runs and passes. |
| • | A scan tool clears the DTC from PCM history. |
| • | The PCM clears the DTC from the PCM history if the vehicle completes 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without an emission related diagnostic fault occurring. |
| • | The PCM cancels the DTC default actions when the fault no longer exists and the ignition is OFF long enough in order to power down the PCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Check for Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) in circuits 400 and 401. EMI may be induced if the harness is routed along the spark plug wires. |
| • | Inspect the wiring at the PCM, the Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) connector and all other circuit connecting points for the following conditions: |
| - | A backed out terminal |
| - | A damaged terminal |
| - | Reduced terminal tension |
| - | A chafed wire |
| - | A broken wire inside the insulation |
| - | Moisture intrusion |
| - | Corrosion |
| • | When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test equipment for a change. |
| • | Ensure that the VSS is securely tightened to the case extension. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step verifies that the PCM is receiving a signal from the vehicle speed sensor.
-
This step verifies that no opens exist in the circuitry from the vehicle speed sensor to the PCM connector.
-
This step performs a resistance test on the VSS circuits from the PCM connector.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Were you sent here from the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||||
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool in order to record the Freeze Frame and Failure Records. Using the Clear Info function erases the Freeze Frame and Failure Records from the PCM. Notice: Support the lower control arms in the normal horizontal position in order to avoid damage to the drive axles. Do not operate the vehicle in gear with the wheels hanging down at full travel. With drive wheels rotating, does Transmission Output Speed increase when wheel speed increases? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||||
Is the measured voltage greater than the specified value? | 0.4 V | |||||||||||||
Select ohms on the DMM. Is the resistance between terminals 64 and 65 greater than the specified value? | 1,864 ohms | |||||||||||||
5 |
Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Was a condition found? | -- | ||||||||||||
6 | Does the DMM display a value less than the resistance specified? | 981 ohms | ||||||||||||
7 | Inspect circuits 400 and 401 for a short together. Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Was a condition found? | -- | ||||||||||||
8 |
Is either resistance lower than the specified value? | 50 K ohms | ||||||||||||
9 | Inspect circuits 400 and 401 for a short to ground. Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Was a condition found? | -- | ||||||||||||
10 | Disconnect the VSS and connect a DMM from terminal A to terminal B of the VSS. Is the measured resistance within the specified range? | 981-1,864 ohms | ||||||||||||
11 | Remove the VSS and inspect the sensor rotor on the final drive carrier assembly for damage, looseness or misalignment. Refer to Unit Repair. Was a condition found and corrected? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||||
12 | Replace the vehicle speed sensor. Refer to Vehicle Speed Sensor Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
13 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming in Engine Controls. Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
14 | Repair the wiring as needed. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
15 | Perform the following in order to verify the repair:
Has the test run and passed? | -- | System OK |
