Cuts Out, Misses Symptom
Checks
| Action
|
DEFINITION: A steady pulsation
or jerking that follows engine speed, usually more pronounced as the engine
load increases. The exhaust has a steady spitting sound at idle, low
speed or on hard acceleration.
|
Preliminary Checks
|
|
Sensor Checks
| Inspect the mass air flow (MAF) sensor operation. Run the engine to
normal operating temperature. Turn OFF all accessories and observe the MAF
sensor at idle with a scan tool. If the MAF sensor reading is more than
3.5 g/s refer to
DTC P0101 Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Performance
.
|
Fuel System Checks
|
| • | Check for water contamination of the fuel. |
|
Ignition
System Checks
|
| • | Check for an ignition system misfire: |
| | Important: Do not perform this test for more than 2 minutes in order to
prevent damage to the catalytic converter.
|
| 2. | Remove one ignition coil at a time using insulated pliers. |
| 4. | Check for spark on the suspected cylinders with a J 26792
spark tester or equivalent if there
is no RPM drop on one or more cylinders. |
| 6. | If there is spark, check the spark plugs for any of the following
conditions: |
| - | Any wet or fuel fouled plugs |
| - | A terminal screw that is bent or loose |
| - | A ceramic insulator that has cracks, carbon tracking, or red or
black dust deposits. |
| - | A tip insulator that has cracks or carbon tracking, any oil, carbon,
glazing, or fuel additive deposits, or is loose. |
| - | A center electrode that is loose and wiggles side to side. |
| - | An incorrect spark plug gap |
| • | Check the ignition coil boots for carbon tracking or cracks. |
| • | Check the ignition system for moisture, dust, cracks, burns, etc. |
|
Engine Mechanical Checks
|
| • | Check for any of the following engine mechanical problems: |
| - | Any faulty hydraulic lifter assemblies |
| - | Any broken or weak valve springs |
| - | An incorrect valve timing |
| - | An incorrect or worn camshaft |
| • | Check the intake and exhaust manifold passages for casting flash. |
| • | Refer to Engine Mechanical. |
|
Additional Checks
|
| • | An engine miss condition can be caused by electromagnetic interference
(EMI) on the reference circuit. EMI can usually be detected by monitoring
the engine RPM with a scan tool. A sudden increase in RPM with little
change in the actual engine RPM change indicates EMI is present.
If a problem exists, check the routing of the secondary ignition
wires and the high voltage components. |
| • | Verify the PCM grounds are clean, tight, and in the proper locations.
Refer to
Power and Ground
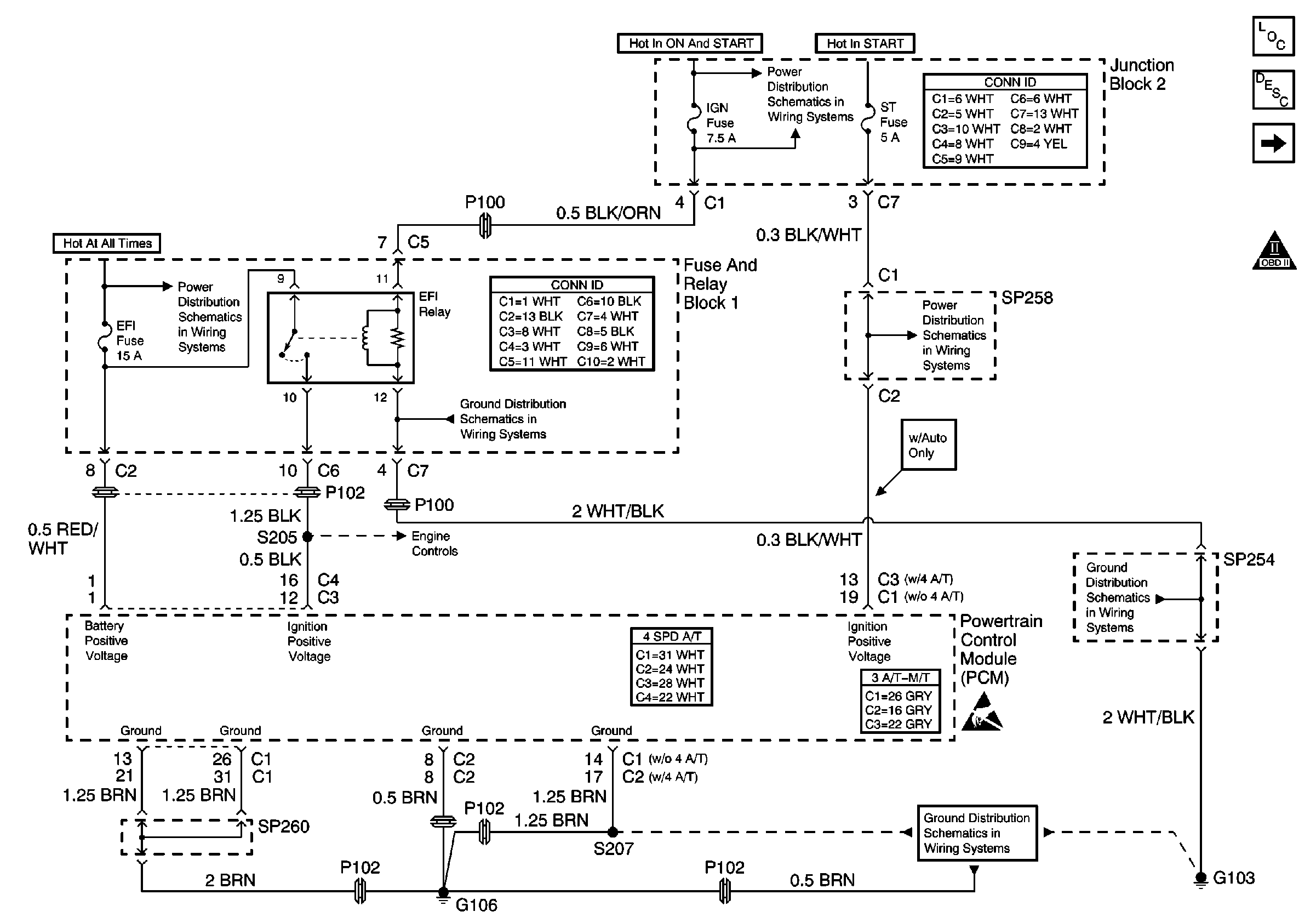
. |
|

