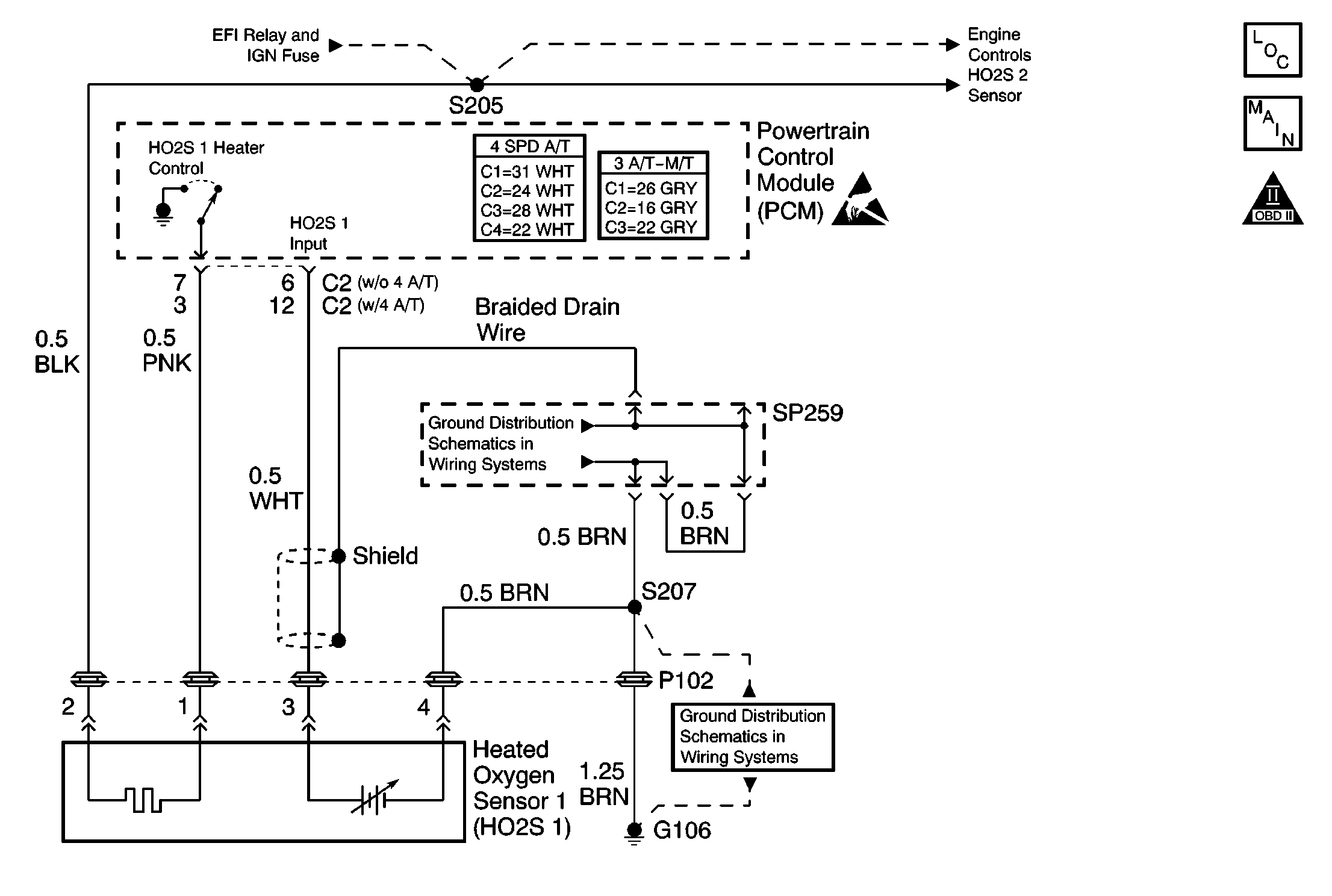
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) continuously monitors the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) activity. The PCM counts the number of times that the a rich-to-lean and lean-to-rich response is indicated and adds the amount of time required to complete all the transitions. The PCM uses this information in order to determine an average time for each transition. A DTC P0133 will set if the average transition time is too slow.
A lean-to-rich transition is indicated when the HO2S voltage changes from less than 300 mV to more than 600 mV. A rich-to-lean transition is indicated when the HO2S voltage changes from more than 600 mV to less than 300 mV. An HO2S that responds too slowly may be faulty and should be replaced.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine coolant temperature is more than 70°C (158°F). |
| • | The engine is running at idle. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The response time necessary for the HO2S voltage to change from rich-to-lean, or from lean-to-rich, is 1.1 seconds or more.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 2 consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault active. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information is stored in the Freeze Frame buffer. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL turns OFF after 3 consecutively passing trips without a fault present. |
| • | A History DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | Use the scan tool Clear DTC Information function in order to clear the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for a contaminated HO2S. Silicon contamination of the HO2S can cause a low signal voltage to be indicated. Silicon contamination is indicated by a powdery white deposit on the portion of the HO2S exposed to the exhaust stream. Before replacing the HO2S determine the cause of the contamination and correct the condition.
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by fault in the HO2S 1 electrical circuit. Inspect the wiring harness and components for any intermittent conditions. Refer to Intermittent Conditions .
The information included in the Freeze Frame data can be useful in determining the vehicle operating conditions when the DTC first set.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
-
The OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the freeze frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
This step checks whether the malfunction that caused the DTC P0133 is still present. Operating the vehicle in Check mode enhances the diagnostic capabilities of the PCM. The HO2S 1 diagnostic can be monitored on the scan tool under the MIL/System Status selection of System Information. When the HO2S test displays a YES status, indicating that the heated oxygen sensor system diagnostic is completed, check for a DTC P0133 in the Last Test Failed screen of the scan tool. If there is no DTC P0133 displayed the HO2S diagnostic has run and passed, indicating that no malfunction was present this time. The DTCs MUST be cleared in order to view the Current Status of the system diagnostics being performed. Do not forget that the MIL/System Status tests only indicate that the test has run, not whether the test passed or failed. The Last Test Failed screen must be checked for related DTCs in order to determine the outcome of the diagnostic test involved. For additional information on Check mode operation refer to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis .
-
In this step the DMM is used as a low current voltage source taking the place of the HO2S. This step verifies whether the PCM is able to receive and process a signal from the HO2S 1.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | |||||||||||
Did DTC P0133 set? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||
3 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||||
4 |
Was an exhaust leak found? | -- | ||||||||||
Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 1155 mV | |||||||||||
6 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||||
7 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||||
8 | Repair the open in the HO2S 1 ground circuit between the HO2S 1 and G106. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
9 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
10 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
11 |
Are any DTCs displayed on the scan tool? | -- | System OK |
