The purpose of the DBC 7 Antilock Brake System (ABS) is to minimize wheel
slip during heavy braking. DBD 7 performs this function by monitoring the speed
of each wheel independently during a braking event. This allows the driver to retain
directional stability and better steering capability.
Basic Knowledge Required
Before using this section, it is important that you have a basic knowledge of
the following items. Without this basic knowledge, it will be difficult to use the
diagnostic procedures contained in this section.
| • | Basic Electrical Circuits: You should understand the basic theory of electricity
and know the meaning of potential (voltage), current (amperes) and resistance (ohms).
You should understand what happens in a circuit with open or shorted wire. You should
be able to read and understand a wiring diagram. |
| • | Use of Circuit Test Tools: You should be familiar with meter controls
and how to use them correctly. You should be able to measure voltage, resistance and
current. You should know how to use jumper sire to bypass components for testing circuits. |
ABS System Components
Caution: Certain components in the Antilock Brake System (ABS) are not intended
to be serviced individually. Attempting to remove or disconnect certain system
components may result in personal injury and/or improper system operation.
Only those components with approved removal and installation
procedures should be serviced.
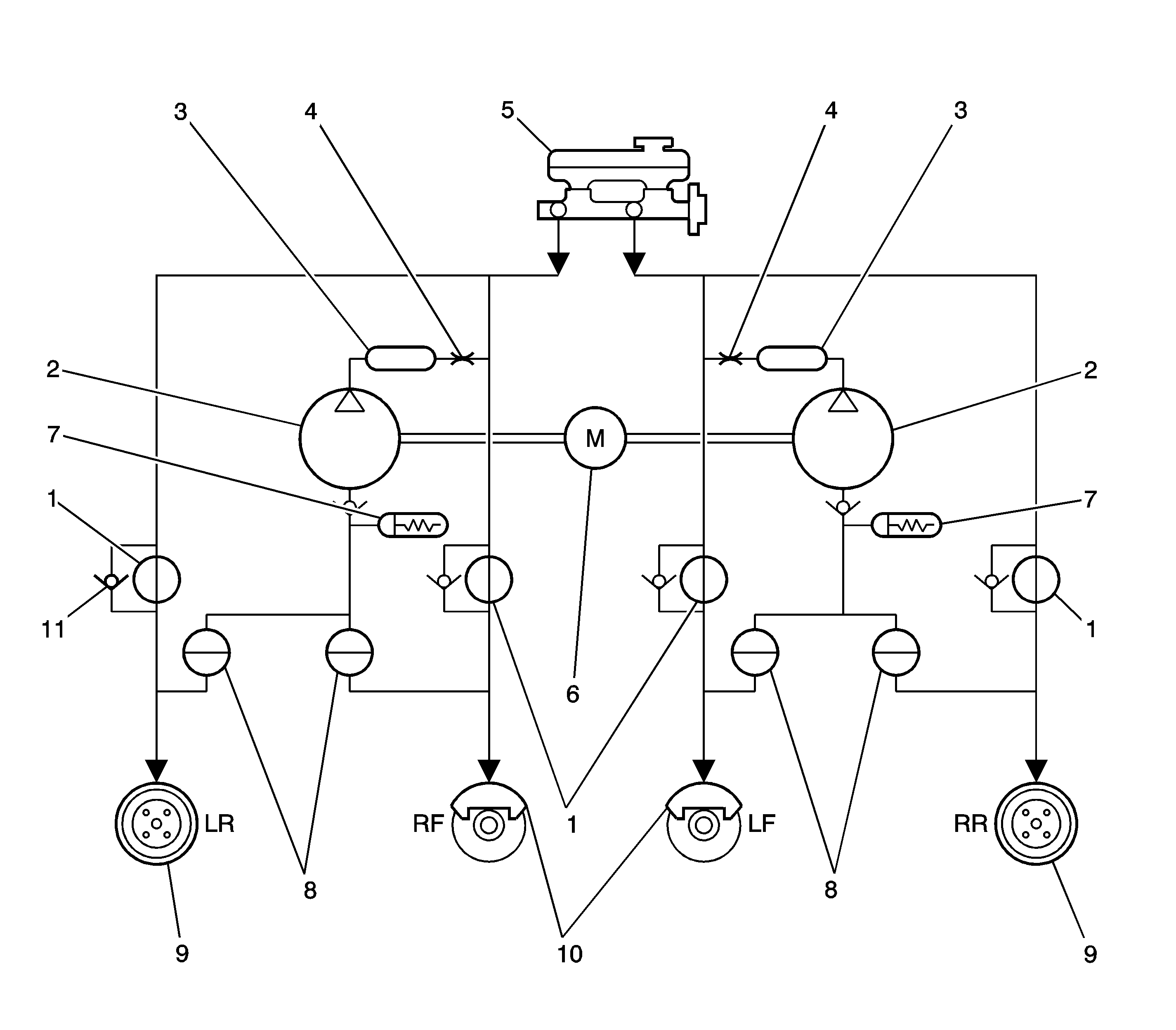
The DBC 7 Antilock Brake System (ABS) consists of a conventional hydraulic
brake system plus antilock components. The conventional brake system includes a vacuum
booster, master cylinder, front disc brakes, rear drum brakes, interconnecting hydraulic
brake pipes and hoses, brake fluid level sensor and the brake warning lamp indicator.
The ABS components include a hydraulic unit, an EBCM (Electronic Brake Control
Module), system fuse, four wheel speed sensor (one at each wheel) interconnecting
wiring, ABS indicator, the DDRP (De-coupled Dynamic Rear Proportioning) indicator
(which is connected to the parking lamp) and the rear drum brakes. See "ABS
Component Locator" in this section for the general layout of this system.
The hydraulic unit with the attached EBCM is located between the surge tank
and the fire wall on the left side of the vehicle.
The basic hydraulic unit configuration consists of hydraulic check valves, two
solenoid valves for each wheel, a hydraulic pump, two accumulators, and two dampers.
The hydraulic unit controls hydraulic pressure to the front calipers and the rear
wheel cylinder by modulating hydraulic pressure to prevent wheel lockup.
Base Braking Mode
The baseline braking mode of the DBC 7 Antilock Braking System (ABS)
system used in this vehicle is a diagonal split system. In this system, one master
cylinder circuit supplies pressure to the right front and the left rear brakes; the
other circuit supplies pressure to the left front and the right rear brakes. All valves
in the hydraulic modulator are in their normal, non-energized positions as shown in
the drawings found in "ABS System Components" in this section.