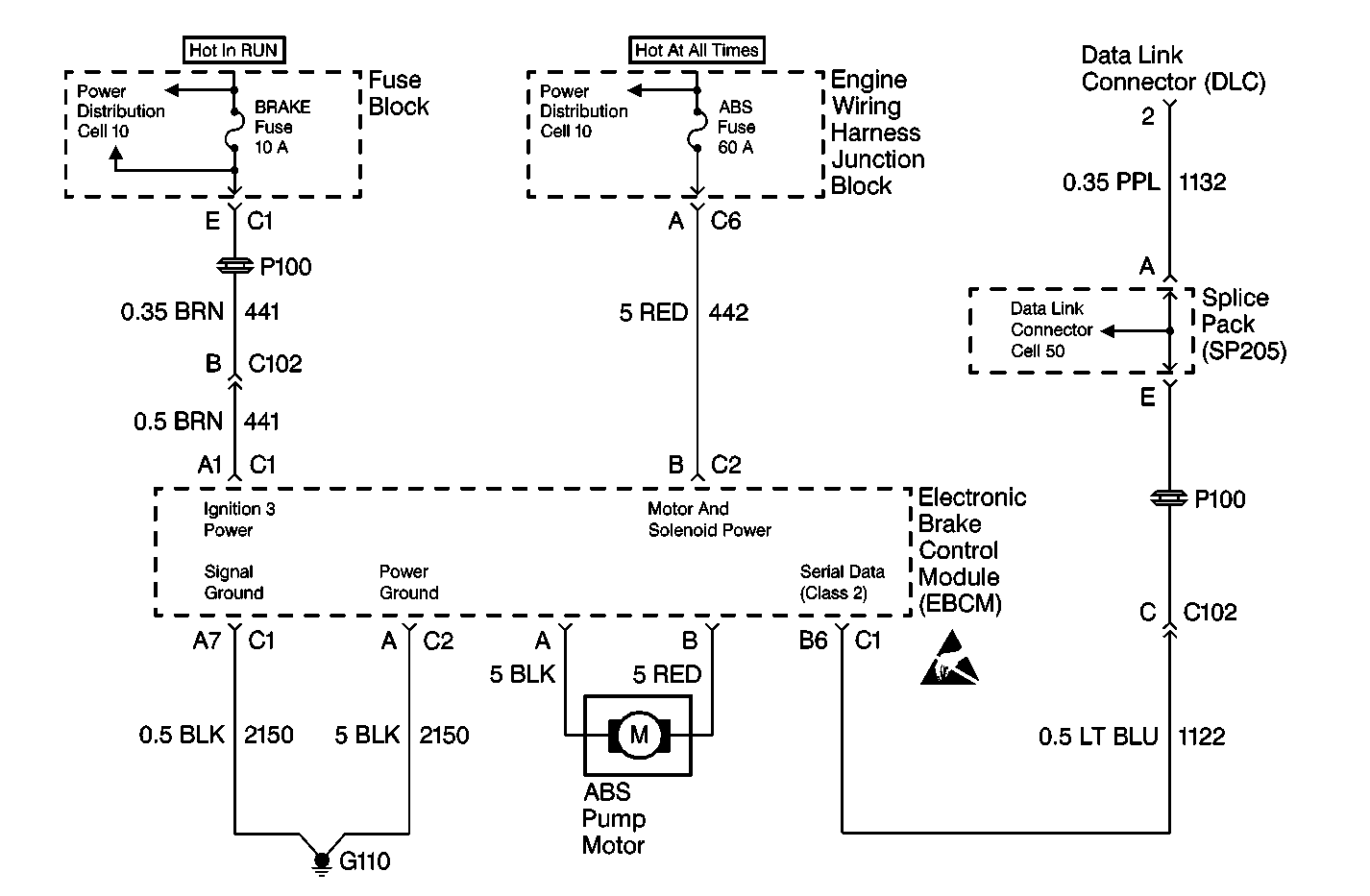
Circuit Description
The ABS Diagnostic System Check is an organized approach to identify problems associated with the EBCM. This check must be the starting point for any EBCM complaint, and will direct you to the next logical step in diagnosing the complaint. The EBCM is a very reliable component and is not likely the cause of the malfunction. Most system complaints are linked to faulty wiring, connectors, and occasionally to components. Understanding the ABS system and using the tables correctly will reduce diagnostic time and prevent unnecessary parts replacement.
Diagnostic serial data is transmitted/received by the EBCM through connector C2, terminal B6. The EBCM is supplied battery voltage through connector C1, terminal B and switched ignition voltage through connector C2, terminal A1. Grounds are provided through connectors C1, terminal A, and C2 terminal A7.
Diagnostic Aids
Excessive resistance in the ground or power supply circuits will not allow communication with the EBCM. If communication with the EBCM is not possible, ensure that the ABS ground connection is good and that there is no excessive resistance in any of the power supply circuits.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the steps in the diagnostic table:
-
This step checks for normal ABS indicator lamp operation.
-
This step checks for ignition voltage at the EBCM.
-
This step checks for high resistance in the ground circuit.
-
This step checks for high resistance in the ignition voltage circuit.
-
This step checks for a short to ground in the ignition voltage circuit.
-
Checks for a short to ground in the EBCM.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Is data being received from the EBCM? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 4 |
2 | Using the Scan Tool , check for any DTCs. Are any current or history DTCs displayed? | -- | Go to Appropriate DTC Table | Go to Step 3 |
Did the ABS indicator lamp turn on for three seconds and then turn off? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | Go to Step 12 | |
Is the voltage measured within the specified range? | 10-15 V | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 9 | |
Is the resistance measured within the specified range? | 0-2 ohms | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 13 | |
6 |
Is the terminal contact or the connection poor? | -- | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 8 |
7 | Replace the terminals or repair the poor connection. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 1 | -- |
8 | Reconnect the EBCM connectors and the battery cables. Are the EBCM connectors and the battery cables reconnected? | -- | Go to Step 9 | -- |
Is the resistance measured within the specified range. | 0-2 ohms | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 14 | |
Is the resistance measurement equal to the specified value? | OL | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 15 | |
11 |
Is the resistance measured within the specified range? | OL | Go to Diagnostic Aids. | Go to Step 16 |
12 | Observe the ABS indicator lamp. Does the ABS indicator lamp stay on? | -- | Go to ABS Indicator Always On | |
13 | Repair open or high resistance in CKT 150. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 1 | -- |
14 | Repair short to ground in CKT 130 or CKT 145. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 1 | -- |
15 | Repair short to ground in CKT 139 or CKT 145. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Check circuit breaker #9 for correct operation. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 1 | -- |
16 | Inspect CKT 139 and the 24-way EBCM connector for physical damage which may result in a short to ground with the 24-way EBCM harness connector connected to the EBCM. | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 18 |
17 | Repair terminals which are damaged. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 1 | -- |
18 | Replace the EBCM. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement . Check circuit breaker #9 for damage. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 1 | -- |
