For 1990-2009 cars only
Connecting Rod Measurement
- Clean the connecting rods in solvent and dry with compressed air.
- Inspect the connecting rods for the following:
- If the connecting rod bores contain minor scratches or abrasions, clean the bores in a circular direction with a light emery paper. DO NOT scrape the rod or rod cap.
- Measure the piston pin to connecting rod bore using the following procedure:
- If there is not a great enough interference fit, replace the piston pin.
| • | Signs of being twisted, bent, nicked, or cracked |
| • | Scratches or abrasion on the rod bearing seating surface |
| 4.1. | Using an outside micrometer, take two measurements of the piston pin in the area of the connecting rod contact. |
| 4.2. | Using an inside micrometer, measure the connecting rod piston pin bore. |
| 4.3. | Subtract the piston pin bore diameter from the piston pin diameter. |
| 4.4. | The interference fit should not be less than 0.025 mm (0.0098 in). |
Piston Measurement
- Clean the piston skirts and the pins with a cleaning solvent. DO NOT wire brush any part of the piston.
- Clean the piston ring grooves with a groove cleaner. Make sure oil ring holes and slots are clean.
- Inspect the pistons for the following conditions:
- Replace pistons that show any signs or damage or excessive wear.
- Measure the piston pin bore to piston pin clearances using the following procedure:
- Measure the piston ring end gap using the following procedure:
- Measure the piston ring side clearance using the following procedure:
- The top compression ring may be installed with either side up. There is a locating dimple on the 2nd compression ring near the end for identification of the top side. Install the 2nd compression ring with the dimple facing up.
- If the new ring does not reduce the clearance to 0.027 mm (0.0011 in) or less, install a new piston.
- Measure piston width using the following procedure:
- If the clearance obtained through measurement is greater than these specifications and the cylinder bores are within specification, replace the piston.
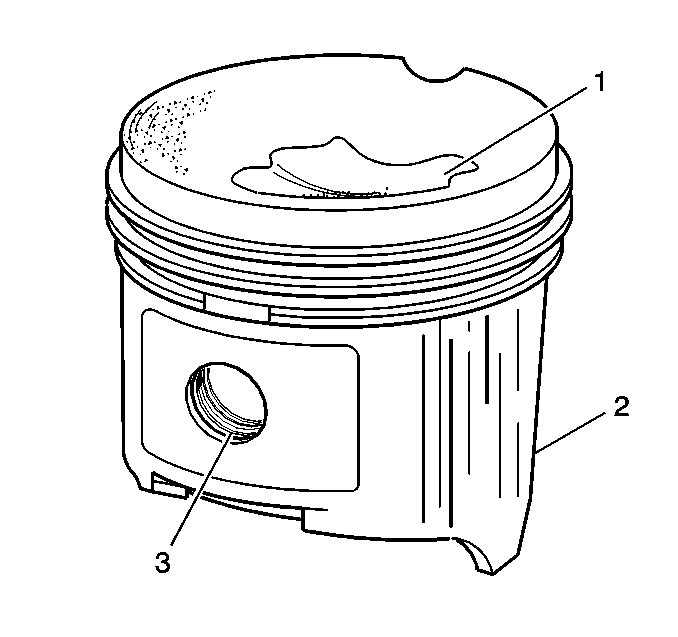
| • | Cracked ring lands, skirts, or pin bosses |
| • | Ring grooves for nicks, burrs that may cause binding |
| • | Warped or worn ring lands |
| • | Eroded areas at the top of the piston (1) |
| • | Scuffed or damaged skirts (2) |
| • | Worn piston pin bores (3) |
| 5.1. | Piston pin bores and pins must be free of varnish or scuffing. |
| 5.2. | Use an outside micrometer to measure the piston pin in the piston contact areas. |
| 5.3. | Using an inside micrometer, measure the piston pin bore. |
| 5.4. | Subtract the measurement of the piston pin bore from the piston pin. The clearance should not exceed 0.008-0.016 mm (0.0003-0.0008 in). |
| 5.5. | If the clearance is excessive, determine which component is out of specification. |
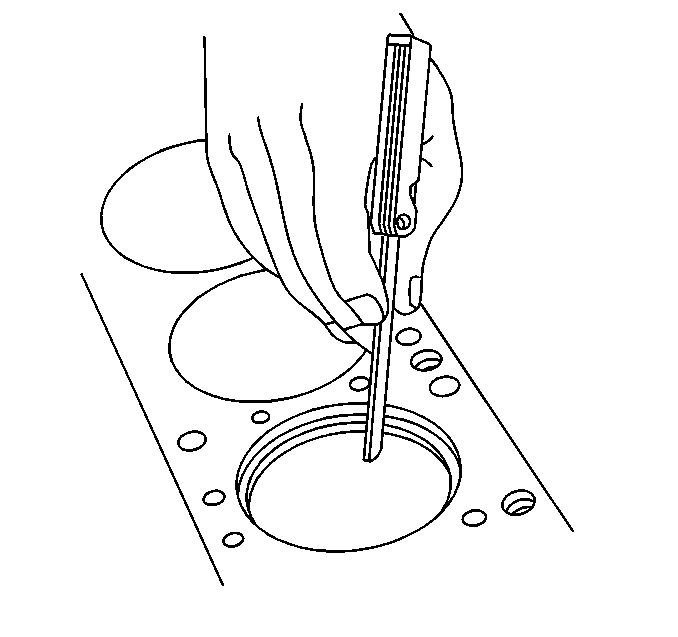
| 6.1. | Place the piston ring in the area of the bore where the piston ring will travel (approximately 25 mm or 1 inch down from the deck surface). Be sure the ring is square with the cylinder bore by positioning the ring with the piston head. |
| 6.2. | Measure the end gap of the piston ring with feeler gages. Compare the measurements with those provided below: |
| • | The top compression ring end gap should be 0.25-0.50 mm (0.010-0.020 in). |
| • | The second compression ring end gap should be 0.25-0.50 mm (0.010-0.020 in). |
| • | The oil ring end gap should be 0.25-1.27 mm (0.010-0.050 in). |
| 6.3. | If the clearance exceeds the provided specifications, the piston rings must be replaced. |
| 6.4. | Repeat the procedure for all the piston rings. |
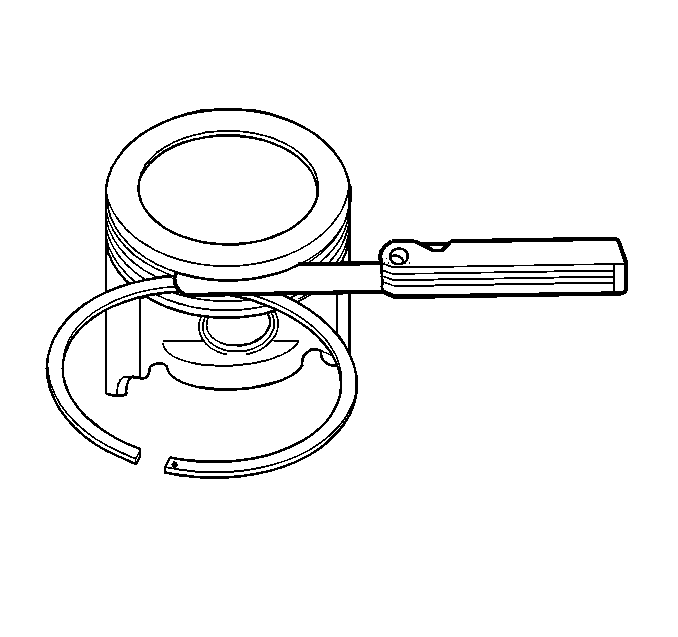
| 7.1. | Roll the piston ring entirely around the piston ring groove. If any binding is caused by the ring groove, dress the groove with a fine file. If any binding is caused by a distorted piston ring, replace the ring. |
| 7.2. | With the piston ring on the piston, use feeler gages to check clearance at multiple locations. |
| 7.3. | The clearance between the surface of the piston ring and the ring land should be no greater than 0.027 mm (0.0011 in). |
| 7.4. | If the clearance is greater than specifications, replace the piston rings. |
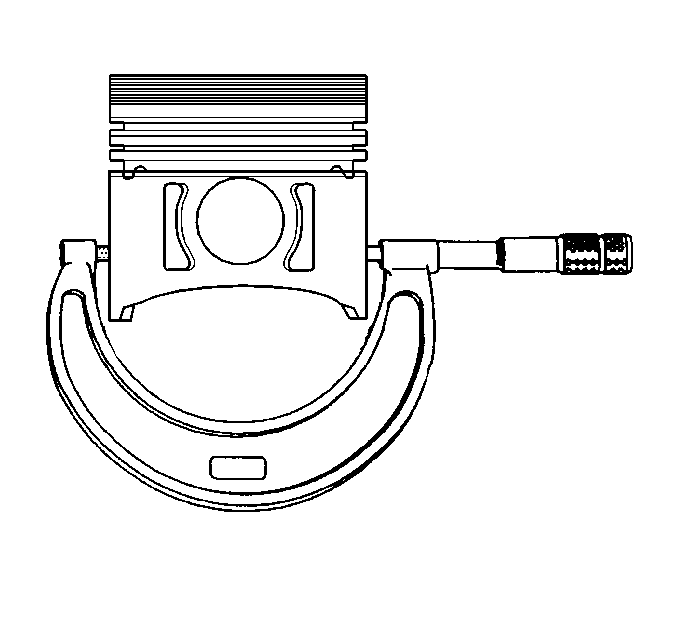
| 10.1. | Using an outside micrometer, measure the width of the piston 11 mm (0.437 in) above the bottom of the piston skirt at the thrust surface perpendicular to the centerline of the piston pin. |
| 10.2. | Compare the measurement of the piston to its original cylinder by subtracting the piston width from the cylinder diameter. |
| 10.3. | The proper clearance specification for the piston is 0.015-0.047 mm (0.0006-0.0018 in). |
Connecting Rod Measurement
- Clean the connecting rods in solvent and dry with compressed air.
- Inspect the connecting rods for the following:
- If the connecting rod bores contain minor scratches or abrasions, clean the bores in a circular direction with a light emery paper. DO NOT scrape the rod or rod cap.
- Measure the piston pin to connecting rod bore using the following procedure:
- If there is not a great enough interference fit, replace the piston pin.

| • | Signs of being twisted, bent, nicked, or cracked |
| • | Scratches or abrasion on the rod bearing seating surface |
| 4.1. | Using an outside micrometer, take two measurements of the piston pin in the area of the connecting rod contact. |
| 4.2. | Using an inside micrometer, measure the connecting rod piston pin bore. |
| 4.3. | Subtract the piston pin bore diameter from the piston pin diameter. |
| 4.4. | The interference fit should not be less than 0.021 mm (0.00081 in). |
Piston Measurement
- Clean the piston skirts and the pins with a cleaning solvent. DO NOT wire brush any part of the piston.
- Clean the piston ring grooves with a groove cleaner. Make sure oil ring holes and slots are clean.
- Inspect the pistons for the following conditions:
- Replace pistons that show any signs or damage or excessive wear.
- Measure the piston pin bore to piston pin clearances using the following procedure:
- Measure the piston ring end gap using the following procedure:
- Measure the piston ring side clearance using the following procedure:
- The top compression ring may be installed with either side up. There is a locating dimple on the 2nd compression ring near the end for identification of the top side. Install the 2nd compression ring with the dimple facing up.
- If the new 2nd compression ring does not reduce the clearance to 0.08 mm (0.0031 in) or less, install a new piston.
- Measure piston width using the following procedure:
- If the clearance obtained through measurement is greater than these specifications and the cylinder bores are within specification, replace the piston.

| • | Cracked ring lands, skirts, or pin bosses |
| • | Ring grooves for nicks, burrs that may cause binding |
| • | Warped or worn ring lands |
| • | Eroded areas at the top of the piston (1) |
| • | Scuffed or damaged skirts (2) |
| • | Worn piston pin bores (3) |
| 5.1. | Piston pin bores and pins must be free of varnish or scuffing. |
| 5.2. | Use an outside micrometer to measure the piston pin in the piston contact areas. |
| 5.3. | Using an inside micrometer, measure the piston pin bore. |
| 5.4. | Subtract the measurement of the piston pin bore from the piston pin. The clearance should not exceed 0.0079-0.018 mm (0.0031-0.00071 in). |
| 5.5. | If the clearance is excessive, determine which component is out of specification. |

| 6.1. | Place the piston ring in the area of the bore where the piston ring will travel, approximately 25 mm (1 in) down from the deck surface. Be sure the ring is square with the cylinder bore by positioning the ring with the piston head. |
| 6.2. | Measure the end gap of the piston ring with feeler gauges. Compare the measurements with those provided below: |
| • | The top compression ring end gap should be 0.25-0.50 mm (0.010-0.020 in). |
| • | The second compression ring end gap should be 0.30-0.45 mm (0.0012-0.0177 in). |
| • | The oil ring end gap should be 0.25-0.76 mm (0.010-0.030 in). |
| 6.3. | If the clearance exceeds the provided specifications, the piston rings must be replaced. |
| 6.4. | Repeat the procedure for all the piston rings. |

| 7.1. | Roll the piston ring entirely around the piston ring groove. If any binding is caused by the ring groove, inspect the groove for distress, burrs, and foreign material. If there is any distress, burrs, or foreign material on the ring groove, replace the piston. If any binding is caused by a distorted piston ring, replace the ring. |
| 7.2. | With the piston ring on the piston, use feeler gauges to check clearance at multiple locations. |
| 7.3. | The clearance between the surface of the top compression ring and the ring land should be no greater than 0.09 mm (0.0035 in). |
| 7.4. | If the clearance is greater than specifications, replace the piston rings. |
| 7.5. | If the new top compression ring does not reduce the top ring side clearance to 0.09 mm (0.0035 in) or less, install a new piston. |

| 10.1. | Using an outside micrometer, measure the width of the piston 42.7 mm (1.68 in) above the top of the piston at the thrust surface perpendicular to the centerline of the piston pin. |
| 10.2. | Compare the measurement of the piston to its original cylinder by subtracting the piston width from the cylinder diameter. |
| 10.3. | The proper clearance specification for the piston is 0.055-0.087 mm (0.0022-0.0034 in). |
