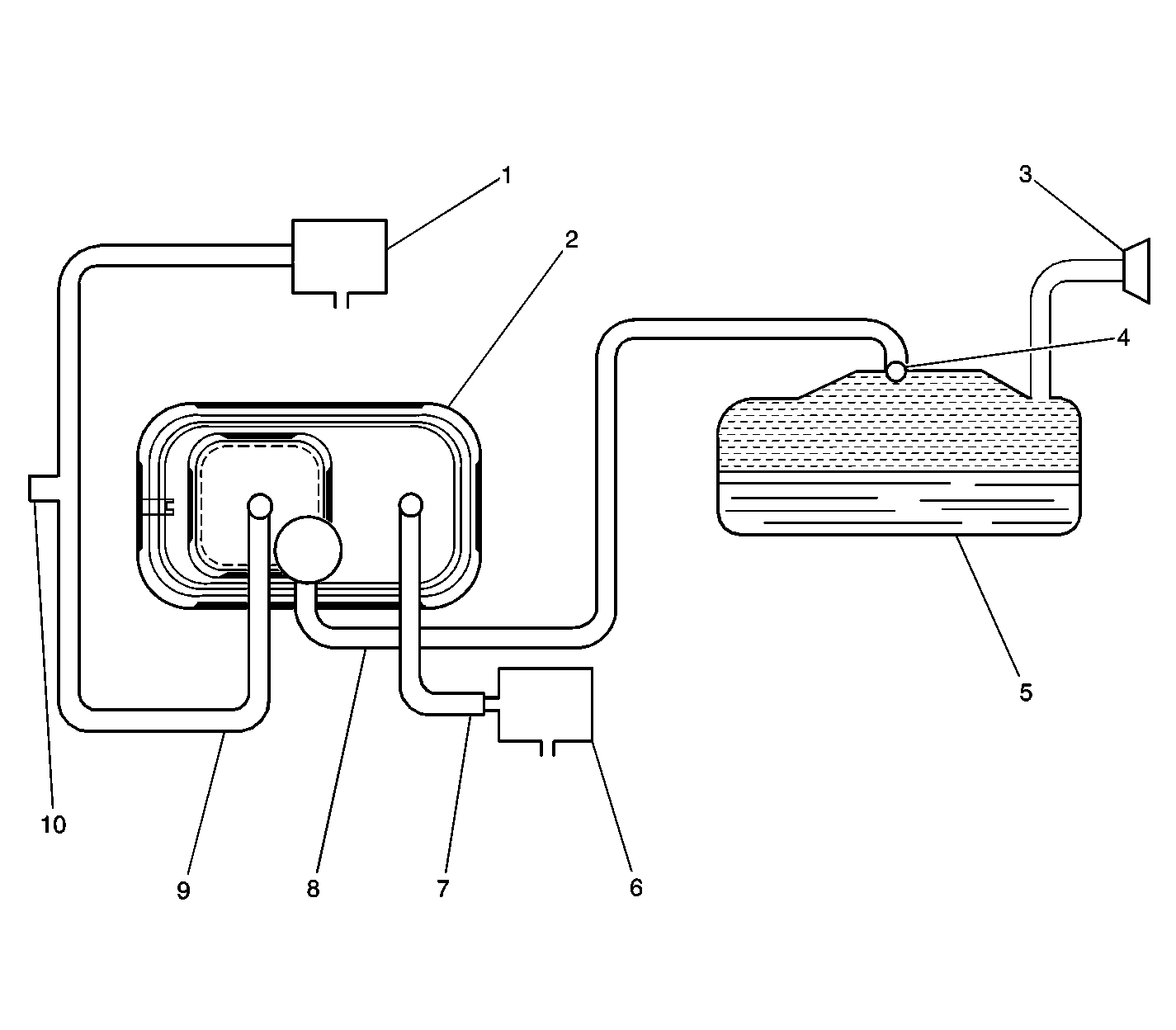
EVAP System Operation
The evaporative emission (EVAP) control system limits fuel vapors from
escaping into the atmosphere. Fuel tank vapors are allowed to move from the
fuel tank due to pressure in the tank, through the vapor line, into the EVAP
canister. Carbon in the canister absorbs and stores the fuel vapors. Excess
pressure is vented through the vent line and EVAP vent solenoid to atmosphere.
The EVAP canister stores the fuel vapors until the engine is able to use
them. At an appropriate time, the PCM will command the EVAP purge valve open,
allowing the engine vacuum to be applied to the EVAP canister. With the EVAP
vent valve open, fresh air will be drawn through the valve and vent line to
the EVAP canister. Fresh air is drawn through the canister, pulling fuel
vapors from the carbon. The air/fuel vapor mixture continues through the
EVAP purge line and EVAP purge valve into the intake manifold to be consumed
during normal combustion. The EVAP system requires the PCM be able to detect
a leak as small as 0.040 inches in the EVAP system. The PCM uses several
tests to determine if the EVAP system is sealed.
Weak Vacuum Test
This tests for large leaks and blockages in the EVAP system. The PCM
will command the EVAP vent valve ON (close), and the EVAP purge valve ON (open)
with the engine running, allowing engine vacuum into the EVAP system. The
PCM monitors the fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor to verify that the system
is able to reach and hold a predetermined level of vacuum within a set amount
of time. If the PCM does not detect the predetermined vacuum level on two
consecutive tests, a DTC P0440 will set.
Vacuum Decay Test
If the weak vacuum test passes, the PCM will command the EVAP purge
valve OFF, sealing the EVAP system. The PCM tests for vacuum decay in the
EVAP system by monitoring the fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor for a change
in voltage over a period of time. If the decay rate is more than a calibrated
value, the PCM will rerun the test. If the test fails again, DTC P0442 will
set.
EVAP Vent Restriction Test
A restricted or blocked EVAP vent path is detected by the PCM commanding
the purge valve ON (open) and the vent valve ON (closed) allowing a vacuum
to be applied to the EVAP system. Once a calibrated vacuum level has been
reached, the PCM commands the purge valve OFF (closed) and the vent valve
OFF (open) while monitoring the FTP sensor for a decrease in vacuum. If the
vacuum does not decrease to near 0 inches H2O in a calibrated
time, DTC P0446 will set.
Purge Valve Leak Test
If the EVAP purge valve does not seal properly, fuel vapors could enter
the engine at an undesired time causing driveability concerns. The PCM tests
for this by commanding the EVAP purge and vent valves closed, sealing the
system, and monitoring the FTP for an increase in vacuum. If the PCM detects
an increase in vacuum, DTC P1441 will set.
EVAP System Components
EVAP System Overview