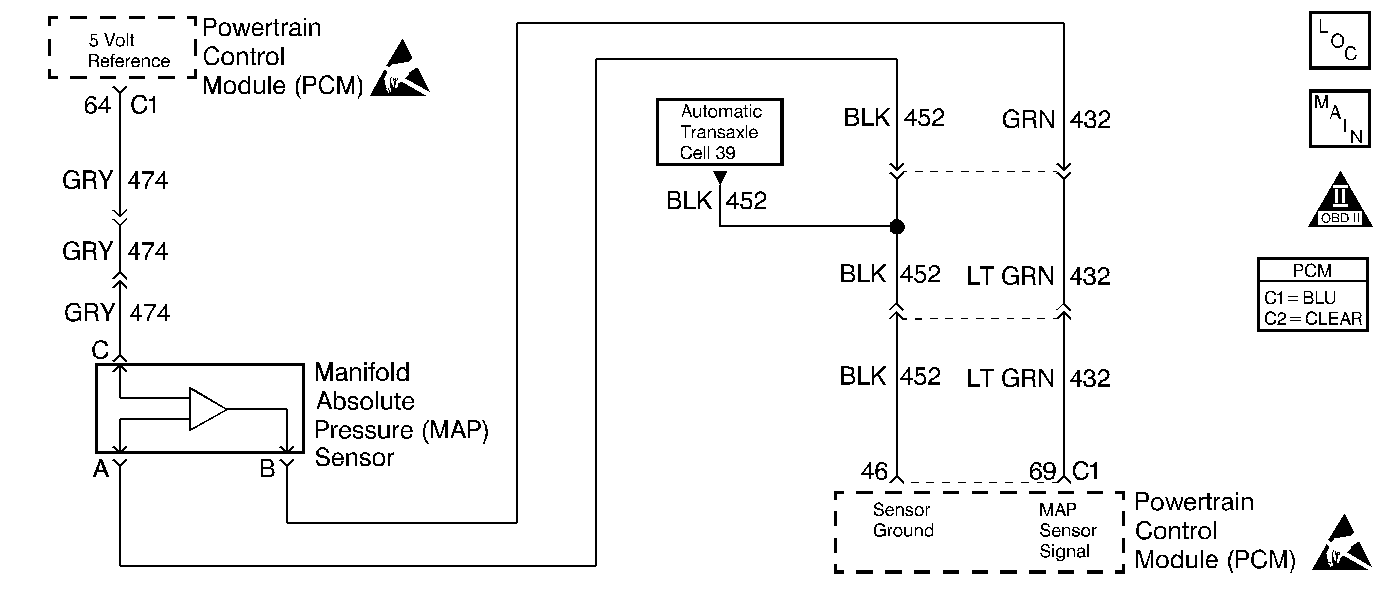
Circuit Description
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor is a sensor that changes resistance based upon manifold vacuum. The PCM provides a 5 volt reference and ground. The MAP sensor signal varies between ground and 5 volts as manifold vacuum varies. As MAP decreases, voltage decreases, low engine load, high vacuum. As MAP increases, voltage increases, high engine load, low vacuum. The PCM uses the MAP sensor values as an indicator of engine load. This diagnostic test monitors the MAP signal by comparing the reading to calculated BARO. If the values of the MAP signal and the calculated BARO are too close together at idle, DTC P1108 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0107, P0108, P0122, P0123, not set. |
| • | Throttle position at idle, calculated by the PCM. |
| • | TP sensor 18 degrees or less. |
| • | Engine speed 400 RPM or greater. |
| • | Barometric pressure 75 kPa or greater. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Difference between MAP and Calculated BARO is 11 kPa or less for 15 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | PCM disables long term fuel trim. |
| • | PCM uses a substitute MAP value based on engine RPM and throttle angle. |
| • | PCM uses 92.2 kPa for barometric pressure. |
| • | PCM disables Evaporative Emission (EVAP) control solenoid. |
| • | PCM disables torque management. |
| • | Transaxle shift adapts are maintained at current levels. |
| • | The PCM will illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM will record operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information will be stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A Last Test Failed (current) DTC will clear when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A History DTC will clear after forty consecutive warm-up cycles with no failures of any emission related diagnostic test. |
| • | Use a scan tool to clear DTCs. |
| • | Interrupting PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes in Powertrain Control Module Description . |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
MAP at idle should be 30 to 50 kPa, depending on engine load. BARO should be 85 to 105 kPa, depending on altitude. The difference between the two should always be greater than 11 kPa with the engine running at or near idle.
-
Check for vacuum at the throttle body with a vacuum gage. At idle, typical vacuum readings are 14 to 20 Hg, depending on engine load.
-
MAP display should read 10-16 kPa disconnected.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
Is difference between BARO and MAP values the same or less than the value specified? | 11 kPa | Go to Step 3 | Fault not present. Go to DTC P0106 Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) System Performance | |
With engine idling, check engine vacuum with a vacuum gage at the MAP sensor port. Does vacuum measure greater than the value specified? | 14 Hg (47 kPa) | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 9 | |
Is the display the same or less than the value specified? | 16 kPa | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 6 | |
5 |
Is the resistance the same or less than the value specified? | 5 ohms | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 7 |
6 | Measure the voltage to ground at MAP sensor terminal B (harness side). Is the voltage more then the value specified? | 0.5 volts | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 12 |
7 | Repair the open in the MAP Sensor Ground circuit. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- |
8 | Repair the short to voltage on the MAP Sensor Signal circuit, possibly the signal and 5 volt reference circuits shorted together. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- |
9 | Check and repair causes of intake manifold vacuum leaks or low engine vacuum. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- |
10 |
Was terminal contact repaired? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | Go to Step 11 |
11 | Replace the MAP sensor. Refer to Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- |
12 |
Was terminal contact repaired? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | Go to Step 13 |
13 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- |
