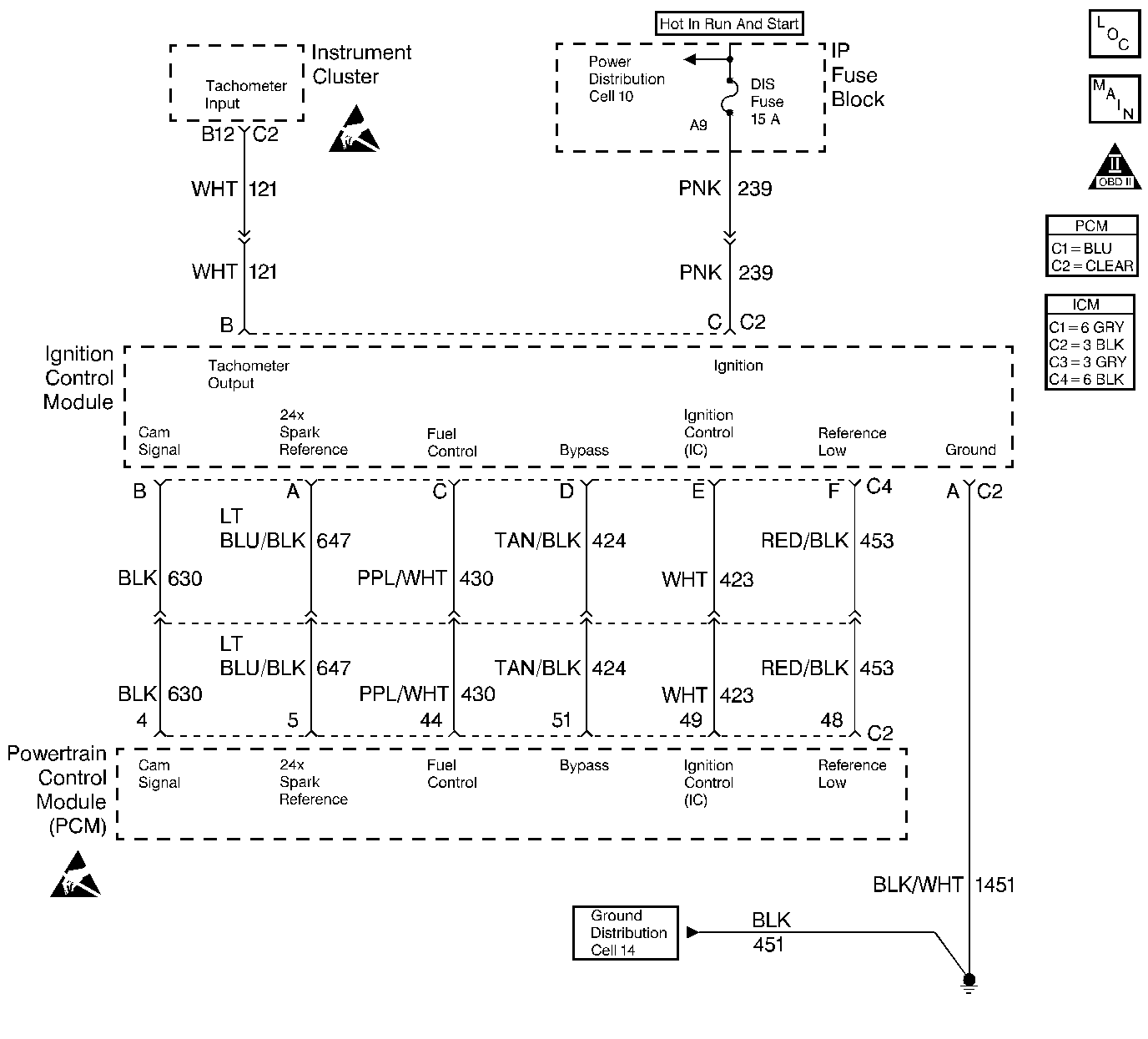
Circuit Description
Under normal system operation when the key is turned ON and until engine rpm is high enough for the PCM to control spark, the PCM will open the bypass circuit (CKT 424) to the Ignition Control Module, the IC module will then ground the Ignition Control circuit (CKT 423). This is called module mode because the IC module is controlling spark. Once the engine speed is high enough, about 65 rpm, 4X reference pulses are received and no PCM faults are detected the PCM will close the bypass line and in response the IC module will unground the IC circuit, this allows PCM control of spark. This is called the ignition control mode. This diagnostic test is used to check for faults in both the bypass circuit and the IC circuit. To inspect both circuits this diagnostic runs two tests, one during crank and one while running. If Ignition Control pulses are detected by the PCM on the IC line while in module mode, cranking, or if no Ignition Control pulses are detected by the PCM while in ignition control mode, running, DTC P1350 will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | Cranking test. |
| - | DTC P1376 not set. |
| - | At least 1 4X reference pulse has been received by the PCM. |
| • | Running test. |
| - | DTC P0322 and P1376 not set. |
| - | At least 1 4X reference pulse has been received by the PCM. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | Cranking test. |
| Ignition Control pulses are received by the PCM when cranking or running test has failed THIS ignition cycle. |
| • | Running test. |
| No Ignition Control pulses are received by the PCM while engine is running. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | PCM ignition control is disabled for ignition cycle. |
| • | PCM disables EGR. |
| • | Transaxle shift adapts are maintained at current levels. |
| • | The PCM will illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM will record operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information will be stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A Last Test Failed (current) DTC will clear when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A History DTC will clear after forty consecutive warm-up cycles with no failures of any emission related diagnostic test. |
| • | Use a scan tool to clear DTCs. |
| • | Interrupting PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes in Powertrain Control Module Description . |
Diagnostic Aids
If fault is not present inspect terminal contact at the IC module and PCM connectors.
Test Description
-
When checking for shorts to ground, resistance of more than 10K ohms is usually acceptable although most readings should be infinite (OL).
When checking for circuit continuity (opens) resistance should be 5 ohms or less.
When checking for shorts to voltage take measurements with the ignition ON and OFF.
Disconnect the circuit from all components before performing any circuit check.
Always check or zero the meter before performing resistance checks.
-
A diagnostic jumper can be created with the terminals supplied in the J 38125-A Terminal Repair Kit. Assemble the jumpers and terminals and cover the exposed terminals with heat shrink tubing. Do not cover the spade of the male terminals.
If the vehicle stalls during this step turn the ignition OFF and wait 30 seconds then restart the engine before attempting to measure the circuit voltage.
-
If the vehicle stalls during this step turn the ignition OFF and wait 30 seconds then restart the engine before attempting to measure the circuit voltage.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||||||||
2 | Are DTC's P0322, P0372, P1323, P1371, P1375 or P1376 also set? | -- | Go to DTC (s) that are set | Go to Step 3 | ||||||||||||
3 |
Does P1350 fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 4 | Fault not present. Refer to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||||
Was a repair made to any circuit? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | Go to Step 5 | |||||||||||||
5 |
Is the voltage less than the value specified? | 1.0 volts | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 11 | ||||||||||||
OR:
Is the voltage fixed near the value specified? | 1.7 volts | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 11 | |||||||||||||
Measure the DC voltage to ground on the Bypass circuit FROM the PCM. Is the voltage less than the value specified? | 1.0 volts | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 11 | |||||||||||||
8 |
Is the voltage the same or more than the value specified? | 4.7 volts | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 11 | ||||||||||||
9 |
Was terminal contact repaired? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | Go to Step 10 | ||||||||||||
10 | Replace the Ignition Control Module. Refer to Ignition Control Module Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- | ||||||||||||
11 |
Was terminal contact repaired? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | Go to Step 12 | ||||||||||||
12 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- |
