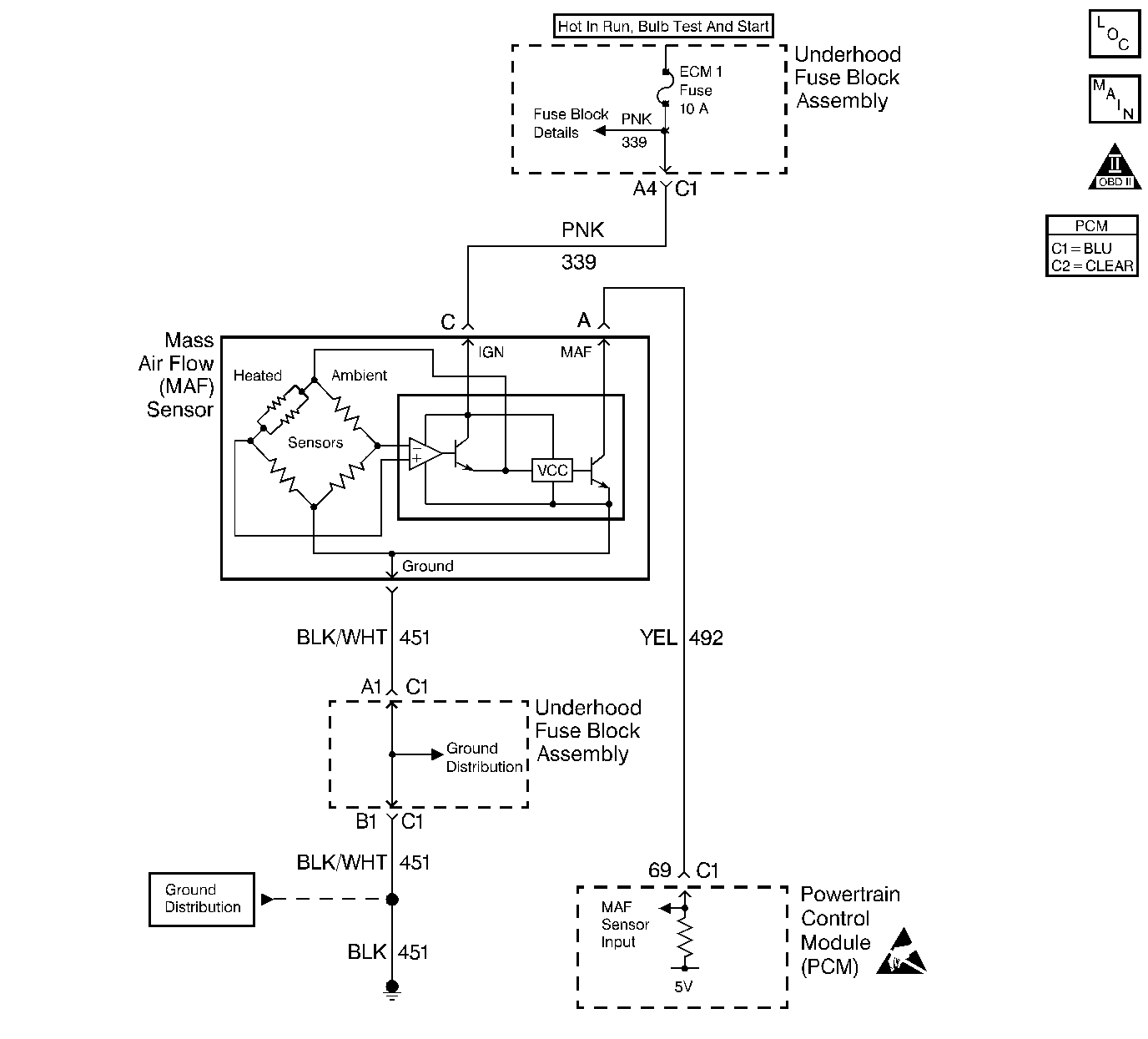
Circuit Description
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor measures the amount of air that is ingested by the engine. Direct measurement of air entering the engine is more accurate than calculating airflow from other sensor inputs. The MAF sensor has an ignition feed, a ground, and a signal circuit.
The MAF sensor used on this vehicle is a hot wire type and is used to measure air flow rate. The frequency of the MAF sensor signal is a function of the power required to keep the air flow sensing elements at a fixed temperature above ambient temperature. Air flowing through the sensor cools the sensing elements. The amount of cooling is proportional to the amount of air flow. As air flow increases, a greater amount of current is required to maintain the hot wire at a constant temperature. The MAF sensor converts the changes in current draw to a frequency signal read by the powertrain control module (PCM). The frequency typically varies from about 2 KHz at idle to about 10 KHz at maximum engine load. The PCM calculates air flow based on this signal.
The PCM monitors the MAF sensor signal frequency and can determine if the sensor signal voltage is too low, too high, or not indicating the expected airflow for a given operating condition.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine is running. |
| • | System voltage is between 9V and 18V. |
| • | The throttle is steady and TP angle is below 50%. |
| • | MAP is steady |
| • | EGR duty cycle is below 50%. |
| • | EGR pintle position is below 50%. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | MAF signal frequency indicates an airflow significantly higher or lower than a predicted value based on barometric pressure, throttle position and engine RPM. |
| • | The above conditions are present for at least 10 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
The PCM calculates an airflow value based on idle air control valve position, throttle position, RPM and barometric pressure.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns the MIL Off after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A last test failed (current DTC) clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles, if this or any other emission related diagnostic does not report any failures. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL/DTC. |
| • | Interrupting the PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Description , Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes. |
Diagnostic Aids
Notice: Use the connector test adapter kit J 35616-A for any test that
requires probing the following items:
• The PCM harness connectors • The electrical center fuse/relay cavities • The component terminals • The component harness connector
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Skewed or stuck TP sensor. A malfunctioning TP sensor or TP sensor circuit can cause the PCM to incorrectly calculate the predicted mass air flow value. Observe the Throttle Angle displayed on the scan tool with the throttle closed. If the Throttle Angle reading is not 0%, check for the following conditions and repair as necessary: |
| - | Throttle plate sticking or excessive deposits on the throttle plate or in the throttle bore. |
| - | TP sensor signal circuit shorted to voltage. |
| - | Poor connection or high resistance in the TP sensor ground circuit. |
| - | If none of the above conditions are noted and the Throttle Angle reading at closed throttle is not 0%, replace the TP sensor. |
| • | Plugged intake air duct or dirty air filter element. A wide-open throttle acceleration from a stop should cause the Mass Air Flow displayed on a scan tool to increase from about 4-7 gm/s at idle to 100 gm/s or greater at the time of the 1-2 shift. If not, check for a restriction. |
| • | Skewed or unresponsive MAP sensor. The barometric pressure used to calculate the default Mass Air Flow value is based on the MAP sensor reading. A skewed MAP sensor at key ON will cause the BARO reading to be incorrectly calculated. Also, with the engine running, an unresponsive MAP sensor (due to poor vacuum connections, damaged vacuum source, or defective vacuum hose(s), unmetered air into the manifold) will cause inaccurate BARO reading updates during wide-open throttle conditions. Both of these conditions result in a difference between the actual MAF sensor signal and the predicted MAF value (PCM calculated). If a large difference between these two values occurs DTC P0101 will set. This condition may also cause abnormal IAC counts. With the IAC at an incorrect count value, a hard start / no start condition may occur. |
If DTC P0101 cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Fail Records data can be useful in determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set. This may assist in determining how often the DTC sets.
If the problem is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
The MAF system performance or rationality diagnostic uses the MAP and TP sensor signals along with other inputs in order to calculate an expected airflow rate. The PCM then compares the expected flow rate to the actual measured airflow from the MAF sensor. Diagnose the listed DTCs before running this table.
-
Using the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If you cannot duplicate the DTC, the information included in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data can help determine how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also help determine how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass and/or a fail. Operate the vehicle within the same freeze frame conditions (RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature etc.) that you observed. This will isolate when the DTC failed.
-
Any un-metered air may cause this DTC to set. Check the PCV system for vacuum leaks. Make sure that the dipstick is fully seated and the oil fill cap is secure.
-
This step verifies the signal circuit from the MAF sensor electrical connector to the PCM.
-
This step verifies whether a ground and B+ circuit is available.
-
This step checks the signal circuit for an open.
-
This step checks the signal circuit for a short to B+.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Is DTC P0102, P0103, P0107, P0108, P0121, P0122, P0123, or P1635 also set? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table. | ||
3 |
Did the MAP sensor value change smoothly through the entire range of the test without any erratic readings? | -- | ||
4 | Apply 20 inches Hg vacuum to the MAP sensor. Is the MAP sensor reading on the scan tool the same or less than the specified value? | 34 kPa | ||
5 | Disconnect the vacuum source from the MAP sensor. Does the MAP sensor reading return to the original value? | -- | ||
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic failed this ignition? | -- | Refer to Diagnostic Aids. | ||
Check for the following conditions:
Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | |||
Is the voltage near the specified value? | 5.0V | |||
Connect a test lamp J 35616-200 between the MAF sensor ignition feed and the ground circuit at the MAF sensor harness connector. Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | |||
Is the voltage less than the specified value? | 4.5V | |||
Does the voltage measure near the specified value? | 0.0V | |||
12 | Connect a test lamp J 35616-200 between the MAF sensor ignition feed circuit and the battery ground. Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | ||
13 | Check for poor connections/terminal tension at the MAF sensor. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis . Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||
14 | Check the MAF sensor signal circuit between the PCM and the MAF sensor for the following:
Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||
15 | Locate and repair the open in the ground circuit to the MAF sensor. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
16 | Locate and repair the open in the ignition feed circuit to the MAF sensor. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
17 | Locate and repair the short to voltage in the MAF sensor signal circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
18 | Replace the MAF sensor. Refer to Mass Airflow Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
19 | Replace the MAP sensor. Refer to Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
20 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
21 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||
22 | Review Captured Info using the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
