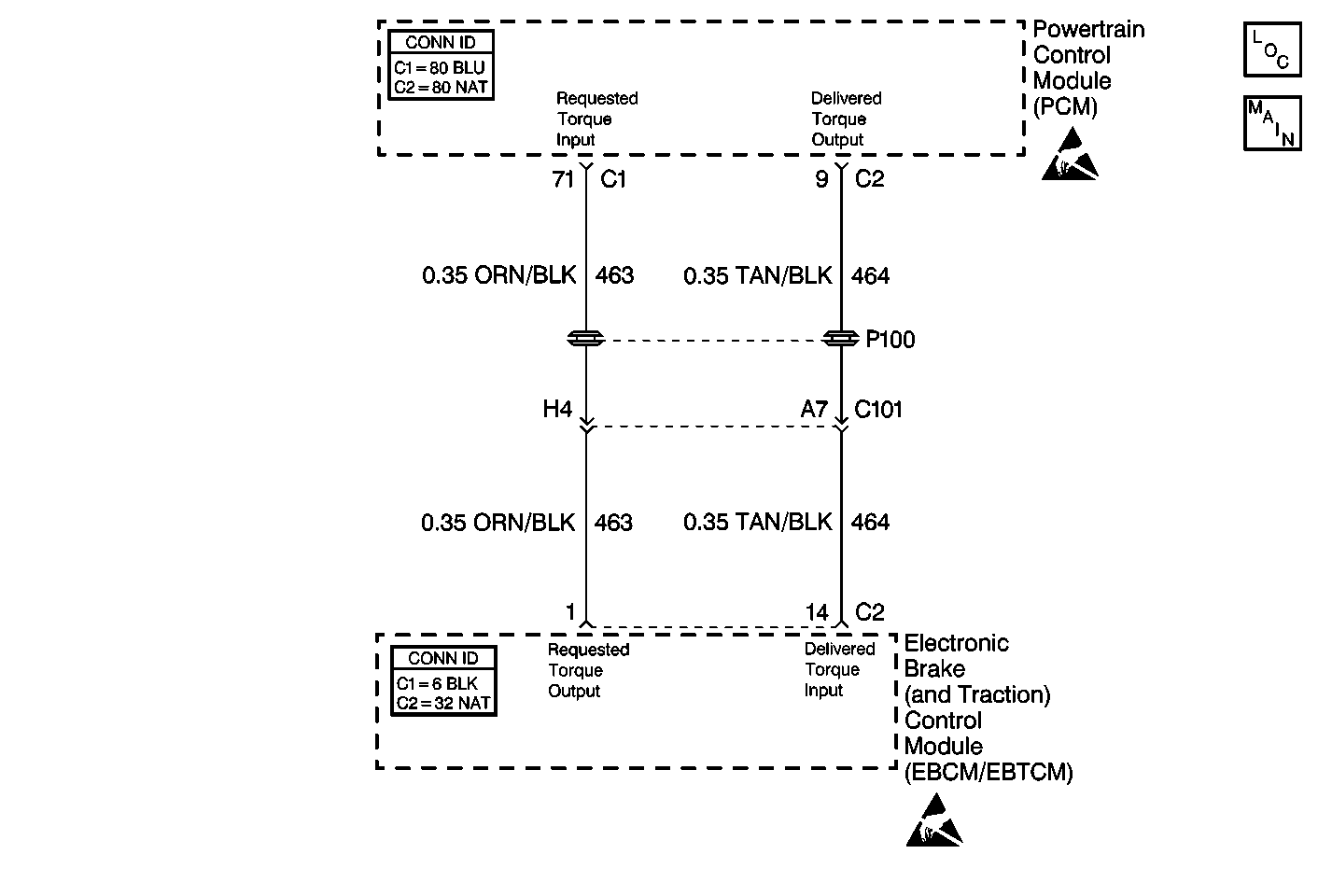
Circuit Description
The EBCM/EBTCM and the PCM simultaneously control the traction control. The PCM sends a Delivered Torque message via a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal to the EBCM/EBTCM confirming the delivered torque level for proper TCS operation. The EBCM/EBTCM supplies the pull up voltage.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The DTC sets if all of the following occur:
| • | The ignition is ON. |
| • | The PWM signal is out of range or no signal is received for 7 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | A malfunction DTC is stored. |
| • | The TCS is disabled. |
| • | The TRACTION OFF indicator is turned ON. |
| • | The ABS remains functional. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The condition for the DTC is no longer present and you used the scan tool Clear DTC function. |
| • | The EBCM/EBTCM does not detect the DTC in 50 drive cycles. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | It is very important that a thorough inspection of the wiring and connectors be performed. Failure to carefully and fully inspect wiring and connectors may result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with reappearance of the malfunction. |
| • | An intermittent malfunction can be caused by poor connections, broken insulation, or a wire that is broken inside the insulation. |
| • | If an intermittent malfunction exists, refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. |
| • | The following conditions can cause this concern: |
| - | An open in the Delivered Torque circuit. |
| - | An short to ground or voltage in the Delivered Torque circuit. |
| - | A wiring problem, terminal corrosion, or poor connection in the Delivered Torque circuit. |
| - | A communication frequency problem. |
| - | A communication duty cycle problem. |
| - | The EBCM/EBTCM is not receiving information from the PCM. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the ABS Diagnostic System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||
2 | Inspect the following grounds in order to ensure that each ground is clean, tight, and free of damage:
Did you find any loose, damaged, or corroded grounds? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 | ||||
3 | Repair the grounds as needed. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||
Is the duty cycle within the specified range? | 5-15% | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 7 | |||||
Use the J 39200 DMM in order to measure the DC Hz between the J 39700 terminal 14 and terminal B. Is the frequency within the specified range? | 121-134 Hz | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 13 | |||||
6 | Replace the EBCM/EBTCM. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||
7 |
Is the voltage within the specified range? | Battery voltage | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 10 | ||||
8 |
Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 1.0 V | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 12 | ||||
9 | Repair the short to voltage in CKT 464 (TAN/BLK). Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||
10 |
Does the resistance equal the specified value? | OL (infinite) | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 11 | ||||
11 | Repair the short to ground in CKT 464 (TAN/BLK). Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||
12 | Use the J 39200 DMM in order to measure the resistance between the J 39700 terminal 14 and the PCM connector C2 terminal 9. Is the resistance less than the specified value | 2 ohms | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 14 | ||||
13 | Inspect the PCM. Refer to Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check in Engine Controls - 3.8L. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||
14 | Repair the open in CKT 464 (TAN/BLK). Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- |
