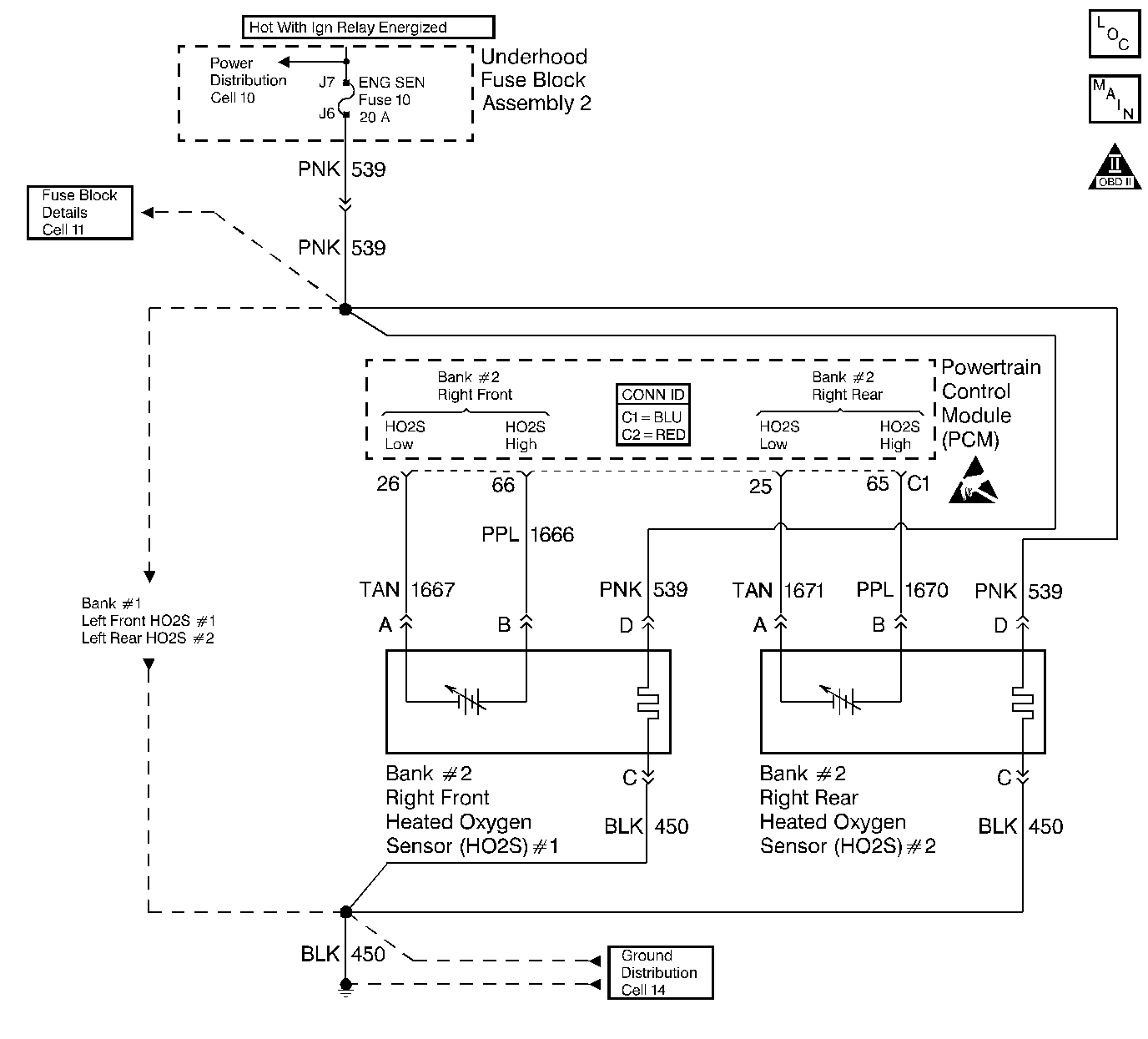
Circuit Description
The PCM supplies a voltage of about 450 mV between the HO2S high and low signal circuits. The oxygen sensor varies the voltage over a range from about 1,000 mV when the exhaust is rich, down through about 10 mV when the exhaust is lean.
The PCM monitors and stores the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) voltage information. The PCM evaluates the HO2S voltage samples in order to determine the amount of time the HO2S voltage was out of range. The PCM compares the stored HO2S voltage samples taken within each sample period and determines if majority of the samples are out of the operating range.
The PCM monitors the HO2S voltage for being fixed below a predetermined voltage. If the PCM detects the voltage is below a predetermined voltage, this DTC sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0101, P0102, P0103, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0125, P0200, P0335, P0336, P0351-P0358, P1258 not set. |
| • | The ignition voltage is greater than 9.0 volts. |
| • | The fuel system is operating in Closed Loop. |
| • | The AIR, EGR, and the Catalyst diagnostics are not active. |
| • | The TP sensor angle is between 2-70%. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The HO2S signal voltage remains below 200 mV. |
| • | The conditions are present for 33 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A last test failed, or current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL and the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important:
• Remove any debris from the PCM connector surfaces before servicing
the PCM. Inspect the PCM connector gaskets when diagnosing/replacing the PCM.
Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminant
intrusion into the PCM. • For any test that requires probing the PCM or component
harness connectors, use the Connector Test Adapter
Kit J 35616
. Using
this kit prevents any damage to the harness connector terminals.
Refer to
Using Connector Test Adapters
in Wiring Systems.
| • | The PCM sets this DTC when the vehicle runs out of fuel. |
| • | Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) wire: Sensor pigtail may be in contact with the exhaust manifold or the exhaust system. |
| • | An oxygen supply inside the HO2S is necessary for proper operation. The HO2S wires provide the supply of oxygen. Inspect the HO2S wires and connections for breaks or contamination. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Inspect for an intermittent ground in the signal wire between the connector and the sensor. |
| • | Lean injector(s): Perform the Injector Balance Test. Refer to Fuel Injector Balance Test with Tech 2 or Fuel Injector Balance Test with Special Tool . |
| • | Fuel contamination: Water near the in-tank fuel pump inlet can be delivered to the injectors. Refer to Alcohol/Contaminants-in-Fuel Diagnosis . The water causes a lean exhaust and can set a DTC. |
| • | Fuel pressure: System will be lean if fuel pressure is low. Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis . |
| • | Exhaust leaks: An exhaust leak near the HO2S can cause a lean condition. Refer to Exhaust Leakage in Engine Exhaust. |
| • | Vacuum or crankcase leaks can cause a lean condition. |
| • | If the above are OK, the HO2S may be at fault. |
| • | Using the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If you cannot duplicate the DTC, the information included in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data can help determine how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also help determine how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass and/or a fail. Operate the vehicle within the same freeze frame conditions (RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature etc.) that you observed. This isolates when the DTC failed. |
| • | For an intermittent condition, refer to Symptoms . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
If the HO2S voltage is fixed well below 200 mV, this indicates a short to battery ground or chassis ground. If the voltage is fixed near or above 200 mV, this indicates a short to a PCM ground.
The engine must be at the normal operating temperature before performing this test.
-
Using the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If you can not duplicate the DTC, the information included in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data can help determine how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also be used to determine how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass and/or a fail. Operate the vehicle within the same freeze frame conditions (RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature etc.) that the PCM recorded. This isolates when the DTC failed.
-
A sensor that is disconnected should indicate a bias voltage. If the voltage is low inspect the signal circuit for a short to ground.
-
Disconnecting the PCM allows using a DMM in order to test continuity of the circuits. This aids in locating an open or shorted circuit.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
|
Important: Inspect the HO2S for being secure before proceeding with this DTC. A sensor that is loose could cause this DTC to set.
Is the HO2S voltage less than the specified value? | 200 mV | |||
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic failed this ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
Does the scan tool indicate the HO2S voltage within the specified range? | 350-550 mV | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
|
Important: Disconnecting the PCM may eliminate the short to ground if the signal circuit is shorted to another C1 circuit.
Is the HO2S signal circuit shorted? | -- | |||
6 | Repair the HO2S signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
7 |
Important: Program the replacement PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||
9 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
