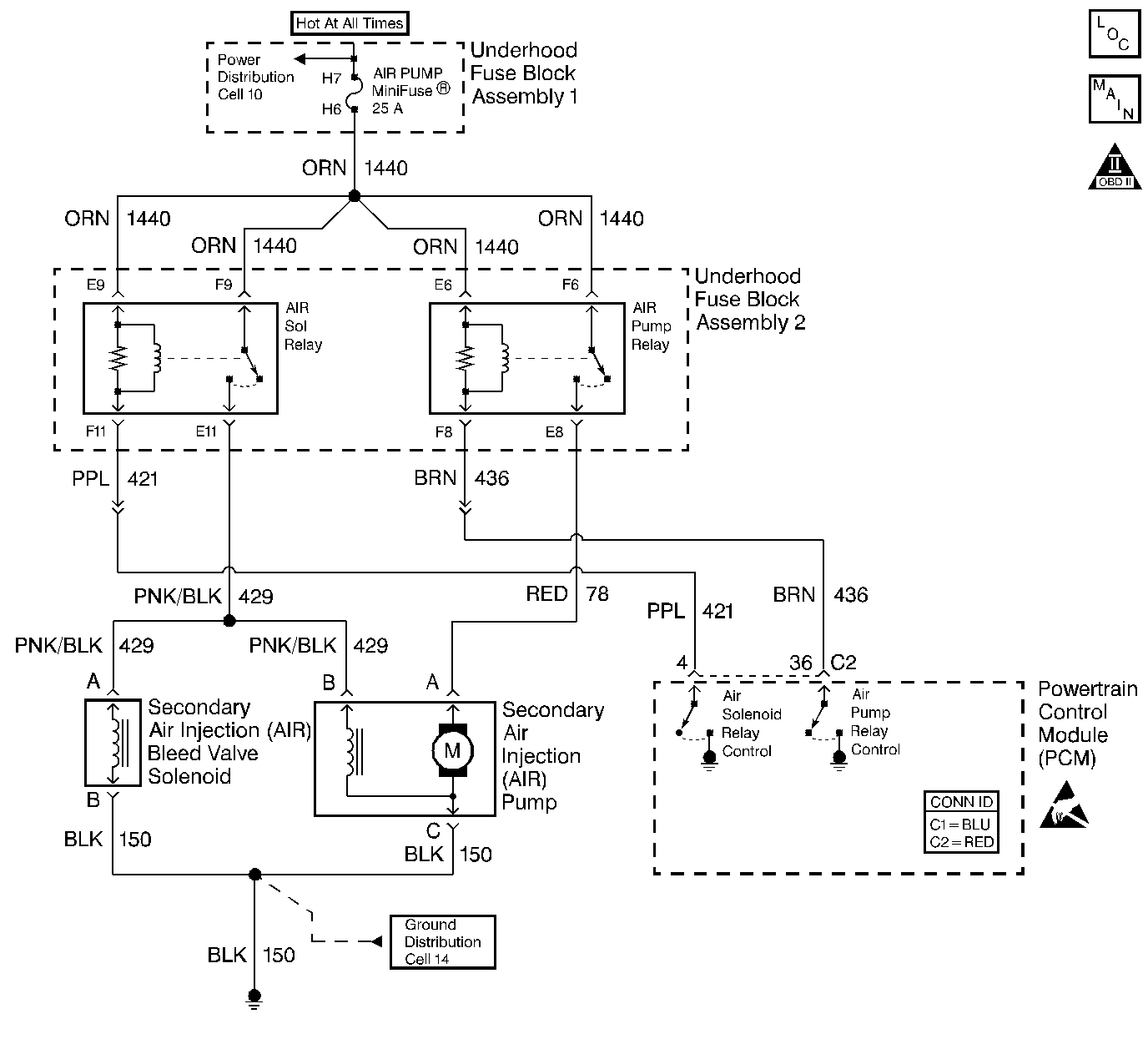
Circuit Description
An AIR pump is used on this vehicle to lower tail pipe emissions on start-up. The PCM supplies a ground to the AIR pump relay, which energizes the AIR pump.
The PCM monitors the HO2S voltages to diagnose the AIR system.
During the AIR test the PCM activates the AIR pump during closed loop operation. When the AIR is activated, the PCM monitors the HO2S voltages and short term fuel trim values for both banks of the engine. If the AIR system is operating properly, the HO2S voltages should go low and the short term fuel trim should go high.
If the PCM determines that the HO2S voltages for BOTH banks did not respond as expected during the tests, DTC P0410 sets. If only one sensor responded, the PCM sets either a DTC P1415 or P1416 to indicate on which bank the AIR system is inoperative.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0101, P0102, P0103, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0171-P0175, P0200, P0300, P0335, P0336, P0351-P0358, P0443, P0500, P0502, P0503, P1258, and HO2S DTCs not set. |
| • | The engine operates for greater than 2.0 seconds. |
| • | The engine run time is greater than 15 seconds after closed loop operation. |
| • | The engine speed is greater than 900 RPM. |
| • | The maximum air flow is 22 g/s. |
| • | The ECT is between 66°C (151°F) and 110°C (255°F). |
| • | The IAT is greater than -10°C (14°F). |
| • | The ignition voltage is greater than 11.7 volts. |
| • | The engine load is less than 42.5%. |
| • | Not operating in power enrichment mode OR deceleration fuel cut-off mode. |
| • | In short term Fuel Trim cells 1, 2, and 5. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | HO2S voltage does not go below 222 mV for 1.0 seconds, when the AIR pump turns ON during closed loop operation. |
| • | Short term fuel trim does not change a predetermined value, when the AIR pump turns ON during closed loop operation. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A last test failed, or current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL and the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important:
• Remove any debris from the PCM connector surfaces before servicing
the PCM. Inspect the PCM connector gaskets when diagnosing/replacing
the PCM. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets
prevent contaminate intrusion into the PCM. • For any test that requires probing the PCM or a component
harness connector, use the Connector Test Adapter Kit J 35616
. Using this kit prevents damage
to the harness/component terminals. Refer to
Using Connector Test Adapters
in Wiring Systems.
| • | Excessive resistance in any circuit related to the AIR system may cause this DTC to set. Listen for an audible click as the AIR solenoid and the AIR relay are commanded ON and OFF. If either component does not operate when commanded ON and OFF, and no other DTC is set, inspect the related circuits for excessive resistance. |
| • | The scan tool offers three modes of AIR output controls. AIR Pump Relay, AIR Solenoid, and AIR System. Select the AIR System function for all AIR diagnostics. |
| • | For underhood fuseblock terminal identification, refer to Electrical Center Identification Views in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Using Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If you cannot duplicate the DTC, the information included in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data can aid in determining how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also aid determining how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass and/or a fail. Operate the vehicle within the same freeze frame conditions (RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature etc.) that you observed. This isolates when the DTC failed. |
| • | For an intermittent, refer to Symptoms . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
If DTCs P0412 and P0418 are also set at the same time, this indicates the AIR pump fuse is open.
-
Excessive resistance in either the control circuit or the B+ circuit will cause an inoperative relay. Command each relay ON and OFF as necessary to verify operation. This step verifies the AIR pump operation.
-
This step isolates if the condition is the AIR integral stop valve or the AIR Bleed Valve solenoid. If no air is present at the outlet of the pump, this indicates a condition with the integral stop valve or circuit.
-
When an engine is started, a vacuum is created in the AIR system. This vacuum causes the integral stop valve from not opening which causes DTC P0410 to set. When the engine is started the PCM commands the AIR Bleed Valve solenoid to open and relieve the vacuum in the AIR system. This step verifies the solenoid is capable of relieving the vacuum.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||
Are both DTCs P0412 AND P0418 also set? | -- | |||||||
3 | Is DTC P0412 or P0418 set? | -- | Go to Applicable DTC table | |||||
|
Important: Listen for an audible click as the relays operate. If no audible click can be heard, inspect the related circuits for excessive resistance.
Does the AIR pump turn ON? | -- | |||||||
5 |
Important: Refer to Electrical Center Identification Views for relay terminal identification.
Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | ||||||
6 |
Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | ||||||
7 |
Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | ||||||
8 |
Important: Refer to Electrical Center Identification Views for relay terminal identification.
Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | ||||||
Is air present at the AIR pump outlet? | -- | |||||||
10 |
Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | ||||||
11 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||
12 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||
13 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||
14 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||
15 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||
16 | Measure the resistance of the AIR Bleed Valve solenoid. Refer to Testing for Continuity in Wiring Systems. Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 15ohms | ||||||
17 |
Does the fuse open? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||
18 |
Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | ||||||
19 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||
Does the vacuum hold before the solenoid was enabled and release when the solenoid is enabled? | 10 in. | |||||||
21 | Repair the open circuit between the fuse and the relay. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
22 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||
23 | Repair the faulty ground connection or open AIR pump ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
24 | Test the continuity between the AIR Solenoid relay and the AIR Bleed Valve Solenoid using the DMM J 39200 . Refer to Testing for Continuity in Wiring Systems. Does the DMM display OL? | -- | ||||||
25 | Repair the short to ground in the ignition feed circuit between the fuse and the relays. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
26 | Repair the short to ground in the circuit between the AIR Pump relay and the AIR pump. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
27 | Repair the short to ground in the circuit between the AIR Solenoid relay and the AIR Bleed Valve Solenoid/AIR pump. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
28 |
Did you find and repair the condition? | -- | ||||||
29 | Replace the AIR Bleed Valve Solenoid. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Bleed Valve Solenoid Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
30 | Replace the AIR pump relay. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Pump Relay Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
31 | Replace the AIR solenoid relay. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Solenoid Relay Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
32 |
Did you find and repair the condition? | -- | ||||||
33 | Replace the AIR pump. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Pump Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
34 | Repair the open B+ supply circuit to the AIR Bleed Valve solenoid. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
35 | Repair the open ground circuit to the AIR Bleed Valve solenoid. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
36 | Repair the vacuum line to the AIR Bleed Valve solenoid for the following:
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
37 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test passed? | -- | ||||||
38 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool. Are any DTCs displayed that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
