Crankshaft and Bearing Cleaning and Inspection Crankshaft and Bearing Inspect
Tool Required
J 7872 Magnetic Base Dial Indicator Set
Important: Use care when handling the crankshaft. Avoid damage to the bearing surfaces.
- Clean the crankshaft with solvent.
- Thoroughly clean all oil passages, and inspect for restrictions or for burrs.
- Dry the crankshaft with compressed air.
- Perform a visual inspection of the crankshaft for damage.
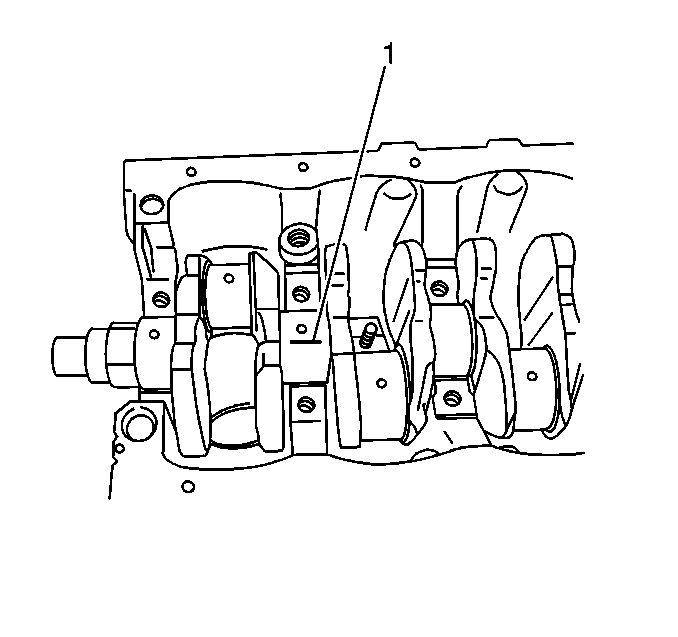
- Inspect the crankshaft journals for wear (1).
- Inspect the crankshaft journals for grooves or for scoring (2).
- Inspect the crankshaft journals for scratches or for wear (3).
- Inspect the crankshaft journals for pitting or for imbedded bearing material (4).
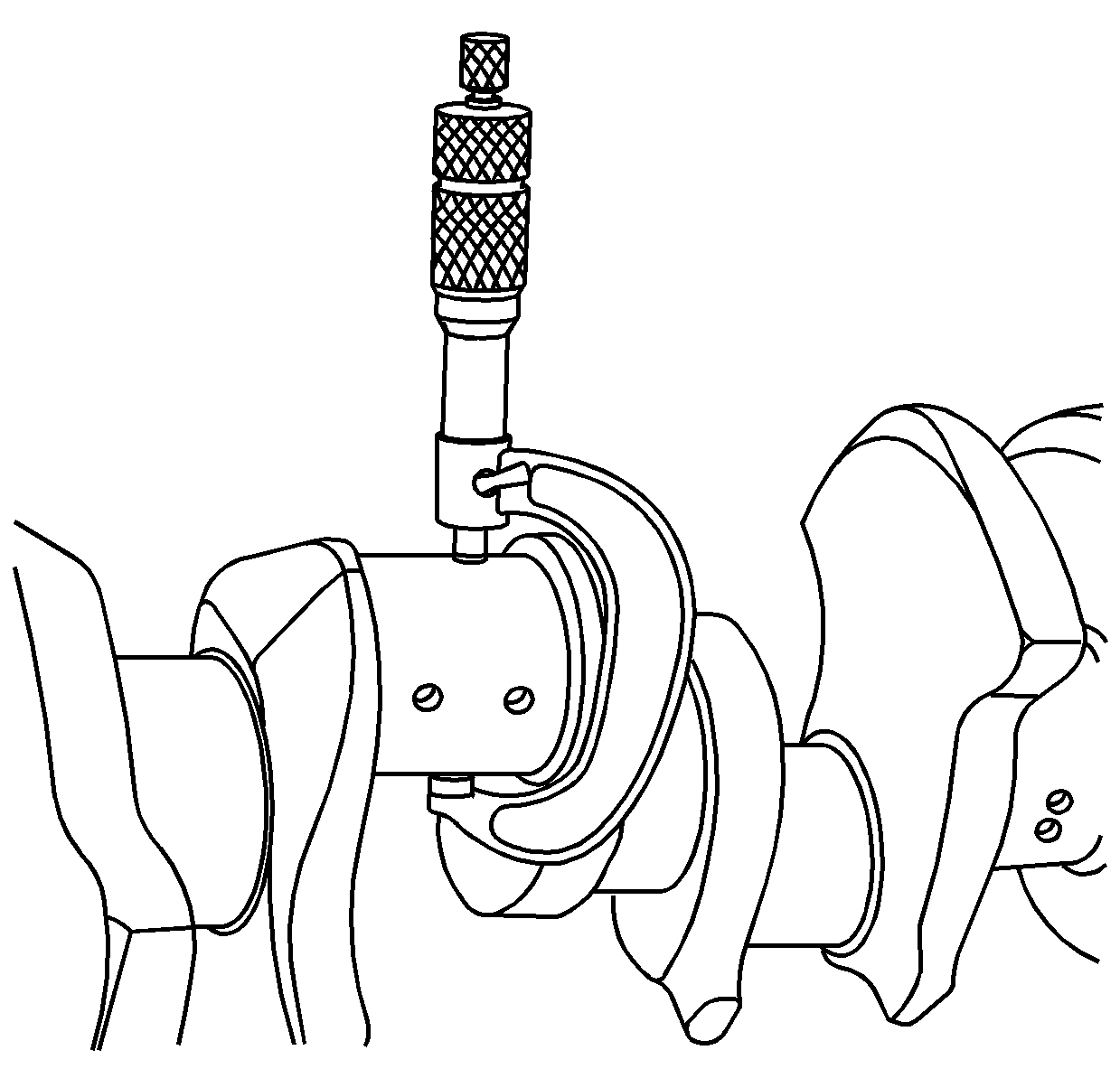
- Measure the crankshaft journals for an out of round condition.
- Measure the crankshaft journals for taper.
- Measure the crankshaft runout.
- Use the J 7872 in order to measure the crankshaft runout at the front and rear intermediate journals.
- Use the J 7872 in order to measure the runout of the crankshaft rear flange.
- Replace or repair the crankshaft if the measurements are not within specifications.
Caution: Wear safety glasses in order to avoid eye damage.
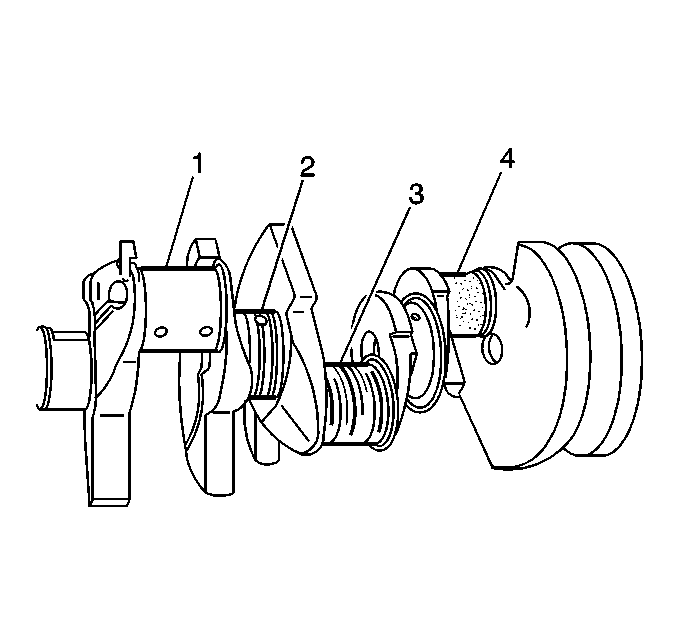
Journals should be smooth without any signs of scoring, without any wear, or without any damage.
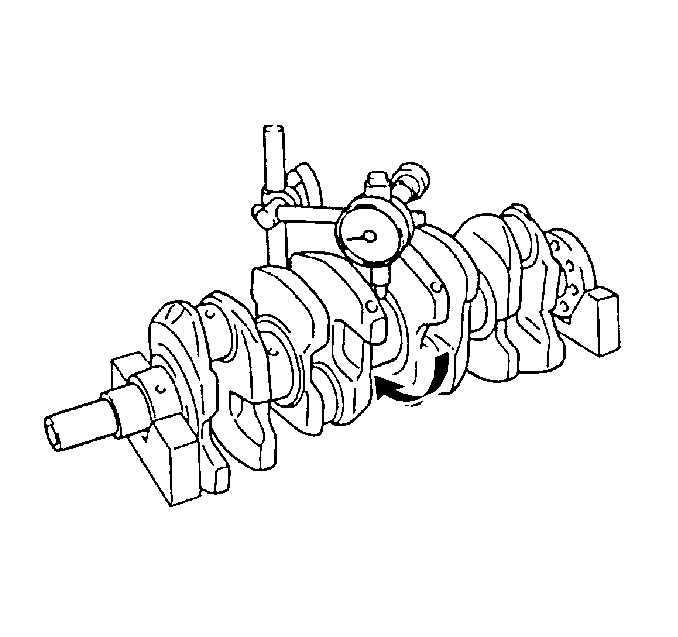
Using wooden V blocks, support the crankshaft on the front journal and on the rear journal.
Crankshaft Main Bearing Inspection
- Inspect crankshaft bearings for craters or for pockets. Flattened sections on the bearing halves also indicate fatigue.
- Inspect the crankshaft bearings for excessive scoring or for discoloration.
- Inspect the crankshaft bearings for dirt or for debris that is imbedded into the bearing material.
- Inspect the crankshaft bearings for incorrect seating that is indicated by bright sections, polished sections of the bearing.
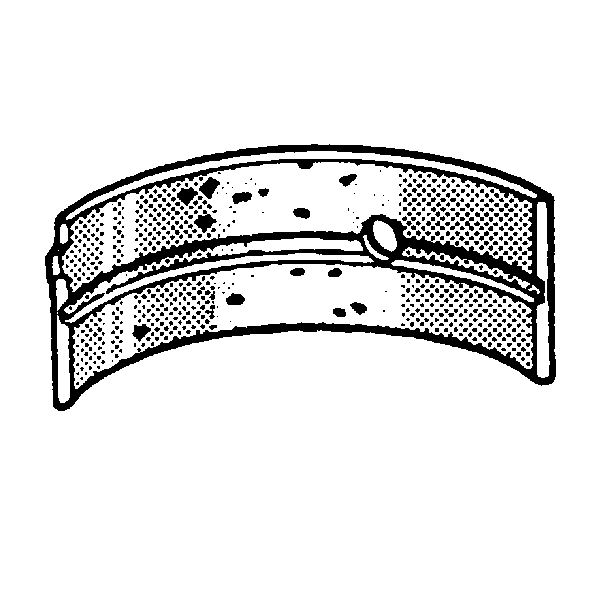
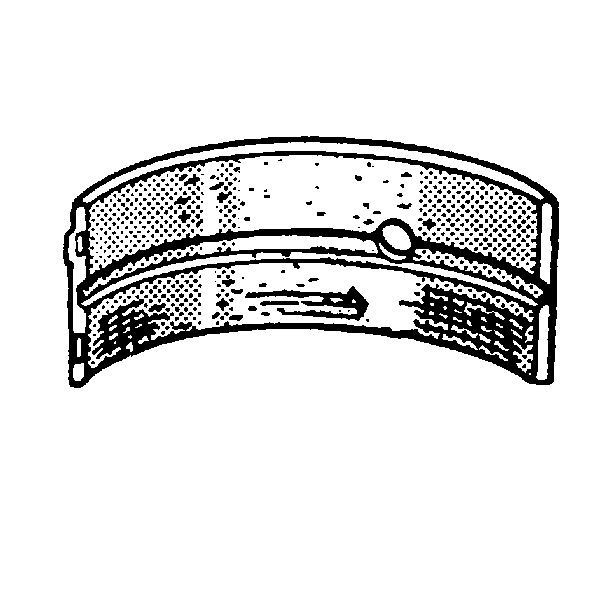
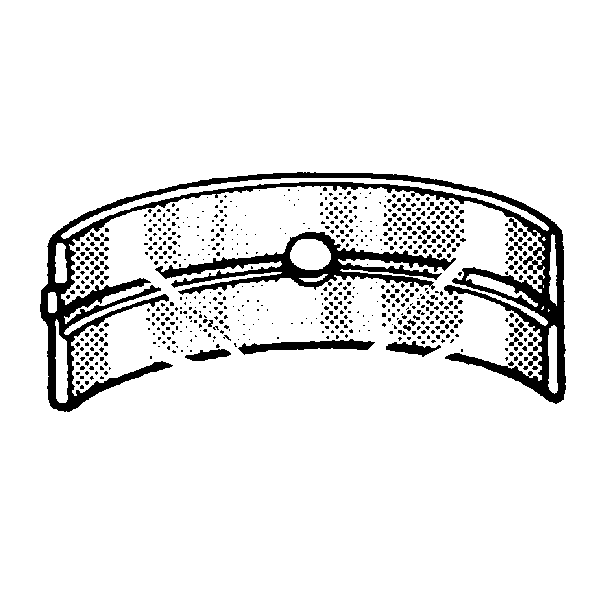
If the lower half of the bearing is worn or damaged, then the upper half and the lower half should be replaced.
Usually, if the lower half is suitable for use, the upper half should also be suitable for use.
Crankshaft and Bearing Cleaning and Inspection Bearing Selection
Crankshaft Main Bearing Selection
- Inspect the connecting-rod bearing bores or the crankshaft main bearing bores using the following procedure:
- Install the original main bearing inserts from the crankshaft onto the cylinder block and onto the main bearing caps.
- Carefully place the crankshaft onto the bearing inserts in the cylinder block.
- Lay a piece of gauging plastic (1) across each crankshaft main journal.
- Carefully place the main bearing caps onto the cylinder block.
- Install the ten main bearing cap bolts.
- After reaching the proper torque, remove the ten main bearing cap bolts from the crankshaft.
- Measure the gauging plastic at the widest point.
- If using a standard bearing, replace the bearing with another bearing having the same color. If the color of the bearing is unclear, select the correct bearing by adding the numbers on the cylinder block and on the crankshaft. Refer to Engine Mechanical Specifications in Engine Mechanical for the bearing selection table.

Important: If crankshaft bearing failure is because of abnormal wear, investigate the cause. Inspect the crankshaft or the connecting-rod bearing bores.
| 1.1. | Tighten the bearing cap to specification. |
| 1.2. | Measure the bearing bore for taper and for an out of round condition. |
| 1.3. | Taper or an out of round condition should not exist. |
Important: Do not turn the crankshaft while measuring the bearing clearance.
Tighten
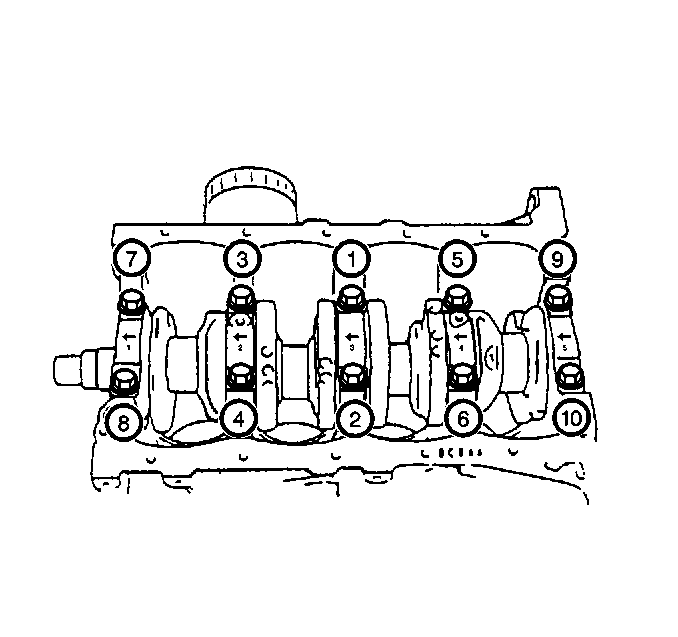
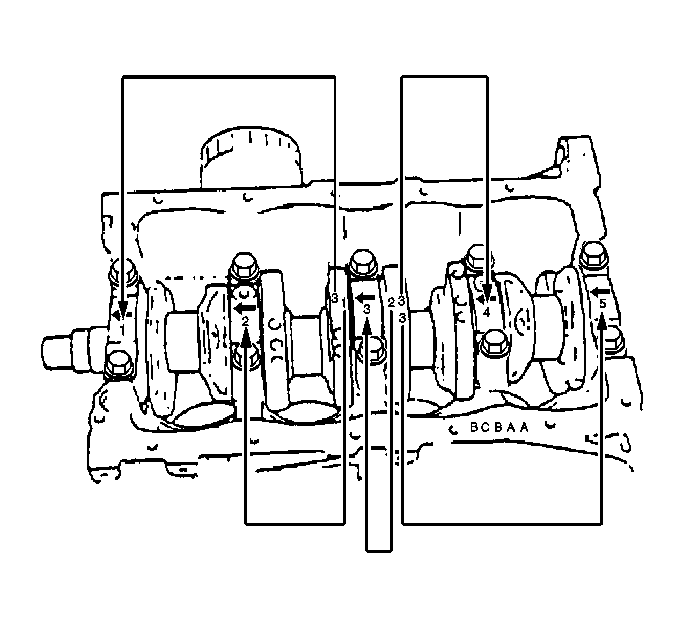
Tighten the main bearing cap bolts of the crankshaft in the sequence that is shown.Use three progressive steps in order to obtain 54 N·m (40 lb ft).
Standard Oil Clearance:
0.020-0.040 mm (0.0008-0.0016 in)
Maximum Oil Clearance:
0.060 mm (0.0023 in)
Crankshaft and Bearing Cleaning and Inspection Bearing Table
Numbers stamped on crank = | -- | 1 | 2 | 3 |
Letters stamped on pan rail = | A | Green | Black | Color- less |
-- | B | Black | Color- less | Yellow |
-- | C | Color- less | Yellow | Blue |
