Valve Cleaning and Inspection
Important: Do not scratch the valve stem with the wire brush.
- Clean the valves of carbon, oil and varnish. Carbon can be removed with
a wire brush, varnish can be removed by soaking in Parts Immersion Solvent
GM P/N 12345368 or equivalent.
- Clean the valve guides.
- Inspect the valve stem for wear. The valve stem end may be reconditioned
by grinding.
- Follow the grinder manufacturer's instructions. Ensure the new
surface is perpendicular to the valve stem.
- Inspect the valve keeper groove chipping or wear. Replace the
valve if chipped or worn.
- Inspect the valve face for burning or cracking. If pieces are
broken off, inspect the corresponding piston and cylinder head area for damage.
- Inspect the valve stem for burrs and scratches. Burrs and minor
scratches may be removed with an oil stone.
- Inspect the valve stem for straightness and the valve head for
bending or distortion. Use V blocks. Bent or distorted valves must be replaced.
- Clean the deposits from the valve face. Inspect the valve face
for grooving.
- Replace the valve if the face is grooved. Valve faces cannot be
machined. If worn, or damaged, the valves must be replaced.
- The valves may be lightly lapped to the valve seats.
Cylinder Head and Gasket Surface Cleaning and Inspection
- Inspect the cylinder head gasket and mating surfaces for leaks,
corrosion and blow-by. If the gasket has failed, use the following faults
to determine the cause:
| 1.1. | Improper installation |
| 1.2. | Loose or warped cylinder head |
| 1.3. | Missing, off location or not fully seated dowel pins |
| 1.4. | Corrosion in the seal area around the coolant passages |
| 1.5. | Chips or debris in the cylinder head bolt holes |
| 1.6. | Bolt holes in the cylinder block not drilled or tapped deep enough |
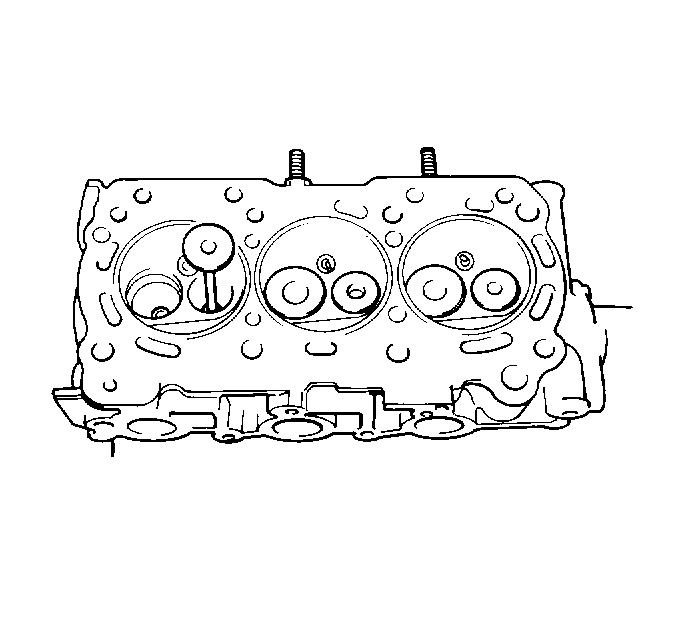
- Inspect the cylinder head
gasket surface.
| • | Cylinder head may be reused if corrosion is found only outside
a 4 mm (0.375 in) band around each combustion chamber. |
| • | Replace the cylinder head if the area between the valve seats
is cracked. |
| • | Replace the cylinder head if corrosion has been found inside
a 4 mm (0.375 in) band around each combustion chamber. |
Important: Do not use a wire brush on any gasket sealing surface.
- Clean the cylinder head. Remove all varnish, soot and carbon to the
bare metal.
- Clean the valve guides.
- Clean the threaded holes. Use a nylon bristle brush.
- Clean the remains of the sealer from the plug holes.
- Replace all suspect bolts.
- Inspect the cylinder head for cracks. Check between the valve
seats and in the exhaust ports.
Important: Do not attempt to weld the cylinder head, replace it.
- Inspect the cylinder head deck for corrosion, sand inclusions and blow
holes.
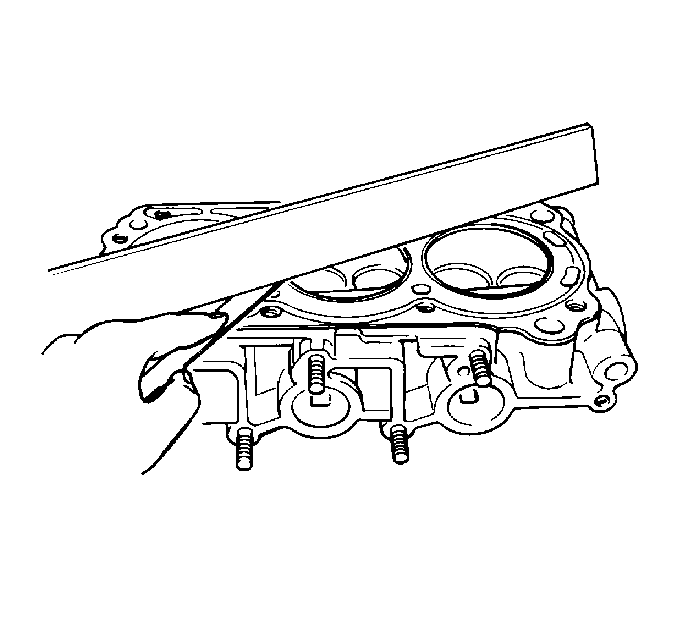
- Inspect the cylinder head
deck for flatness.
Maximum Cylinder Head Warpage
Maximum Warpage: 0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
- If the warpage is greater than the maximum allowed, replace the
cylinder head.
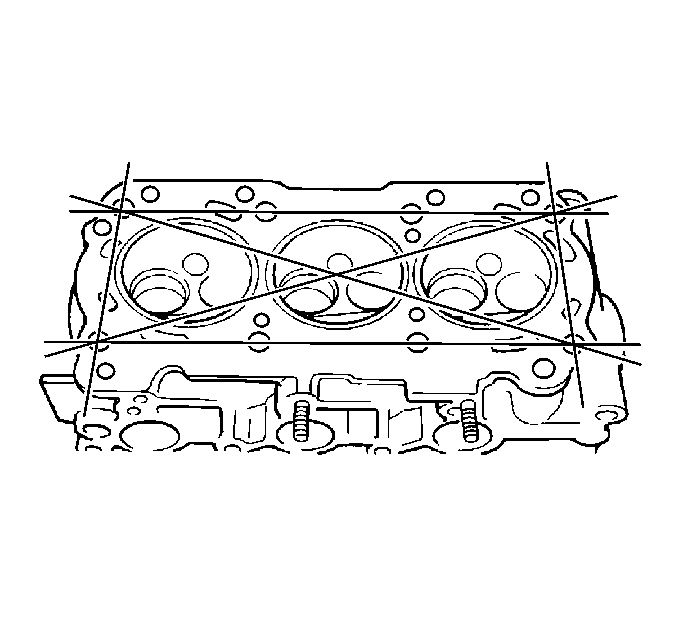
- Measure the cylinder head
deck flatness at several points.
- If the warpage is greater than the maximum allowed at any point,
replace the cylinder head.
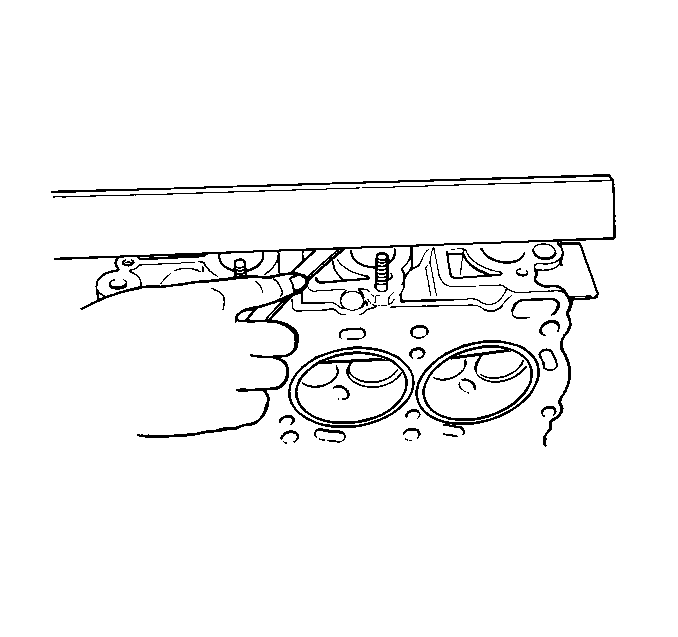
- Inspect the cylinder head
intake manifold mating surface for flatness.
Maximum Cylinder Head Warpage
Maximum Warpage: 0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
- If the warpage is greater than the maximum allowed, replace the
cylinder head.
- Inspect all the threaded holes for damage. Threads may be reconditioned
with thread inserts.
- Inspect the sealing surfaces.
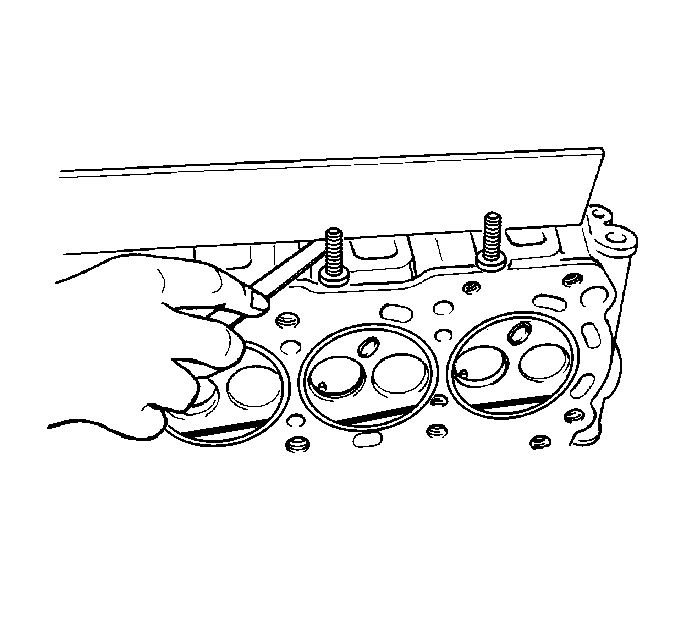
- Inspect the cylinder head
exhaust manifold mating surface for flatness.
Maximum Cylinder Head Warpage
Maximum Warpage: 0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
- If the warpage is greater than the maximum allowed, replace the
cylinder head.
- Inspect all the threaded holes for damage. Threads may be reconditioned
with thread inserts.
- Inspect the sealing surfaces.





