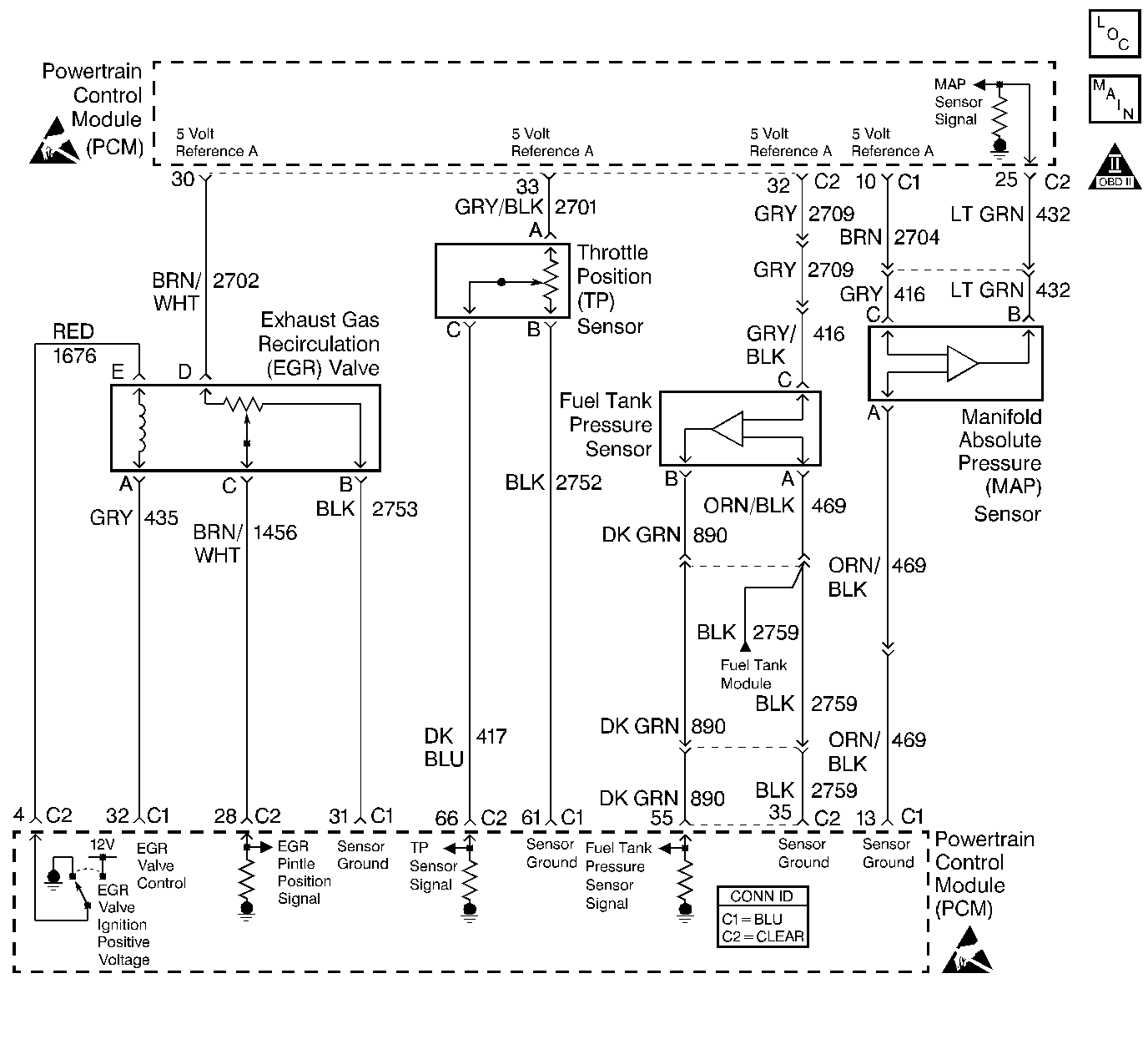
Circuit Description
The Throttle Position (TP) sensor circuit provides a voltage signal that changes relative to throttle blade angle. The signal voltage will vary from below 1 volt at closed throttle to about 4 volts at Wide Open Throttle (WOT).
The TP signal is one of the most important inputs used by the PCM for fuel control and most of the PCM controlled outputs.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The engine is running. |
| • | TP sensor signal is greater than 98 percent. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. |
| • | The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connection at PCM. Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| • | Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the TP sensor display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the TP sensor. A change in the display will indicate the location of the fault. |
| • | Faulty TP sensor: With the key ON, engine OFF, observe the TP sensor display on the scan tool while slowly depressing the accelerator to wide open throttle. If a voltage over 4.71 volts is seen at any point in normal accelerator travel, replace the TP sensor. |
If DTC P0123 cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Fail Records data can be useful in determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set. If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently, performing the DTC P1121 Diagnostic Chart may isolate the cause of the fault.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table:
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic Check performed? | -- | ||
2 |
Is TP Sensor above the specified value? | 4.71V | ||
3 |
Does scan tool indicate DTC P0123 failed? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
4 |
Is TP Sensor near the specified value? | 0.0V | ||
5 | Probe the sensor ground circuit at the TP sensor harness connector with a test lamp connected to battery positive voltage. Is the test lamp ON? | -- | ||
6 |
Was the TP sensor signal circuit shorted? | -- | ||
Does disconnecting any of these components cause the TP Sensor display to change? | -- | |||
8 |
Was the 5 volt reference A circuit shorted? | -- | ||
9 | Check for poor electrical connections at the TP sensor and replace terminals if necessary or open sensor ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did any terminals or ground circuit require repair? | -- | ||
10 | Replace the TP sensor. Refer to Throttle Position Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
|
Important : Replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
12 |
Does scan tool indicate DTC P0123 failed? | -- | System OK |
