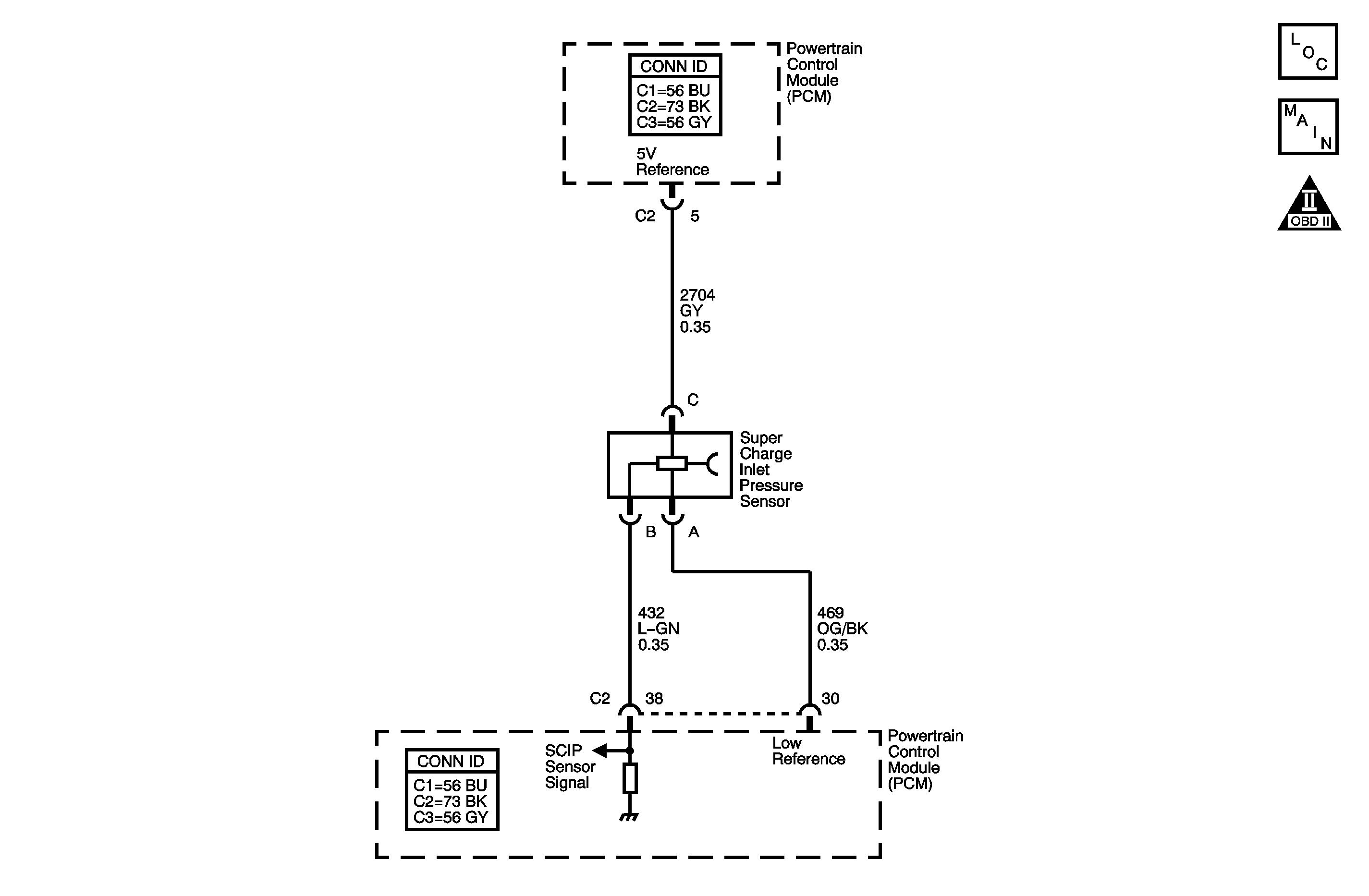
Circuit Description
The supercharger inlet pressure (SCIP) sensor measures both the atmospheric pressure and the vacuum that exists, under different operating conditions, in the supercharger intake plenum. The plenum volume between the throttle body and the supercharger is where this sensor is located, and for the purpose of this diagnostic, this area is considered to be the intake manifold.
The SCIP sensor has the following types of circuits:
| • | A powertrain control module (PCM) supplied and regulated 5-volt reference circuit |
| • | A PCM supplied ground for the low reference circuit |
| • | A sensor signal circuit that supplies a voltage input to the PCM |
The diaphragm within the SCIP sensor responds to the pressure changes in the intake manifold, and provides a signal voltage to the PCM on the signal circuit, relative to those pressure changes.
The PCM monitors the SCIP sensor signal for voltage that is outside of the normal range of a properly operating sensor. If the PCM detects a SCIP sensor signal voltage that is excessively high, DTC P1184 sets.
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTC:
DTC P1184 Supercharger Inlet Pressure (SCIP) Sensor Circuit High Voltage
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0120, P0121, P0220, P0641, P0651, P2135 are not set. |
| • | The engine has been running for a calibrated length of time that is determined by the start-up engine coolant temperature (ECT). The length of time ranges from 2 minutes at less than -30°C (-22°F) to 1 second at more than 30°C (86°F). |
| • | The TP Indicated Angle parameter is less than 90 percent when the engine speed is less than 1000 RPM. |
| OR |
| • | The TP Indicated Angle parameter is less than 98 percent when the engine speed is more than 1000 RPM. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM detects that the SCIP signal voltage is more than 2.4 volts for more than 2 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool. |
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the diagnostic table.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls Connector End Views or Powertrain Control Module Connector End Views | ||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check - Engine Controls? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
Is DTC P0641 set? | -- | Go to DTC P0641 | Go to Step 3 | |
3 | Observe the SC Inlet Pressure Sensor parameter with a scan tool. Is the SC Inlet Pressure Sensor parameter more than the specified value? | 2.40 V | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 4 |
4 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 5 | Go to Inducing Intermittent Fault Conditions in Wiring Systems and Intermittent Conditions |
5 |
Important: The connectors for the following sensors are of the same configuration but are not interchangeable.
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 6 |
6 |
Is the SC Inlet Pressure Sensor parameter less than the specified value? | 0.20 V | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 8 |
7 |
Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 0.20 V | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 10 |
8 | Test the SCIP sensor signal circuit between the powertrain control module (PCM) and the SCIP sensor for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 11 |
9 | Test the SCIP sensor low reference circuit between the PCM and the SCIP sensor for a high resistance or for an open. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 11 |
10 | Test for an intermittent and for shorted terminals and for a poor connection at the SCIP sensor. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 12 |
11 | Test for an intermittent and for shorted terminals and for a poor connection at the PCM. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 13 |
12 | Replace the SCIP sensor. Refer to Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 14 | -- |
13 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 14 | -- |
14 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 15 |
15 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | System OK | |
