- Support the vehicle drive axle on a suitable hoist. Refer to Lifting and Jacking the Vehicle in General Information.
- Remove the tire and wheel assemblies from the drive axle. Refer to Tire and Wheel Removal and Installation in Tires and Wheels.
- Reinstall the wheel nuts in order to retain the brake rotors.
- Run the vehicle at the concern speed while inspecting for the presence of the vibration.
- If the vibration is still present, remove the brake rotors from the drive axle, then run the vehicle back to the concern speed. Refer to Front Brake Rotor Replacement in Disc Brakes.
- If the vibration is eliminated when the brake rotors are removed from the drive axle, repeat the test with one rotor installed at a time. Replace the rotor that is causing or contributing to the vibration concern. Refer to Front Brake Rotor Replacement in Disc Brakes.
- If a brake rotor was replaced as a result of following the previous steps, or if necessary to confirm the results obtained during the previous steps, and/or to check the non-drive axle components, perform the following:
Caution: One or more of the following guidelines may apply when performing specific required tests in the work stall:
• When a test requires spinning the drive wheels with the vehicle jacked up, adhere to the following precautions: - Do not exceed 56 km/h (35 mph) when spinning one drive wheel with the other drive wheel stopped. This limit is necessary because the speedometer indicates only one-half the actual vehicle speed under these conditions. Personal injury
may result from excessive wheel spinning. - If all of the drive wheels are spinning at the same speed, do not exceed 112 km/h (70 mph). Personal injury may result from excessive wheel spinning. - All persons should stay clear of the rotating components and the balance weight areas in order to avoid possible personal injury. - When running an engine in the repair stall for an extended period of time, use care not to overheat the engine and the transmission. • When a test requires jacking up the vehicle and running with the wheels and brake rotors removed, adhere to the following precautions: - Support the suspension at normal ride height. - Do not apply the brake with the brake rotors removed. - Do not place the transmission in PARK with the drive axles spinning. - Turn Off the ignition in order to stop the powertrain components from spinning. • When running an engine in the work stall, use the exhaust removal system to prevent breathing dangerous gases.
Notice: Do not depress the brake pedal with the brake rotors and/or the brake drums removed, or with the brake calipers repositioned away from the brake rotors, or damage to the brake system may result.
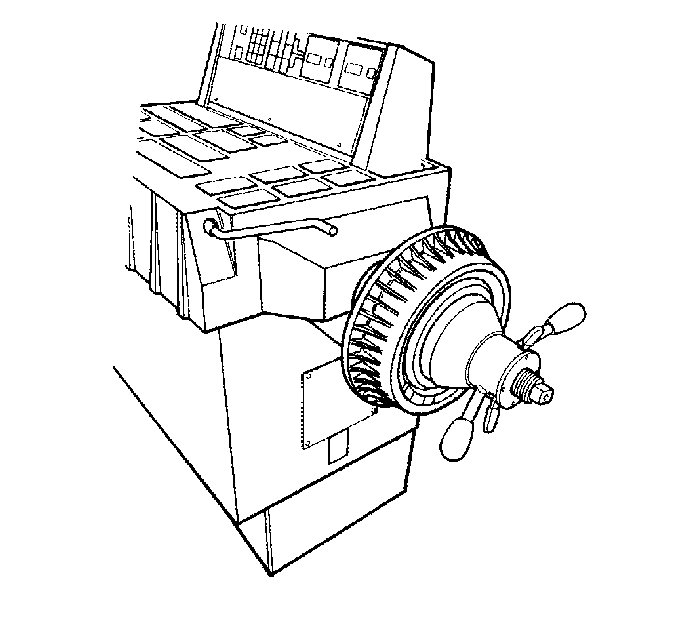
| 7.1. | Mount the brake rotor on a balancer in the same manner as a tire and wheel assembly. |
| Important: Check brake rotors for static imbalance only; ignore the dynamic imbalance readings. |
| 7.2. | Inspect the rotor for static imbalance. |
There is not a set tolerance for brake rotor static imbalance. However, any brake rotor measured in this same manner which is over 21 g (¾ oz) may have the potential to cause or contribute to a vibration. Rotors suspected of causing or contributing to a vibration should be replaced. Any rotor that is replaced should be checked for imbalance in the same manner.
