- Clean the sludge and carbon from the following parts:
Caution: Bodily injury may occur if the carburetor cleaning fluid is exposed
to the skin or if the fumes are inhaled.
Important: It is essential that the piston ring grooves are cleaned of carbon to
the bare metal.
- Clean the varnish from the piston pin by soaking it in carburetor cleaning
solution.
Important: Do not scrape the piston skirt.
- Inspect the connecting rod for bending or twisting.
- Install the connecting rod cap.
- Place the connecting rod assembly on a checking fixture and check
for bending or twisting.
- Do not attempt to straighten the connecting rod. The connecting
rods should not be bent more than 0.18 mm (0.007 in) for every
76.2 mm (3.00 in) of rod length. The connecting rods should
not be twisted more than 0.038 mm (0.0015 in) for every 25.4 mm
(1.00 in) of rod length. Replace it, if it is bent or twisted.
- Check new connecting rods before using them.
- Inspect the outside of the connecting rod bearing and the ID of
the connecting rod lower end for wear indicating high spots in the connecting
rod lower end.
- Inspect the upper end for scoring.
- Inspect the piston pin for the following conditions:
| • | Galling caused by improper installation |
| • | Fit in the connecting rod and piston |
- Inspect the piston for the following conditions:
| • | Broken ring groove lands |
Important: When fitting pistons, both the piston and the cylinder bore condition
must be considered together. Production and service pistons have the same
nominal weight and can be intermixed without affecting engine balance. If
necessary, used pistons may be fitted selectively to any cylinder of the engine,
providing they are in good condition and the same weight. Do not cut oversize
pistons down or engine balance will be affected. Finish hone when selecting
the piston.
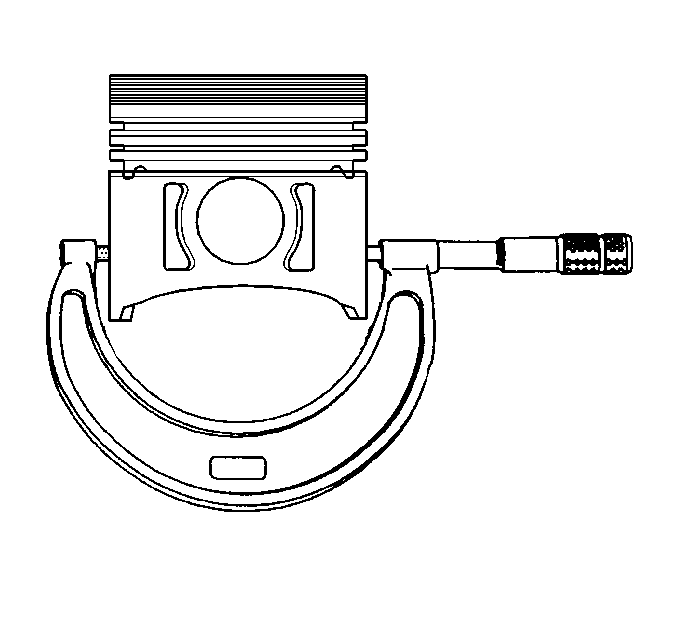
- Measure the piston diameter. When measuring piston for size or taper,
measurement must be made as shown with the piston pin removed. If worn or
damaged, replace with a standard or oversize piston.
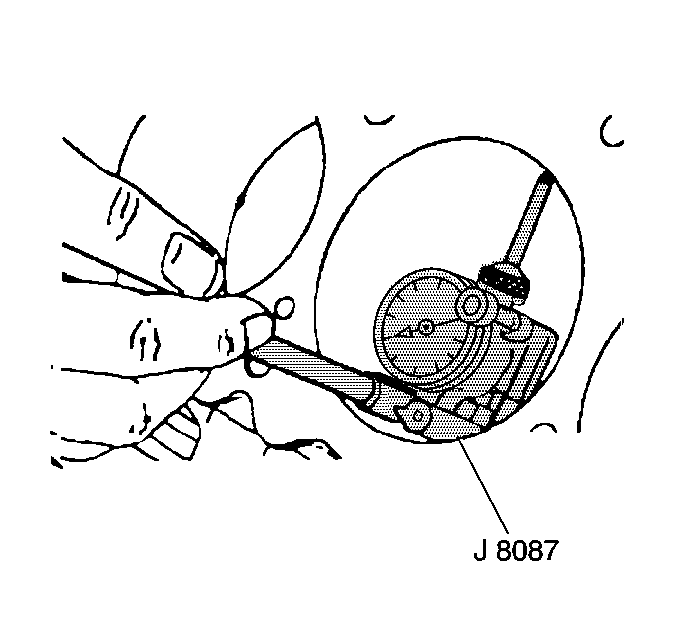
- Measure the cylinder bore, with a telescoping
gauge. If worn beyond specifications, rebore and hone to size.
- Subtract the piston diameter from the cylinder bore diameter in
order to determine the piston-to-bore clearance.
- Compare the piston-to-bore clearance with specifications in order
to determine if the clearance is in acceptable range.
- If a used piston is not acceptable, check the service piston sizes
and determine if a new piston can be selected. Service pistons are available
in standard, and several oversizes.
- If the cylinder bore must be reconditioned, measure the new piston
diameter then hone the cylinder bore to the correct clearance.
- Select the new piston and mark the piston in order to identify
the cylinder for which it was fitted.
- Measure the piston pin bore diameter with an inside micrometer.
- Measure the piston pin diameter with a micrometer.
- Subtract the piston pin bore diameter from the piston pin diameter
in order to determine the clearance.
- Compare the clearance with specifications in order to determine
if clearance is in an acceptable range. Replace the piston assembly if it
is not acceptable.
Important: Do not reuse piston rings. Fit rings in order to match the cylinder
they will be used in.
- Place the piston into the cylinder at the bottom of the ring travel.
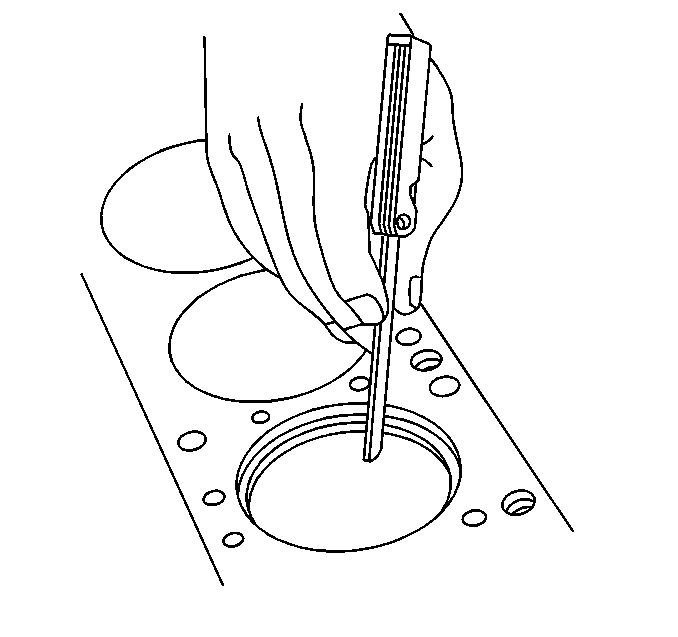
- Place a piston ring on top of the piston.
- Back off the piston.
- Measure the ring gap. If the gap is below specification, increase
the gap by carefully filing off excess material.
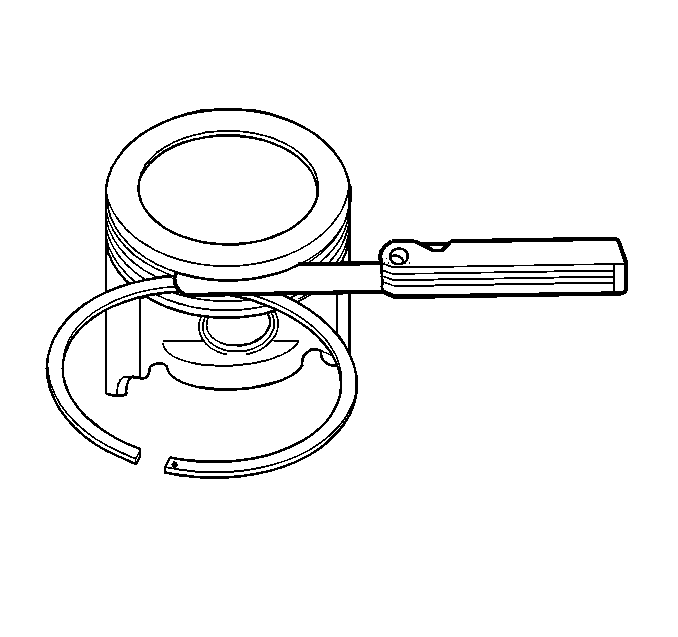
Important: Do not attempt to cut the ring groove, although high spots in the ring
groove may be cleaned up by the careful use of a point file.
- Measure the piston ring side clearance.
- Roll the piston ring around the groove in which it is to be installed,
and measure the side clearance. If the ring is too thick, try another ring.




