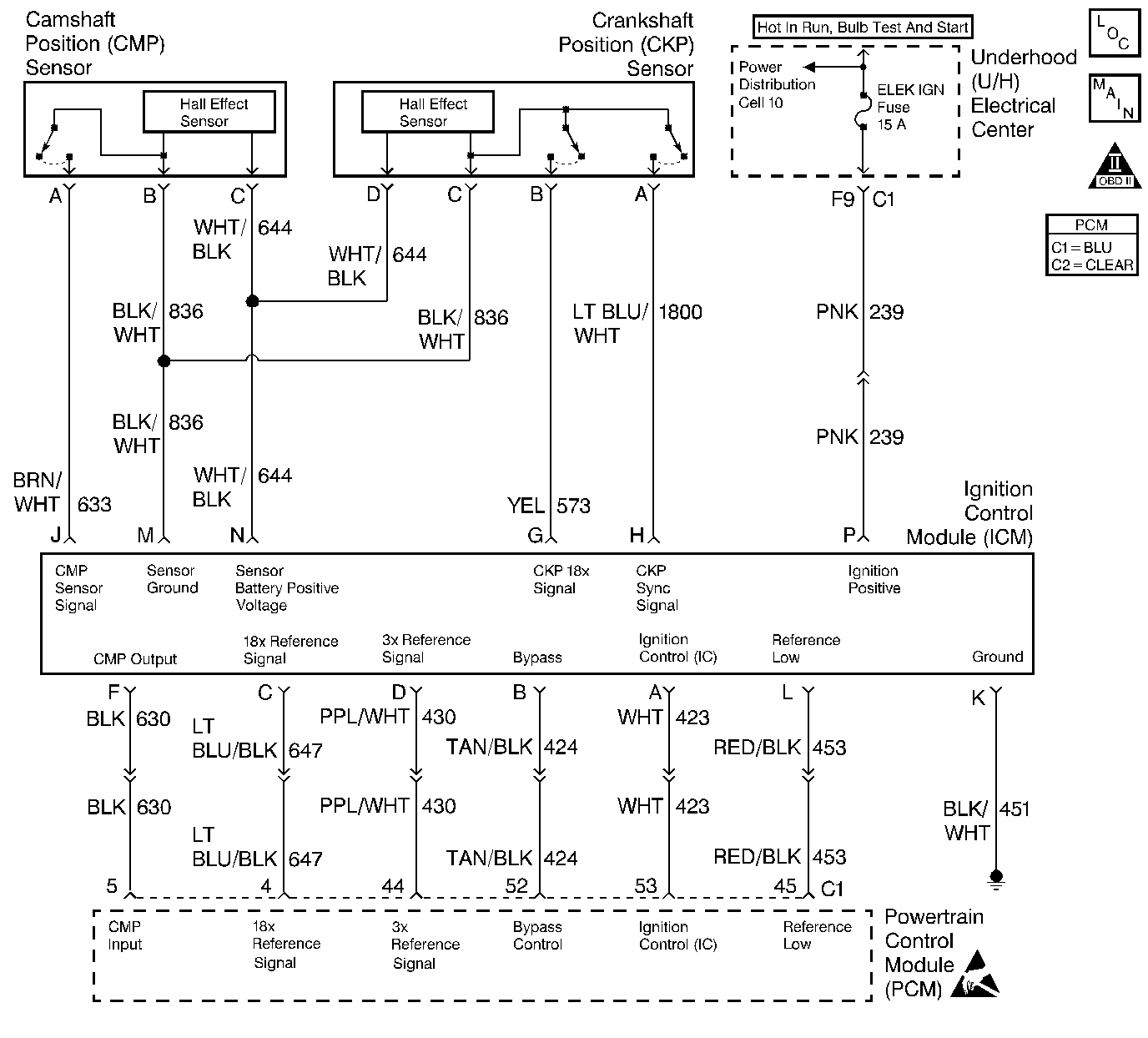
Circuit Description
The Ignition Control Module (ICM) sends signals that the PCM requires for fuel control and spark advance calculations. At the start of engine crank, the ICM controls spark advance (Bypass mode). When the second 3X reference pulse is recognized by the PCM, the PCM applies 5 volts to the Bypass circuit. The 5 volts on the Bypass circuit commands the ICM to switch spark advance to PCM control (IC mode). At this time, The ICM will remove the ground it has applied to the IC circuit. When the IC pulses are not grounded, the ICM can use the IC pulses to control spark advance. A short in the IC circuit or an open or short to ground in the Bypass circuit will cause the PCM to monitor no IC pulses after the PCM has switched the Bypass circuit ON. The PCM will set DTC P1361 under either of these conditions. The engine may be started but will run on Bypass mode timing.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM does not monitor IC pulses while IC mode spark advance is commanded.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the MIL during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame and Fail Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has been run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool Clear Info function or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connection at the PCM. |
| Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| • | Damaged harness. |
| Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect the ICM, turn the ignition ON and observe a digital multimeter connected between the IC circuit and B+ while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the ICM. A change in voltage will indicate the location of the malfunction. |
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 |
Did DTC P1361 set? | -- | Refer to Diagnostic Aids | |
3 |
Is the test light ON? | -- | ||
4 |
Is resistance greater than the specified value? | 6K ohms (6000 ohms) | ||
5 |
Is the test light ON? | -- | ||
6 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||
7 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||
8 |
Is the test light ON? | -- | ||
9 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||
10 | Locate and repair short to ground in the IC circuit. Refer to Repair Procedures in Electrical Diagnosis. Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
11 | Locate and repair short to ground in the bypass circuit. Refer to Repair Procedures in Electrical Diagnosis. Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
12 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||
Replace the PCM. Important:: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is action complete? | -- | -- | ||
14 | Replace the ignition control module. Refer to Ignition Control Module Replacement . Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
15 |
Does the scan tool indicate DTC P1361 failed? | -- | System OK |
