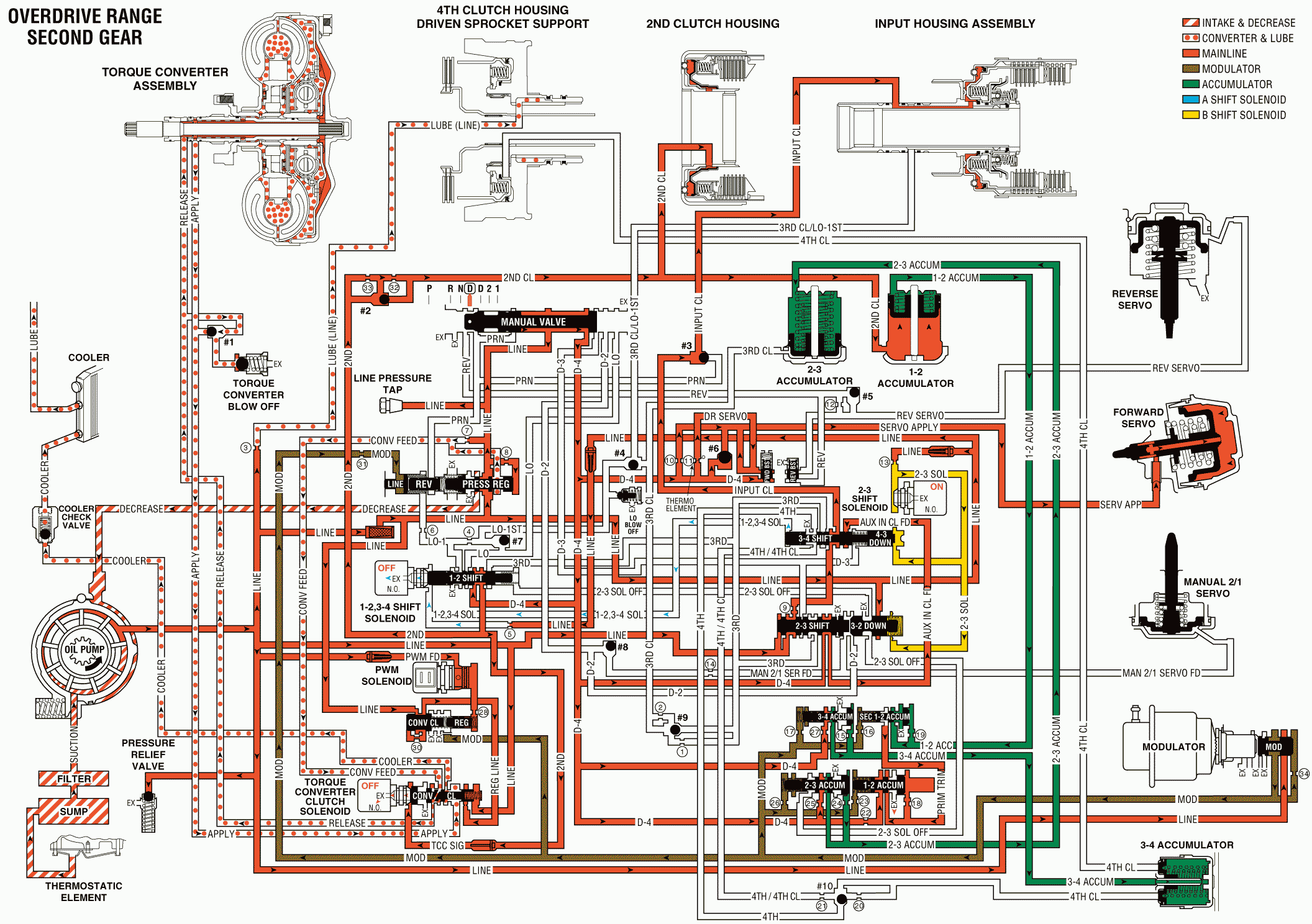
To obtain Second gear, the PCM receives input signals from the Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS), the Throttle Position (TP) sensor, and from other engine sensors. This determines the precise moment to de-energize (turn OFF) the current to the 1-2, 3-4 shift solenoid valve (315). When this occurs, line pressure to the 1-2 shift valve (318) exhausts through the solenoid, allowing spring pressure to move the valve. D4 pressure at the valve during First gear operation can now enter the second fluid passage. Second fluid feeds to the #2 checkball (372) and the fluid seats the checkball, forcing the fluid through a feed orifice before applying the second clutch. At the same time, second clutch fluid is fed to the 1-2 accumulator piston (136). This fluid strokes the piston up against spring pressure and 1-2 accumulator fluid pressure, which cushions the second clutch application. The 1-2 accumulator fluid is then forced through the 1-2 accumulator passage, and the fluid exhausts at the 1-2 secondary accumulator valve (347).
1-2, 3-4 Shift Solenoid Valve (315)
The 1-2, 3-4 shift solenoid valve de-energizes, allowing line pressure to exhaust through the solenoid.
1-2 Shift Valve (318)
With the 1-2, 3-4 shift solenoid valve turned off, spring pressure moves the valve, allowing D4 pressure to enter the second fluid passage. This directs the second fluid to the #2 checkball.
#2 Checkball (372)
The #2 checkball is located in the channel plate (400). Second fluid seats the checkball, and the fluid is forced through an orifice into the second clutch passage to apply the second clutch.
1-2 Accumulator Piston (136)
The 1-2 accumulator piston cushions the application of the second clutch using second clutch fluid. The fluid forces the piston against a spring force and 1-2 accumulator fluid.
Secondary 1-2 Accumulator Valve (347)
The secondary 1-2 accumulator valve regulates the exhaust rate of the 1-2 accumulator fluid during the application of the second clutch.
Overdrive Range, Second Gear