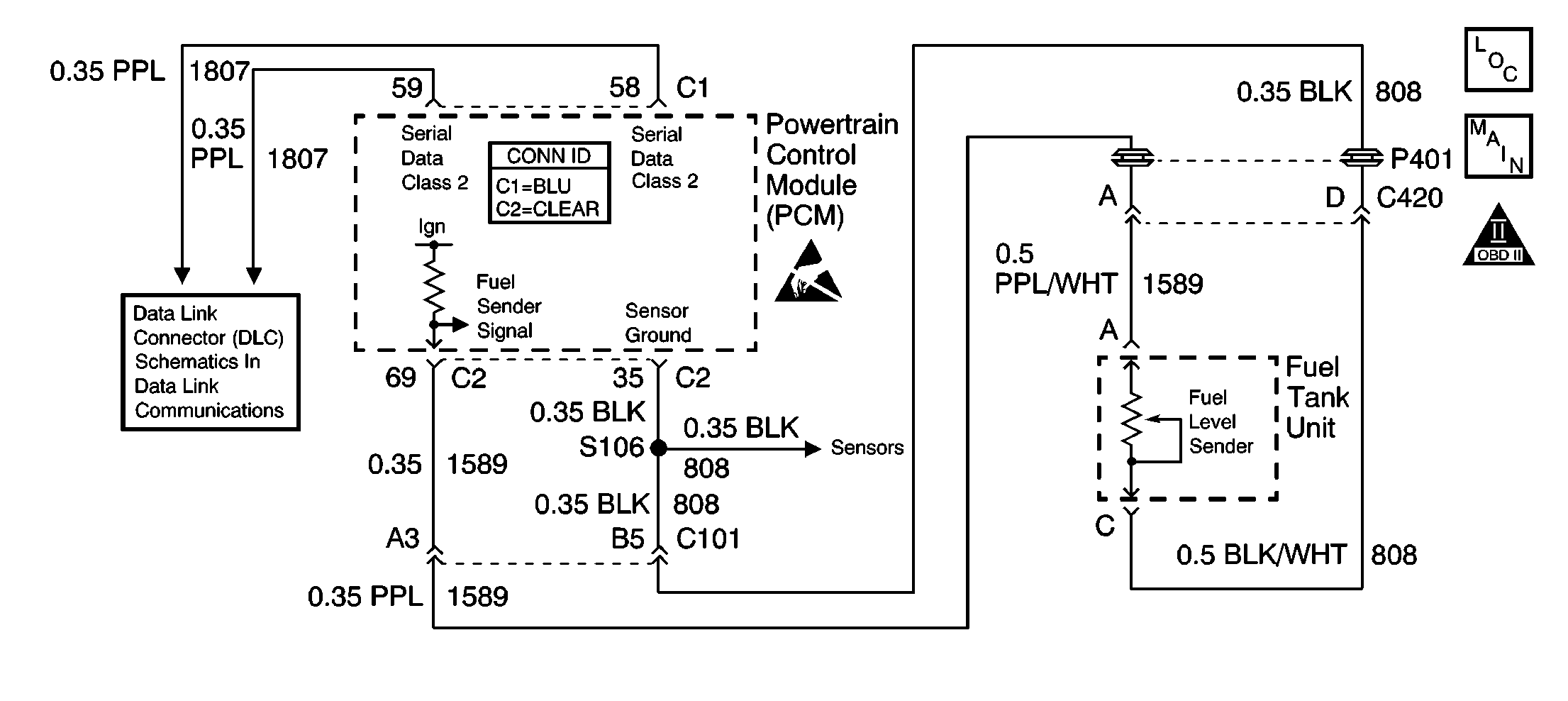
Circuit Description
The fuel level sensor is a device used to determine the level of fuel in the tank. The PCM applies a signal voltage to the sensor. The sensor varies the voltage based on the level of fuel in tank. The sensor resistance is high when the tank is full, and the PCM senses a high signal voltage. As the fuel level in the tank decreases, the sensor resistance drops, and the signal voltage at the PCM is pulled low.
The PCM also sends the fuel level information via class 2 serial data to the IPC. The IPC uses the information to control the fuel gauge.
The PCM monitors the fuel level sensor for signal voltages outside the normal range of the sensor. If the PCM detects a signal voltage above the calibrated range of the sensor, DTC P0463 will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The ignition is ON. |
| • | System voltage is between 11-16 volts. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM detects a fuel level sensor voltage that is more than 3 volts for at least 10 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM stores conditions which were present when the DTC set as Failure Records only. This information will not be stored as Freeze Frame Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The DTC becomes history when the conditions for setting the DTC are no longer present. |
| • | The history DTC clears after 40 malfunction free warm-up cycles. |
| • | The PCM receives a clear code command from the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Fuel level is used to determine EVAP system diagnosis. Always diagnose the fuel level sensor before any other EVAP system components or DTCs.
Refer to Diagnostic System Check - Instrument Cluster .
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may assist in diagnosing the condition. The information may help determine how often the condition that set the DTC occurs.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
The operating range of the fuel level sensor is between 3 and 100 percent. A value that is out of range will set a DTC.
-
Tests for the proper operation of the circuit in the high voltage range.
-
Tests for the proper operation of the circuit in the low voltage range. If the fuse in the jumper opens when you perform this test, the signal circuit is shorted to voltage.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
Does the scan tool indicate that the fuel level parameter is within the specified range? | 3%-98% | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 | |
3 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic failed this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 4 | Go to Intermittent Conditions |
Does the scan tool indicate that the fuel level parameter is greater than the specified value? | 125% | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 6 | |
Does the scan tool indicate that the fuel level parameter is less than the specified value? | 3% | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 7 | |
6 | Test the signal circuit of the fuel level sensor for a short to ground. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 10 |
7 | Test the signal circuit of the fuel level sensor for a short to voltage, a high resistance, or an open. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 8 |
8 | Test the ground circuit of the fuel level sensor for a high resistance or an open. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 10 |
9 | Inspect for poor connections at the harness connector of the fuel level sensor. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 11 |
10 | Inspect for poor connections at the harness connector of the PCM. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 12 |
11 | Replace the fuel level sensor. Refer to Fuel Level Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- |
12 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- |
13 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | Go to Step 2 | System OK |
