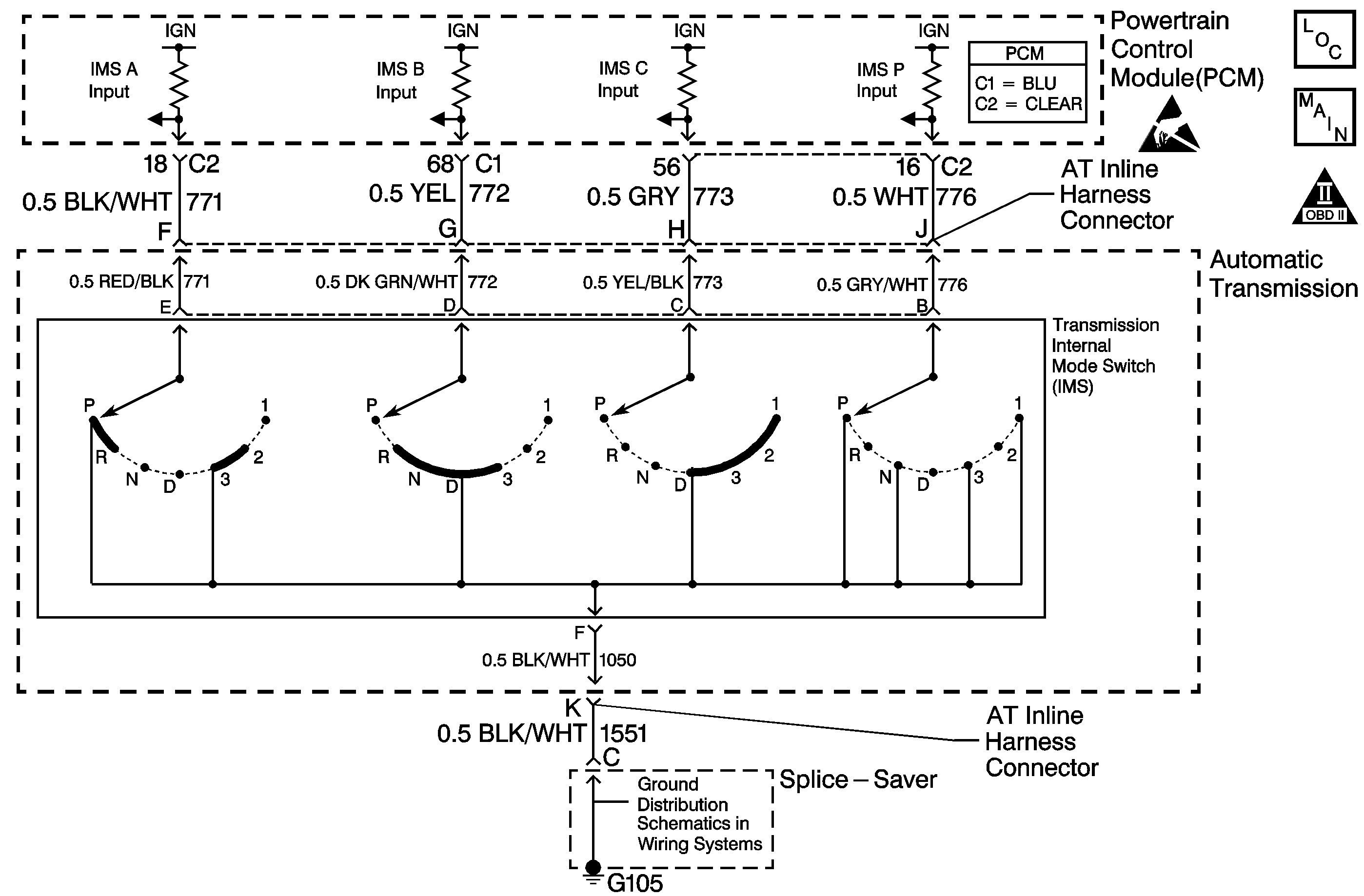
Circuit Description
The transmission internal mode switch (IMS) is a sliding contact switch attached to the selector detent inside the transmission side cover. The four inputs to the PCM from the IMS indicate which position is selected by the transmission selector lever. This information is used for engine controls as well as determining the transmission shift patterns. The input voltage level at the PCM is high (B+) when the IMS is open and low when the switch is closed to ground. The state of each input is available for display on the scan tool. The four input parameters represented are Signals A, B, C and P (Parity).
If the PCM detects that IMS Signal P is always low, then DTC P1823 sets. DTC P1823 is a type C DTC.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The system voltage is 9-18 volts. |
| • | The engine speed is at least 500 RPM for 5 seconds and not in fuel shutoff. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The IMS Signal P is continuously low this ignition cycle, and the following conditions occur:
| • | The IMS indicates PARK for 4 seconds, then; |
| • | The IMS indicates transitional position N-D4, and; |
| • | Engine torque is 95-407 N·m (70-300 lb ft) with no engine torque defaults for 6 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM does not illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions when the Conditions for Setting the DTC are met. The PCM stores this information as Failure Records. |
| • | The PCM stores DTC P1823 in PCM history. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | A scan tool can clear the DTC. |
| • | The PCM clears the DTC from PCM history if the vehicle completes 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a non-emission-related diagnostic fault occurring. |
| • | The PCM cancels the DTC default actions when the fault no longer exists and the ignition switch is OFF long enough in order to power down the PCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Inspect the connectors at the controller, the component and all other circuit connecting points for an intermittent condition. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Inspect the circuit wiring for an intermittent condition. Refer to Testing for Electrical Intermittents in Wiring Systems. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
A LOW signal indicates a short to ground in the vehicle harness or the PCM.
-
This step tests the internal transmission harness without the IMS connected.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain Diagnostic System Check? | -- | Go to Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check in Engine Controls | |
2 |
Important: Before clearing the DTC, use the Scan Tool in order to record the Freeze Frame and Failure Records. Using the Clear Info function erases the Freeze Frame and Failure Records from the PCM. Does the Scan Tool IMS parameter indicate D4? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
Does IMS signal P indicate LOW? | -- | |||
4 | Test the signal circuit P (CKT 776) of the IMS for a short to ground between the PCM connector C2 and the AT Inline 20-way connector. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
Does IMS signal P indicate LOW? | -- | |||
6 | Replace the automatic transmission wiring harness assembly. Refer to Solenoids and Wiring Harness Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |
7 | Replace the lever assembly-manual shaft detent with internal mode switch. Refer to Transmission Overhaul in the 4T65-E Section of the Transmission Unit Repair Manual. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |
8 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming in Engine Controls. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |
9 | Perform the following procedure in order to verify the repair:
Has the test run and passed? | -- | System OK |
