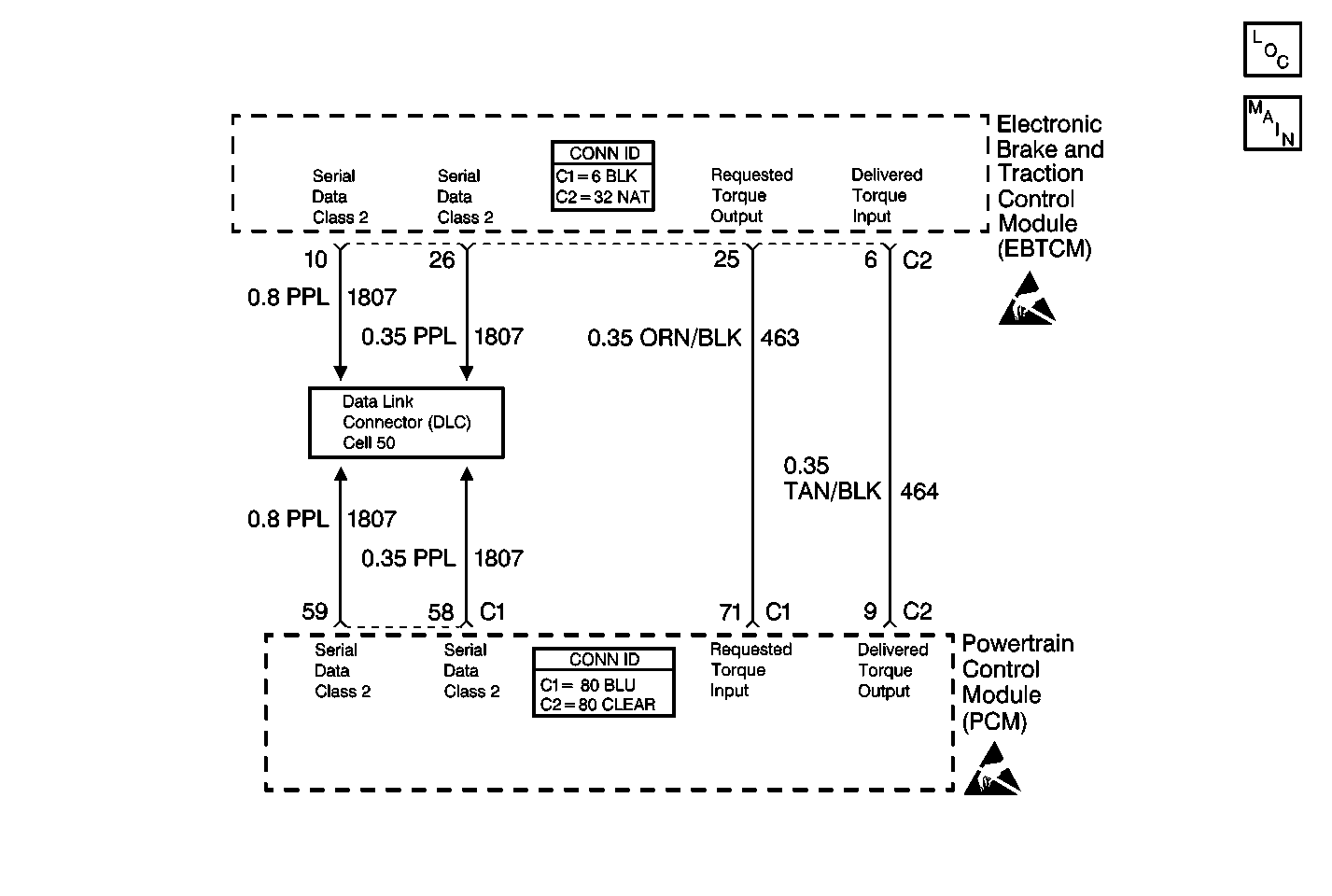
Circuit Description
The EBCM/EBTCM and the PCM simultaneously control the traction control. The PCM receives a Requested Torque message via a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal from the EBCM/EBTCM requesting the desired torque level for proper TCS operation. The PCM supplies the pull up voltage.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The DTC sets if one of the following occur:
| • | An open or short in the Requested Torque line between the EBCM/EBTCM and the PCM. |
| • | A TCS communication malfunction detected by the PCM and indicated to the EBCM/EBTCM via a PWM message. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | A malfunction DTC is stored. |
| • | The TCS is disabled. |
| • | The TRACTION CONTROL indicator is turned ON. |
| • | The ABS remains functional. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The condition for the DTC is no longer present and you used the scan tool Clear DTC function. |
| • | The EBCM/EBTCM does not detect the DTC in 50 drive cycles. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | It is very important that a thorough inspection of the wiring and connectors be performed. Failure to carefully and fully inspect wiring and connectors may result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with reappearance of the malfunction. |
| • | An intermittent malfunction can be caused by poor connections, broken insulation, or a wire that is broken inside the insulation. |
| • | If an intermittent malfunction exists, refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. |
| • | The following conditions can cause this concern: |
| - | An open in the Requested Torque circuit. |
| - | An short to ground or voltage in the Requested Torque circuit. |
| - | A wiring problem, terminal corrosion, or poor connection in the Requested Torque circuit. |
| - | A communication frequency problem. |
| - | A communication duty cycle problem. |
| - | The EBCM/EBTCM is not receiving information from the PCM. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the ABS Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
2 | Inspect grounds G101 and ground G104. Ensure that each ground is clean, tight and free of damage. Were any loose, damaged or corroded grounds found? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 |
3 | Repair the grounds as needed. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
Is the duty cycle within the specified range? | 85-95% | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 6 | |
Using the J 39200 , measure the DC Hz between the J 39700 terminal 25 and terminal B. Is the frequency within the specified range? | 121-134 Hz | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 7 | |
6 |
Is the voltage within the specified range? | 4.5-5.5 V | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 8 |
7 | Replace the EBCM/EBTCM. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Is the voltage greater than the specified value? | 1.0 V | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 10 |
9 | Repair the short to voltage in CKT 463. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the circuit repair complete? | -- | -- | |
10 |
Is the resistance equal to the specified value? | OL (infinite) | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 11 |
11 | Repair the short to ground in CKT 463. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the circuit repair complete? | -- | -- | |
12 | Using the J 39200 DMM, measure the resistance between the J 39700 terminal 25 and the PCM connector C1 terminal 71. Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 2 ohms | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 14 |
13 | Suspect the PCM. Refer to Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check in Engine Controls - 3.8L. Is the diagnosis complete? | -- | -- | |
14 | Repair the open in CKT 463. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the circuit repair complete? | -- | -- |
