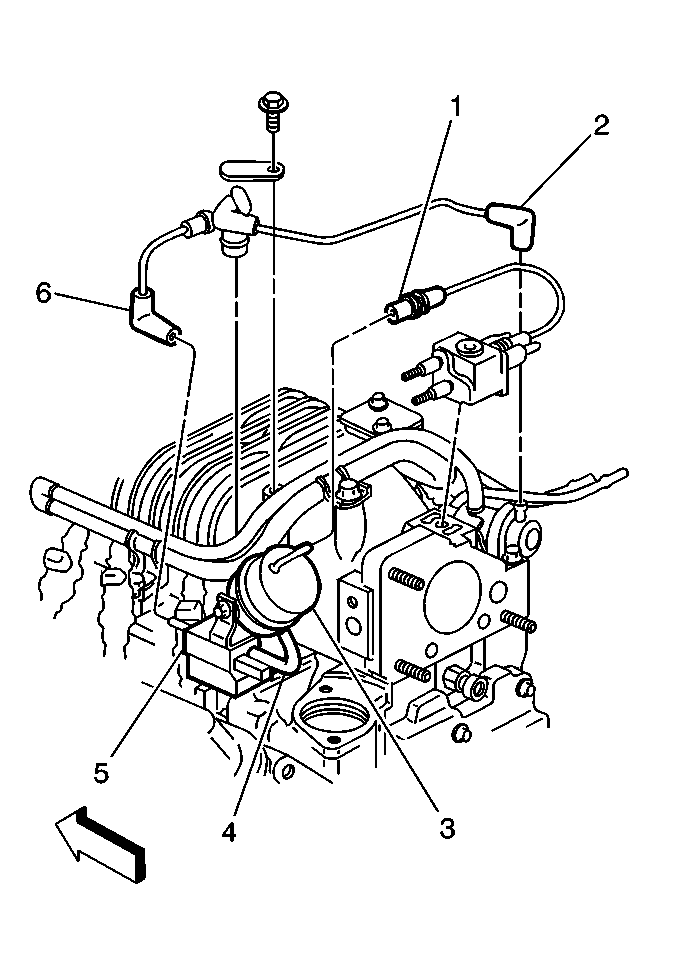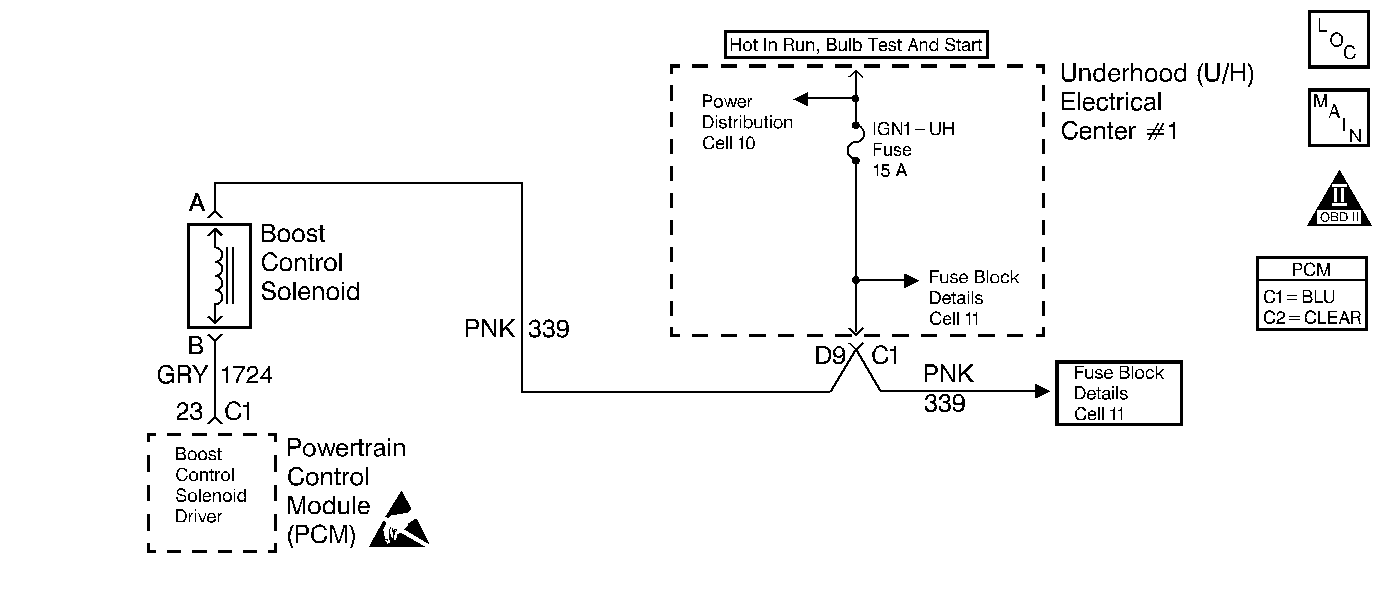
Circuit Description
Under most conditions, the PCM commands the boost control solenoid to operate at a 100% PWM to allow full intake boost pressure upon demand. However, if reverse gear is selected, the PCM detects rapid deceleration, or engine load is extremely high, reduced boost pressure is desired. Under these conditions, the PCM commands the boost control solenoid to operate at a 0% PWM, which opens the bypass valve to reduce boost pressure by recirculating it back through the supercharger inlet.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Intake air temperature greater than -10°C (14°F).
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | Engine torque exceeds a maximum torque threshold value. This value varies depending on commanded gear and engine rpm. |
| • | Above conditions for at least 20 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the MIL during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame and Fail Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has been run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool Clear Info function or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Boost Control Solenoid control circuit shorted to ground. |
| • | Binding Bypass Valve. Refer to Supercharger. |
| • | Sticking or misadjusted Bypass Valve Actuator. Refer to Supercharger. |
An intermittent may be caused by rubbed through wire insulation.
Intermittent test - Disconnect PCM and install a J 39200 Digital Multimeter to monitor voltage between the boost control solenoid control circuit at the PCM harness connector and ground. With the key ON, observe voltage while manipulating related connectors and wiring harness. If the failure is induced, the voltage display will change.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) in the diagnostic table.
-
Checks the Boost Control Solenoid control circuit. A short to ground in the Boost Control Solenoid control circuit will keep the bypass valve closed when the PCM is commanding it open, possibly causing an overboost condition during high engine load situations.
-
No inlet vacuum to the bypass valve actuator may cause the bypass valve to remain closed during deceleration. This condition may be perceived as a sail-on, possibly accompanied by a rough idle.
-
Checks for a sticking boost control solenoid.
-
This vehicle is equipped with a PCM which utilizes an Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM). When the PCM is being replaced, the new PCM must be programmed.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | |||||||
2 | Select DTC info, Last Tst Fail and record any other DTCs set. Are any other DTCs stored? | -- | Diagnose the other DTC first - Refer to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis | |||||
3 |
Is the test light ON? | -- | ||||||
Does the vacuum gauge indicate vacuum greater than the specified value? | 12 in. Hg | |||||||
Does the vacuum gauge indicate vacuum greater than the specified value with the Boost Control Solenoid commanded OFF? | 12 in. Hg | |||||||
6 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||
7 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||
8 | Replace the Bypass Valve actuator. Refer to Supercharger Bypass Valve Actuator . Is action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
9 |
Is the test light ON? | -- | ||||||
10 | Locate and repair short to ground in Boost Control Solenoid control circuit. Refer to Repair Procedures in Electrical Diagnosis. Is action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
11 | Repair restriction
in
inlet vacuum signal hose to the Bypass Valve Actuator or blocked inlet vacuum
source. Refer to
Is action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
12 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||
Replace the PCM. Important:: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Go to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||
14 | Replace the Boost Control Solenoid. Refer to Boost Control Solenoid . Is action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
15 |
Does the scan tool indicate DTC P1257 failed this ign? | -- | System OK |