IDLE STALL OR SLIGHT RPM OSCILLATION

MODELS AFFECTED: 1985-86 SKYHAWKS WITH LQ5 2.0L L-4 ENGINE (VIN CODE P) AND MANUAL TRANSMISSION
If customer comments of idle stall or slight idle RPM oscillation (+/- 200 RPM), after de-clutching or stopping the vehicle, cannot be resolved using the procedures found in Section 6E-2 of the Buick Chassis Service Manual, a new service PROM can be ordered from GMSPO using the part number from the chart below:
Year/Emission Trans./Axle Service PROM ------------- ----------- ------------ 1985/Federal 4-Spd./3.65 1228362 1985/California 4-Spd./3.65 1228364 1986/Federal 4-Spd./3.65 1228365 1986/California 4-Spd./3.65 1228367
Use applicable Labor Time and Labor Operation Number for PROM replacement.
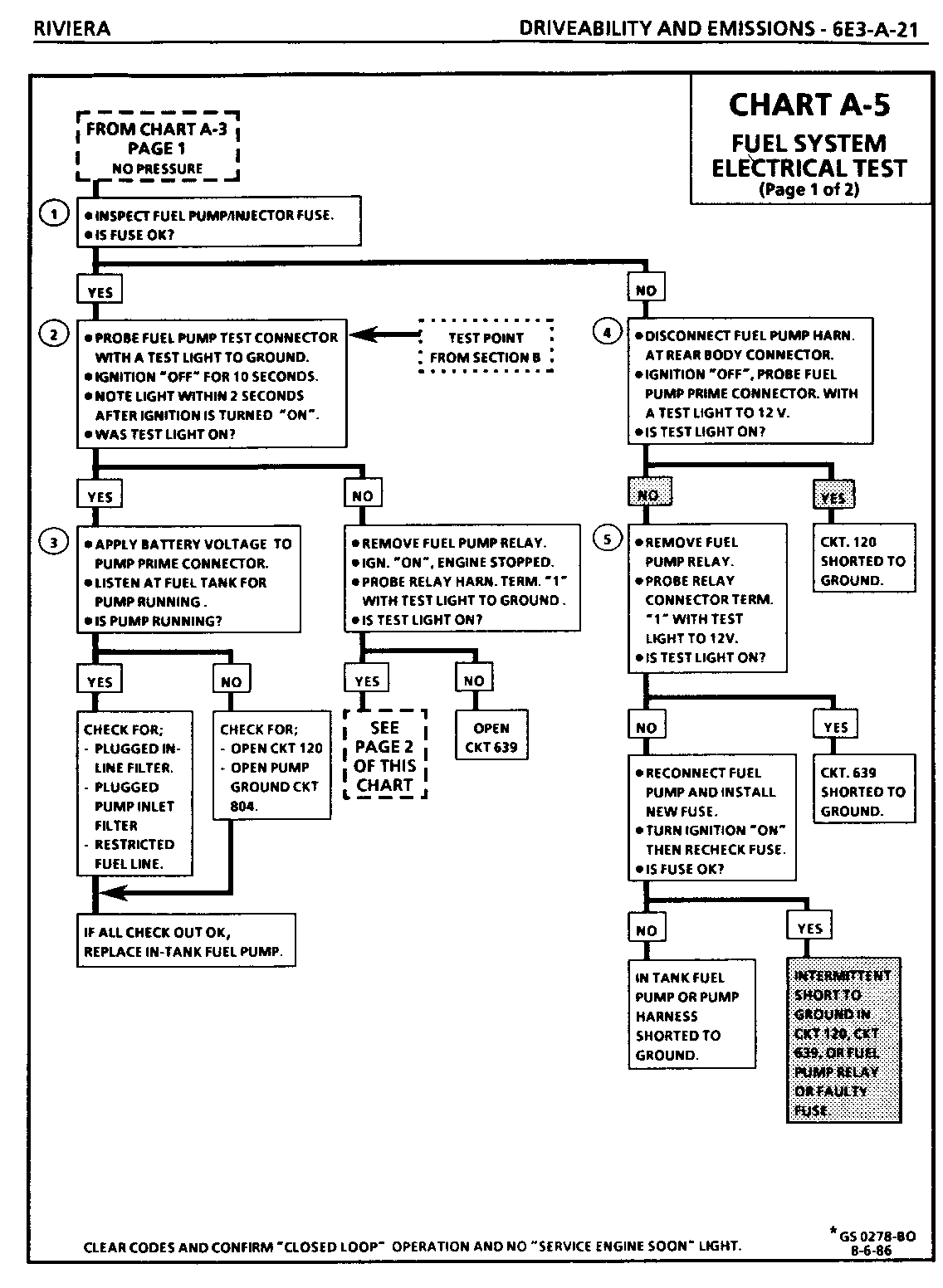
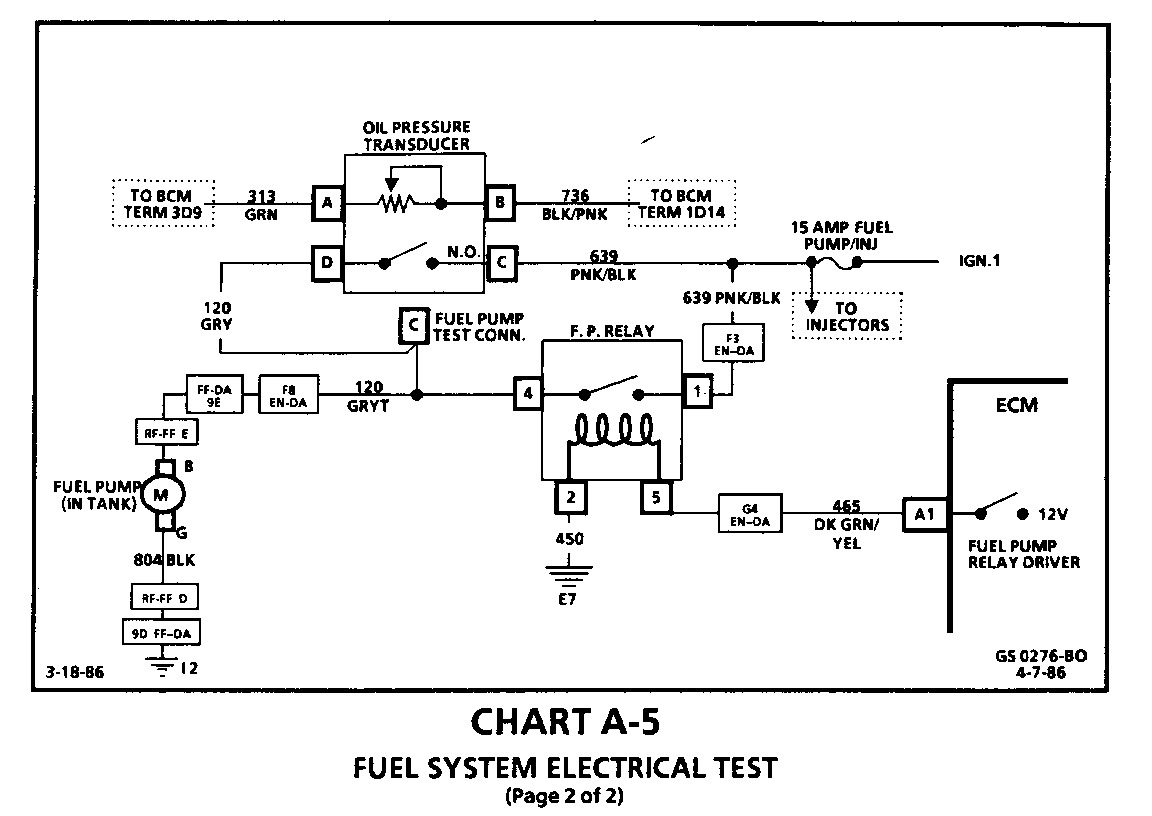
FUEL SYSTEM ELECTRICAL TEST
Circuit Description:
When the ignition switch is turned on, the Electronic Control Module (ECM) will energize the fuel pump relay which completes the circuit to the in-tank fuel pump. It will remain on as long as the engine is cranking or running, and the ECM is receiving "C3I" reference pulses. If there are no reference pulses, the ECM will de- energize the fuel pump relay within 2 seconds after key on, or the engine is stopped.
Test Description: The following numbered steps correspond with the step numbers on diagnostic chart.
6. Checks for open in relay ground, CKT 450 (Terminal "5").
7. Determines if the ECM is in control of the fuel pump relay through circuit 465 (Terminal "2").
8. The fuel pump control circuit includes an engine oil pressure switch with a separate set of normally open contacts. The switch closes at about (4 lbs) 28 kPa of oil pressure and provides a second battery feed path to the fuel pump. If the relay fails, the pump will continue to run using the battery feed supplied by the closed oil pressure switch. This step checks the oil pressure switch to be sure it provides battery feed to the fuel pump should the pump relay fail. A failed pump relay will result in extended engine crank time, because of the time required to build enough oil pressure to close the oil pressure switch and turn on the fuel pump. There may be instances when the relay has failed but the engine will not crank fast enough to build enough oil pressure to close the switch. This or a faulty oil pressure switch can result in "Engine Cranks But Will Not Run".
9. If the fuel pump relay control coil resistance is less than 20 ohms (shorted), repeat ECM failures may result.
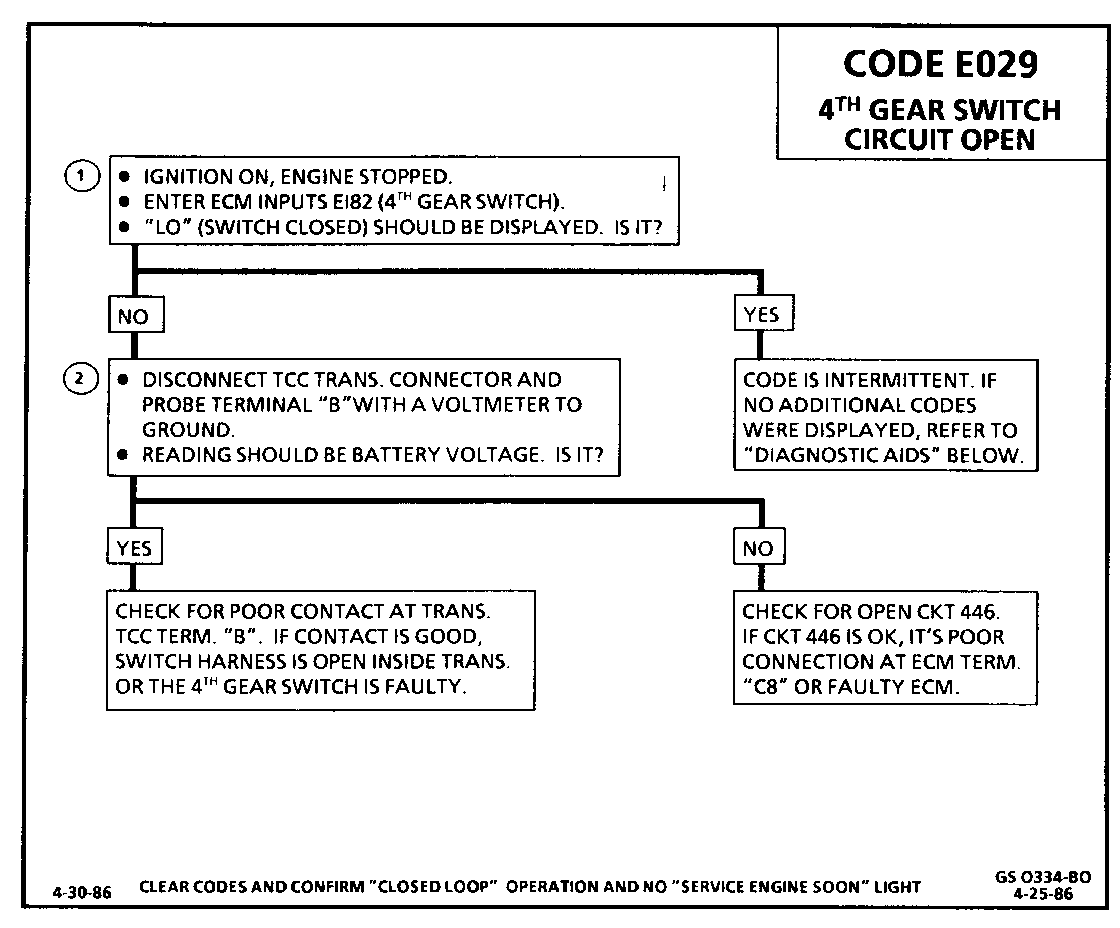
Diagnostic Aids:
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the insutation.
Check For:
o Poor Connection or Damaged Harness: Inspect ECM harness connectors for backed out terminal "C8", improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, poor terminal to wire connection and damaged harness.
o Intermittent Test: If connections and harness checks out ok, monitor E128 (4th Gear Switch) display while moving related connectors and wiring harness. If the failure is induced, the "4th Gear Switch" display will abruptly change. This will help to isolate the location of the malfunction.
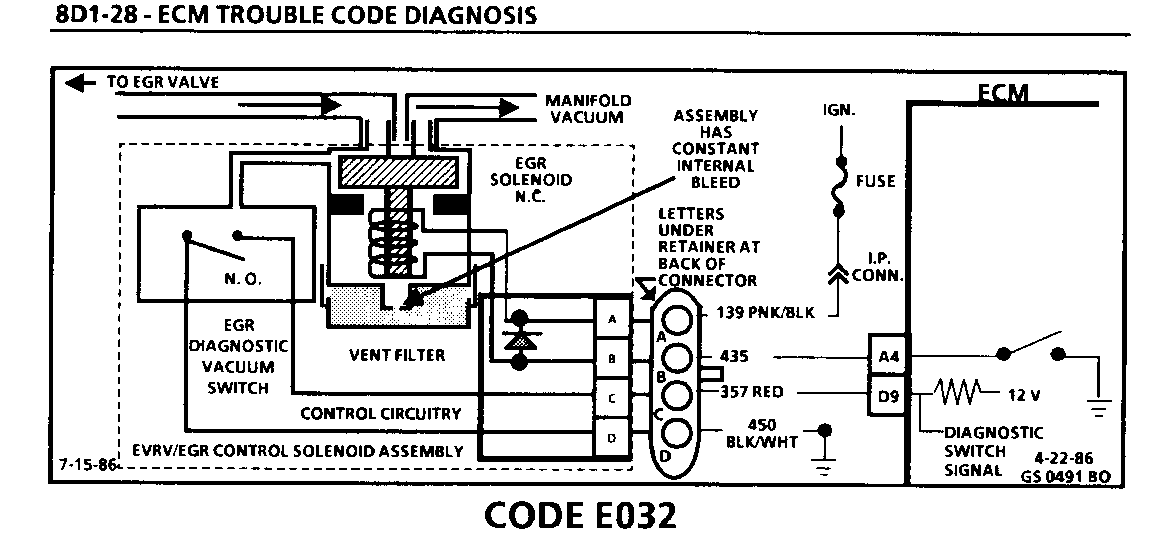
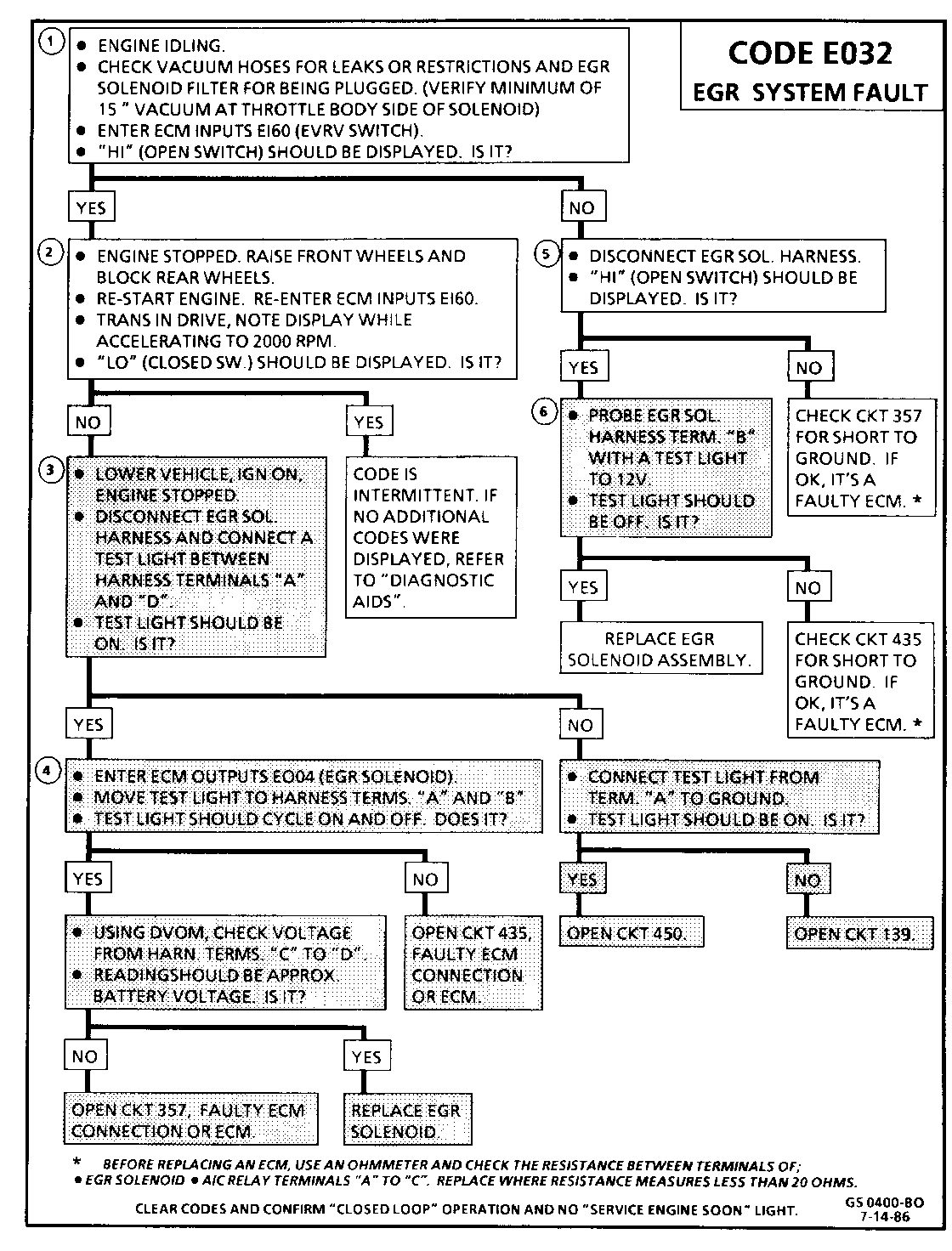
CODE E032 EGR SYSTEM FAULT
Circuit Description:
The EGR Vacuum Control is operated by an Electronic Vacuum Regulator Valve (EVRV). The EVRV is comprised of an EGR Vacuum Control Solenoid and a EGR Diagnostic Vacuum Switch.
The EGR Solenoid is Pulse Width Modulated by the ECM and controls the vacuum to the EGR valve. The Solenoid is vented and is equipped with a filter.
The normally open EGR Diagnostic Vacuum Switch monitors the vacuum to the EGR Valve and signals the ECM when control vacuum is applied to the valve (switch closes). The ECM will not energize the solenoid in "Park", "Neutral", or at idle.
The ECM cycles the EGR valve "ON" and "OFF" (Pulse Width Modulation). For this reason, the EGR valve is never continuously open but always "pulsed" which may be monitored by observing the ECM input E160 (EVRV Switch) during normal EGR operation. "HI" indicates the EGR is off and "LO" indicates it is on.
Code E032 will set if the vacuum switch closes at idle, or if it does not close under load (less than WOT).
o Engine running. o LV8 reading less than 144 cts.
o Code E033 or E034 not present o Conditions exist over 9.6 seconds.
o Coolant temperature above 42.5 DEG Celsius (108 DEG Fahrenheit).
Test Description: The following numbered steps correspond with the step numbers on diagnostic eharts.
1. E160 displays the condition of the EGR diagnostic switch. In park or neutral, the display should read "HI" (open switch).
2. Under moderate engine load, the display will switch ftom "HI" to "LO".
3. *Checks the integrity of the 12V feed and ground circuits. If these circuits check OK, the fault is elsewhere in the EVRV/EGR Control circuit.
4. *A test light connected "A" to "B" will verify the integrity of the ECM wiring and check for proper ECM operation.
5. If "LO" was displayed at idle, disconnect the EVRV harness. If display remains "LO", the fault is either a short to ground in CKT 357 or the ECM.
6. If the E160 display switches from "LO" to "HI" when the EVRV is disconnected, the fault is either in the EVRV/EGR Solenoid, CKT 435 or the ECM. Probing at terminal "B" will further isolate the fault. If the test light is on, disconnect ECM A-B connector before cheeking CKT 435 for a short to ground since the short could be inside the ECM.
Diagnostic Aids: An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the insulation.
Check For:
o Poor Connection or Damaged Harness: Inspect ECM harness connectors for backed out terminal "D9", improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, poor terminal to wire connection and damaged harness.
o Intermittent Test: If connections and harness checks out ok, monitor E160 (EVRV Switch) display while moving related connectors and wiring harness. If the failure is induced, the "EVRV Switch" display will abruptly change. This will help to isolate the location of the malfunction.
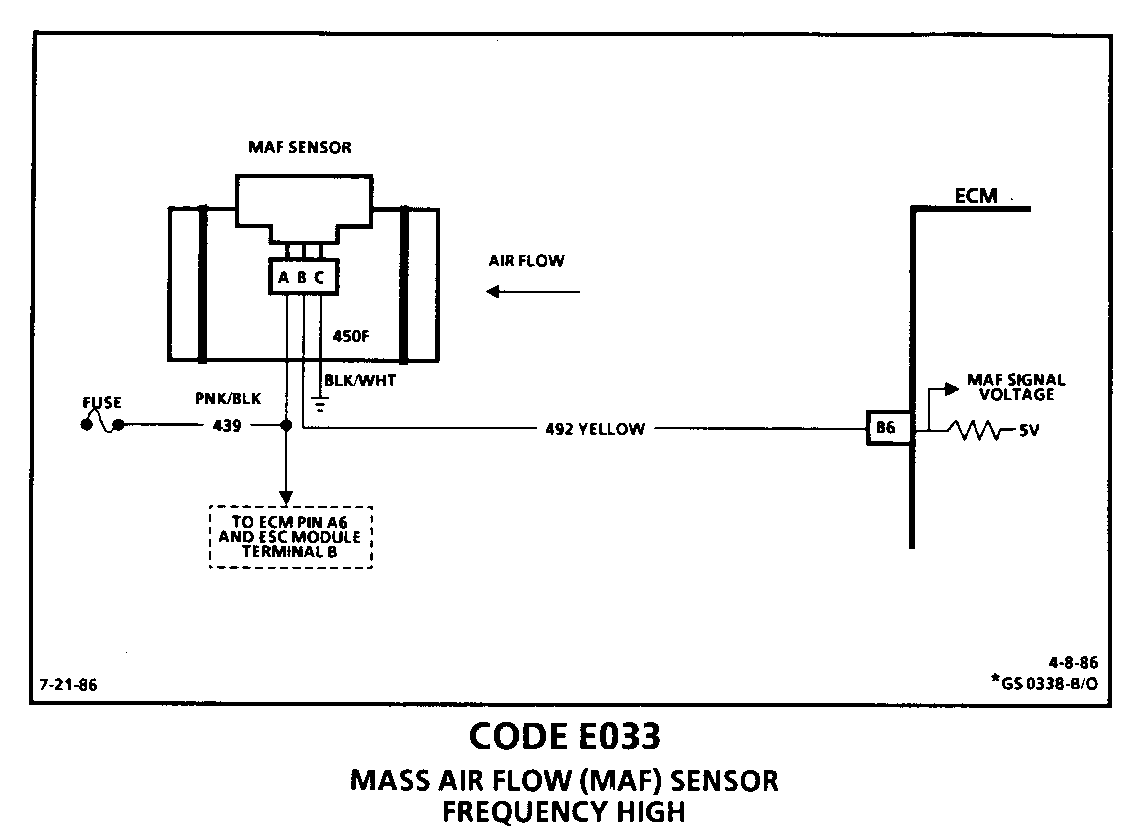
CODE E033 MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR FREQUENCY HIGH Circuit Description: -------------------- The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor measures the amount of air which passes through it in a given time. The ECM uses this information to monitor the operating condition of the engine, in calculating fuel delivery. A large quantity of air movement indicates acceleration, while a small quantity indicates deceleration or idle. diagnosed using the procedures on this chart and with the aid of MAF sensor tester J-36101 or equivalent.
The MAF sensor produces a frequency signal which cannot be easily measured. The sensor can be diagnosed using the procedures on this chart and with the aid of MAF sensor tester J-36101 or equivalent.
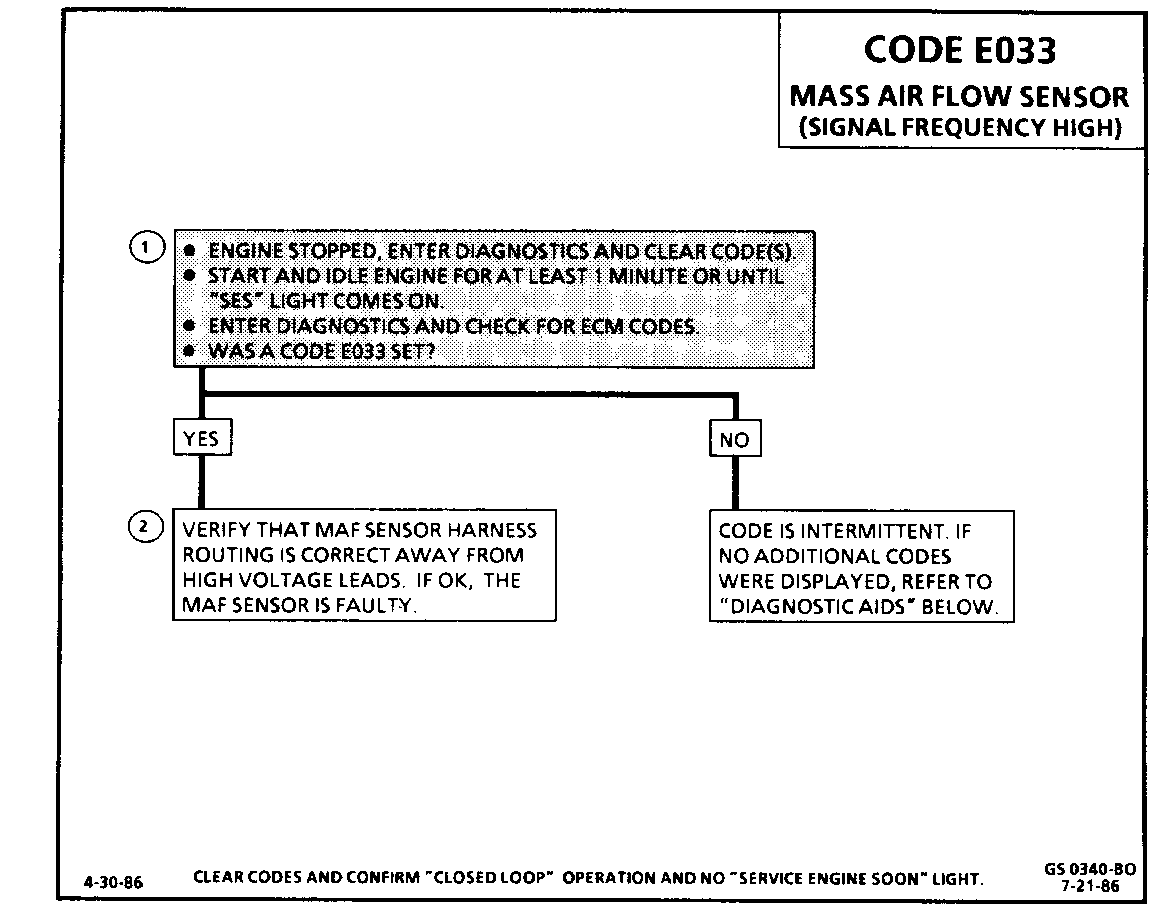
Code E033 will set when the following conditions are met:
o E021 or E022 not present
o Engine is running at less than 800 RPM
o TPS is less than 500mv
o Air Flow more than 150 grams per second
o All of the above are met for 5 seconds or more
Test Description: The following numbered steps correspond with the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. The Diagnostic Display, ED21 (MAF), is of little use in diagnosing this fault, because when the code is set, a default based on TPS is desplayed in place of the actual MAF input to the ECM. If the Mass Air Flow Sensor fault is still present, Code E033 should reset within one minute. If the code does not reset, the fault was intermittent and MAF Sensor tester J-36101 or equivalent should be used to test the sensor.
2. Inspect wire routing of high voltage wires, such as spark plug wires. Such wires routed too closely to MAF wiring harness could possibly cause an intermittent Code E033.
Diagnostic Aids:
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the insulation.
Check For:
o Poor Connection or Damaged Harness: Inspect ECM harness connectors for backed out terminal "B6", improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, poor terminal to wire connection and damaged harness.
o Intermittent Test: If connections and harness checks out ok, monitor ED21 (MAF) display while moving related connectors and wiring harness. If the failure is induced, the "MAF" display will abruptly change. This will help to isolate the location of the malfunction.
o Miss-routed Harness: Inspect MAF sensor harness to insure that it is not too close to high voltage wires, such as spark plug leads.
o Miscalibrated MAF Sensor: The Mass Air Flow Sensor may be tested for being out of specification by using a MAF Sensor test tool J-36101 or equivalent.
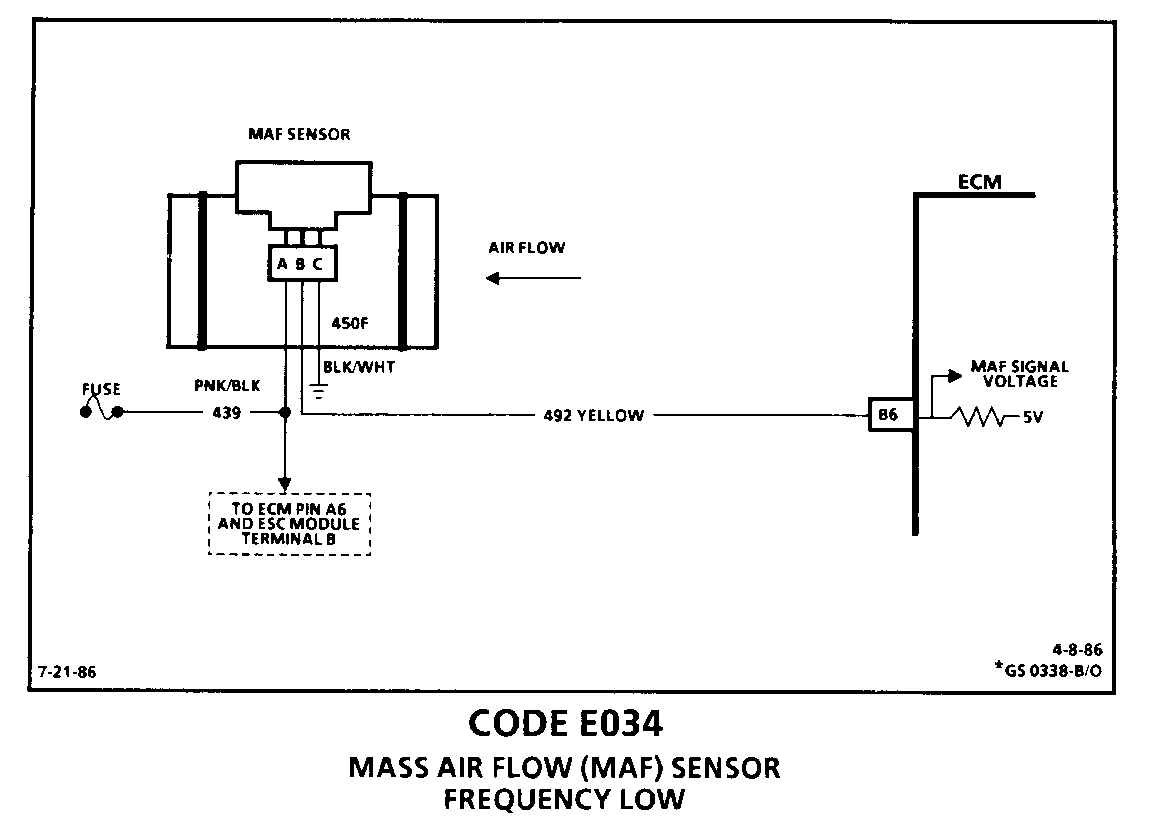
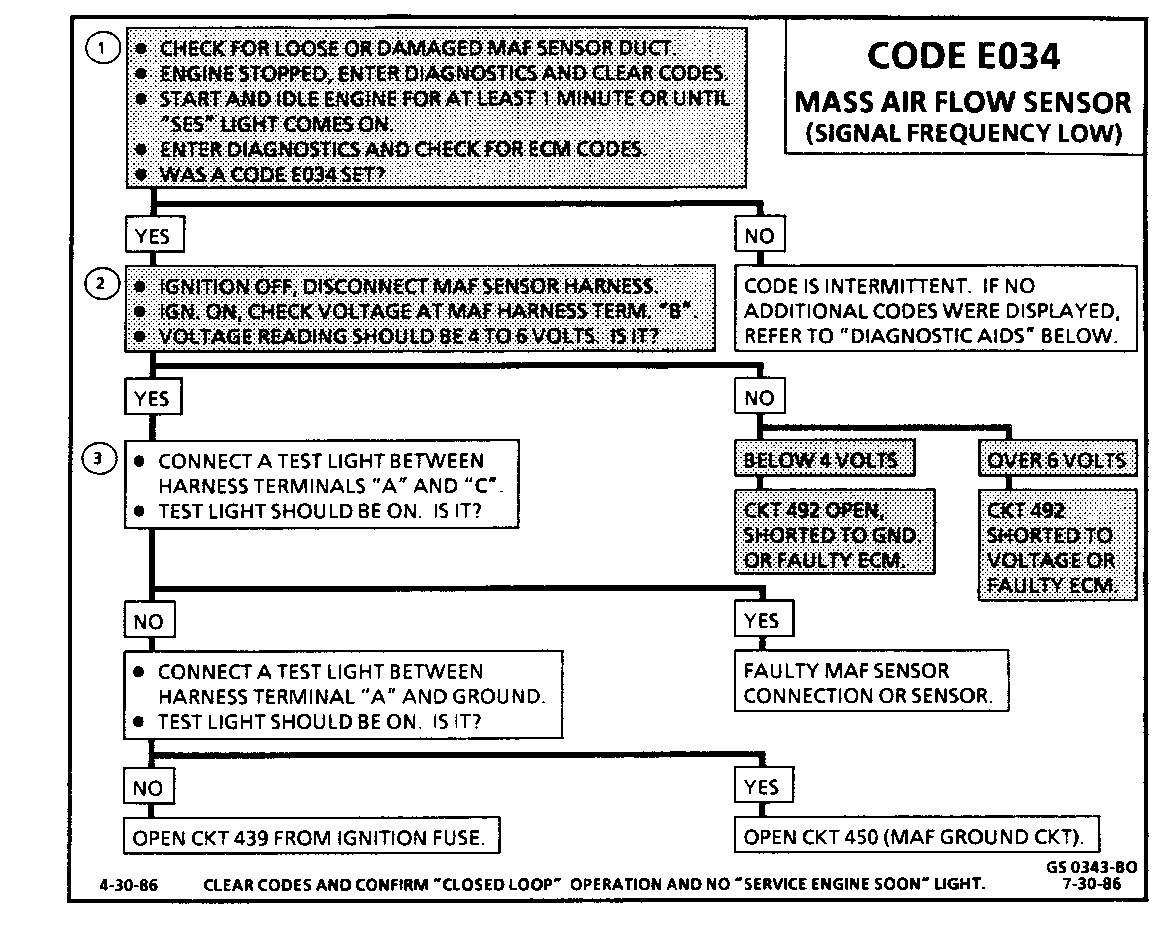
CODE E034 MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR FREQUENCY LOW
Circuit Description:
The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor measures the amount of air which passes through it in a given time. The ECM uses this information to monitor the operating condition of the engine, in calculating fuel delivery. A large quantity of air movement indicates acceleration, while a small quantity indicates deceleration or idle.
The MAF sensor produces a frequency signal which cannot be easily measured. The sensor can be diagnosed using the procedures on this chart and with the aid of MAF sensor tester J-36101 or equivalent.
Code E034 will set when either of the following sets of conditions exists:
o Engine running
o No MAF sensor signal for 250 m sec.
OR
Engine running over 1400 rpm
o TPS over 2.5 volts
o Air Flow less than 10 grams per second (low frequency)
o Above conditions for over 10 sec.
Test Description: The following numbered steps correspond with the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. The Diagnostic Display, ED21 (MAF), is of little use in diagnosing this fault, because when the code is set, a default based on TPS is displayed in place of the actual MAF input to the ECM. A loose or damaged air duct may see a Code E034 and must be checked. If the Mass Air Flow Sensor fault is still present, Code E04 should reset within one minute. If the code does not reset, the fault was intermittent and MAF Sensor tester J- 36101 or equivalent should be used to test the sensor.
2. This step verifies that the reference signal from the ECM is present at MAF sensor harness connector terminal "B". Less than 4 or over 6 volts at this point indicates a faulty CKT 492, connection, or ECM.
3. Verifies that both ignition voltage and a good ground circuit are available.
Diagnostic Aids:
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the insulation.
Check For:
o Poor Connection or Damaged Harness: Inspect ECM harness connectors for backed out terminal "B6", improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, poor terminal to wire connection and damaged harness.
o Intermittent Test: If connections and harness checks out ok, monitor ED21 (MAF) display while moving retated connectors and wiring harness. If the failure is induced, the "MAF" display will abruptly change. This will help to isolate the location of the malfunction.
o Miss-routed Harness: Inspect MAF sensor harness to insure that it is not too close to high voltage wires, such as spark plug leads.
o Miscalibrated MAF Sensor: The Mass Air Flow Sensor may be tested for being out of specification by using a MAF Sensor test tool J-36101 or equivalent.
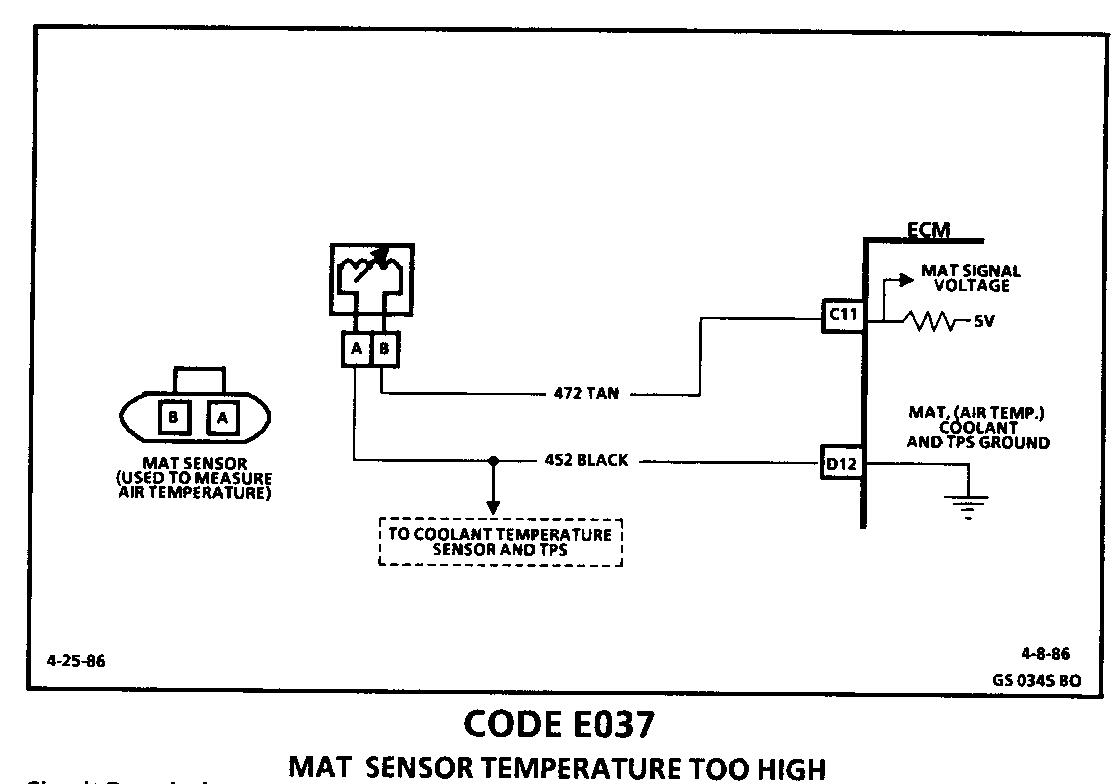
CODE E037 MAT SENSOR TEMPERATURE TOO HIGH
Circuit Description:
The manifold Air Temperature Sensor (MAT) is a thermistor (a resistor which decreases in resistance as temperature increases) mounted in the air cleaner assembly. Low temperature produces a high resistance (100,000 ohms at -40 DEG Celsius/-40 DEG Fahrenheit) while high temperature causes low resistance (70 ohms at 130 DEG Celsius/266 DEG Fahrenheit).
The ECM supplies a 5-volt signal to the sensor through a resistor in the ECM and monitors this voltage. the voltage will be high when the manifold air is cold, and low when the air is hot. By monitoring the voltage, the ECM knows the manifold air temperature.
Code E037 will set if a signal voltage indicates a manifold air temperature less than about 135 DEG C (275 DEG F) and the vehicle speed is greater than 40 MPH for over 16 seconds.
Possible causes of a Code E037 are:
o Faulty wiring or terminals o CKT 472 shorted to ground o A shorted MAT sensor o A faulty ECM
Manifold air temperature is one of the inputs used to calculate: o Fuel delivery o Spark Timing (EST) o Knock Control (ESC) o Idle (IAC)
Test Description: The following numbered steps correspond with the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. With engine warmed up, MAT should be displayed somewhere between -30 DEG Celsius and 130 DEG Celsius. If not, a MAT circuit fault indicated.
2. With the MAT sensor disconnected, ECM Data ED05 should display a "MAT" reading of below 30 DEG Celsius. A display below -30 DEG Celsius indicates fault is in the MAT sensor itself. If the "'MAT" display is warmer than -30 Celsius, there is a short to ground in the wiring harness or the ECM.
Diagnostic Aids:
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the insulation.
Check For:
o Poor Connection or Damaged Harness: Inspect ECM harness connectors for backed out terminal "A11", improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, poor terminal to wire connection and damaged harness.
o Intermittent Test: If connections and harness checks out ok, monitor A Digital Voltmeter connected from ECM terminal "A11" to ground while moving related connectors and wiring harness. If the failure is induced, the voltage reading will abruptly change. This will help to isolate the location of the malfunction.
o Symptom Indicators
- If Cam Signal from Cam Sensor to C31 module is lost while running, engine will not restart after shutdown.
- If Cam Signal output from the module or wiring etc., to the ECM has failed, engine will restart after shutdown.
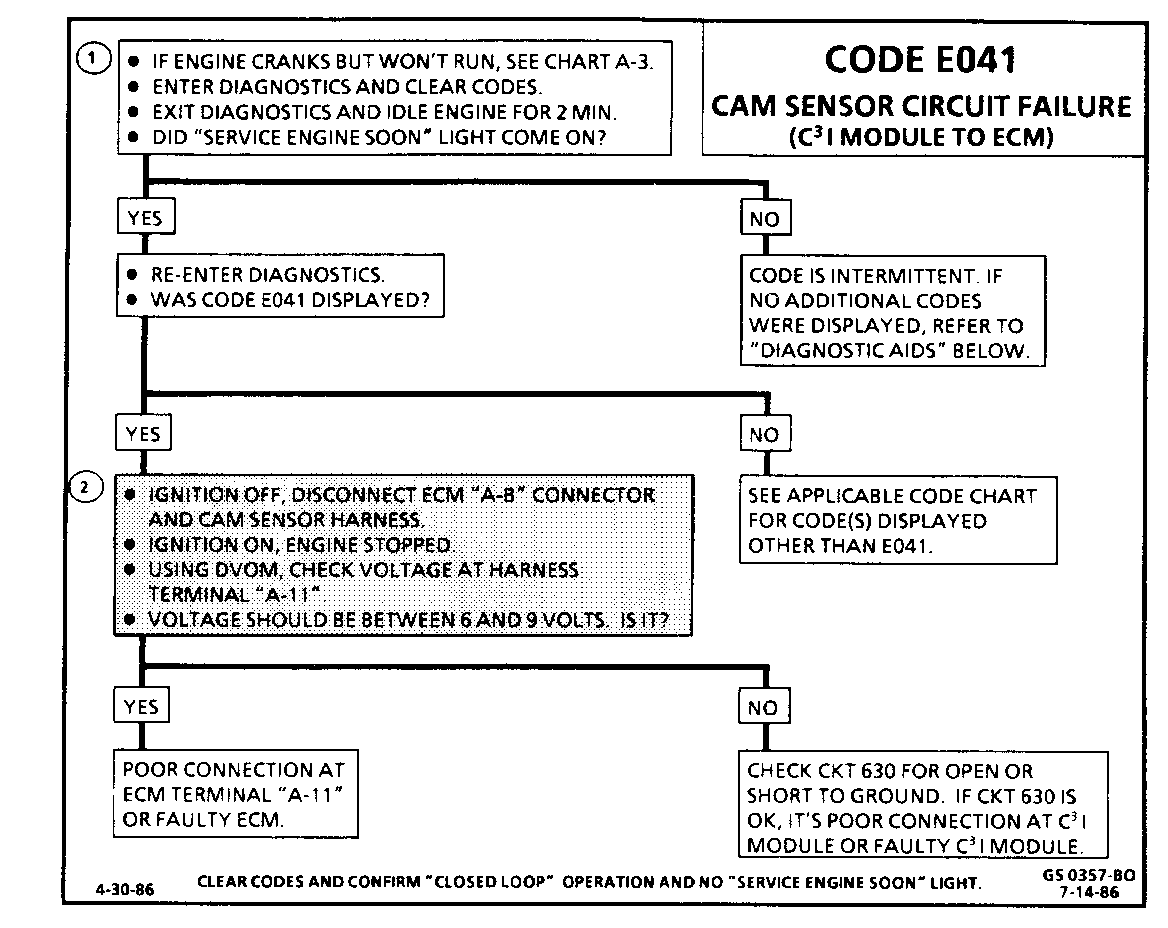
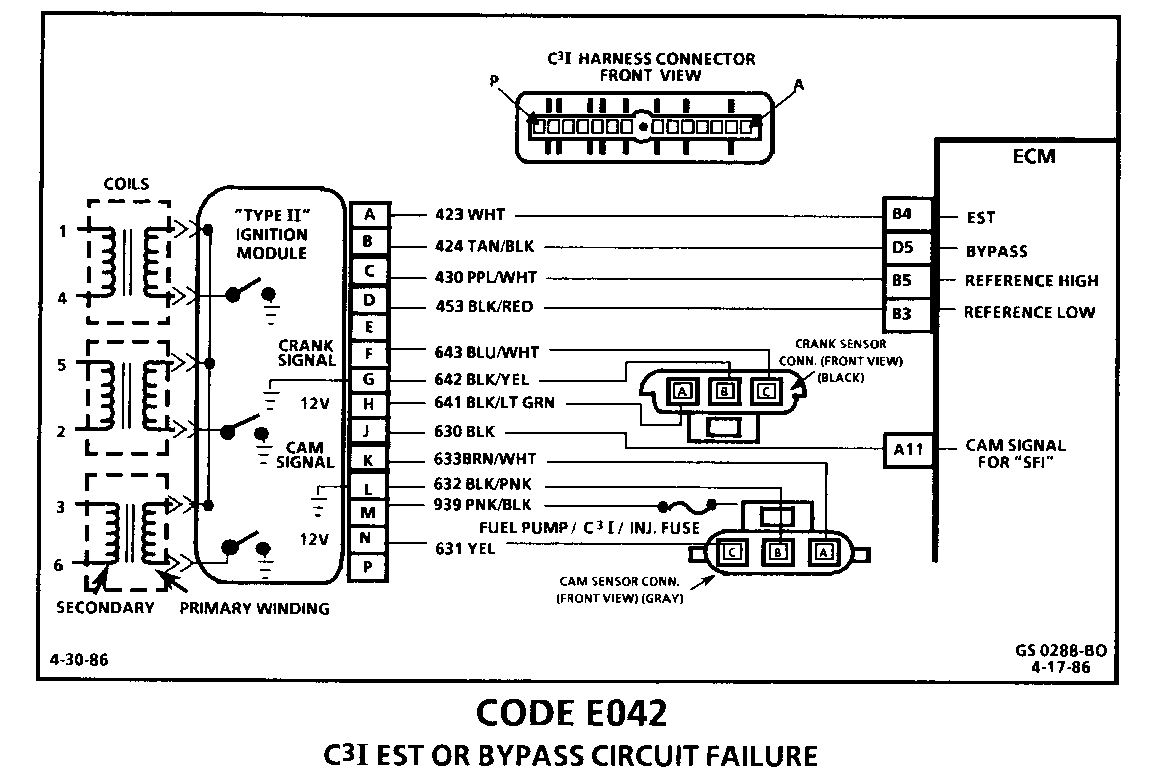
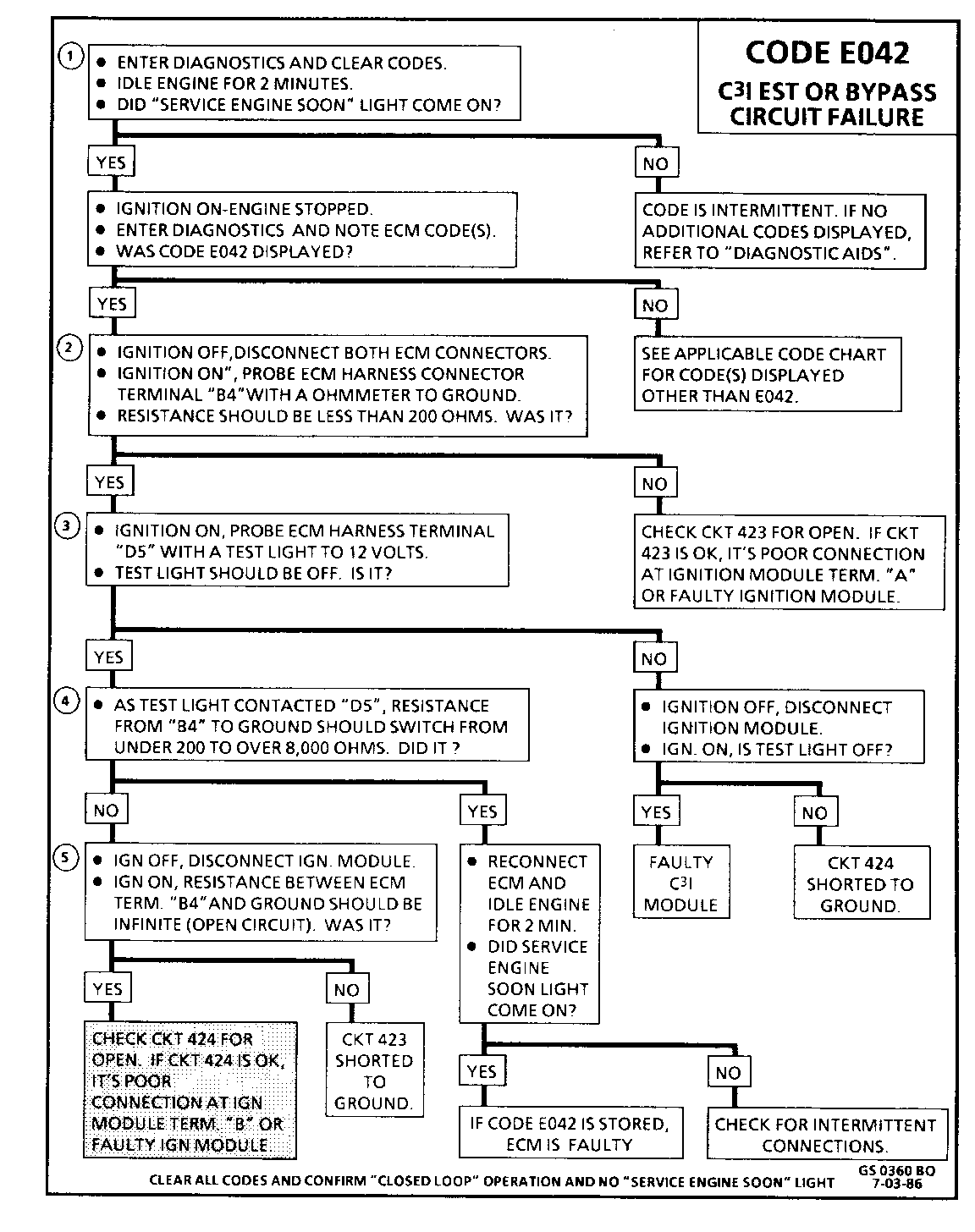
CODE E042 C3I EST OR BYPASS CIRCUIT FAILURE
Circuit Description: The C31 module sends a reference signal to the ECM, when the engine is cranking. While the engine is under 400 RPM, the C31 module controls the ignition timing. When the engine speed exceeds 400 RPM, the ECM sends a 5 volt signal on the By-pass circuit (424) to switch the timing to ECM control, through the EST circuit (423). An open or ground in the EST circuit will stall the engine and set a Code E042. The engine can be re-started but will run on module timing.
To set a Code E042 the following conditions must be met:
o Engine speed greater than 600 RPM. with no EST pulse for 2OO msec. (Open or Grounded circuit423) or,
o ECM commanding By-pass mode. (Open or Grounded circuit424)
Test Description: The following numbered steps correspond with the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. Checks to see if ECM recognizes a problem. If it doesn't set Code E042, at this point, it is an intermittent problem and could be due to a loose connection.
2. With the ECM disconnected, the ohmmeter should be reading less than 200 ohms, which is the normal resistance of the EST circuit through the C31 module. A higher resistance would indicate a fault in CKT 423, a poor C31 module connection, or a faulty C3I module.
3. If test light was on, when connected from 12 volts to ECM harness terminal "D5", either CKT 423 is shorted to ground, or the C31 module is faulty.
4. Checks to see if C31 module switches, when the bypass circuit is energized by 12 volts, through the test light. if the C31 module actually switches, the ohmmeter reading should shift to over 8,000 ohms.
5. Disconnecting the ignition module should make the ohmmeter read as if it were monitoring an open circuit (infinite reading). Otherwise, CKT 423 is shorted to ground.
Diagnostic Aids: An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the insulation.
Check For:
o Poor Connection or Damaged Harness: Inspect ECM harness connectors for backed out terminals "B4" or "D5", improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, poor terminal to wire connection and damaged harness.
o Intermittent Test: If connections and harness checks out ok, a Digital Voltmeter connected from affected terminal to ground while moving related connectors and wiring harness. If the failure is induced, the voltage reading will abruptly change.
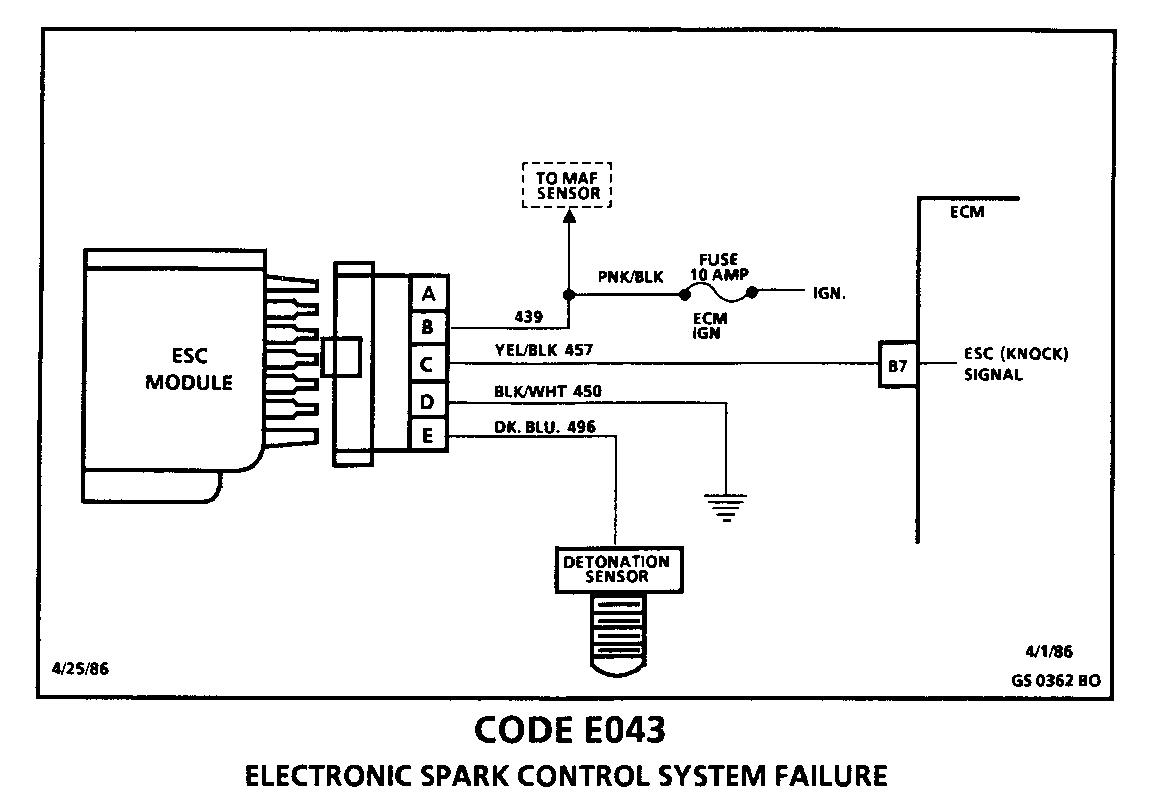
CODE E043 ELECTRONIC SPARK CONTROL SYSTEM FAILURE
Circuit Description:
The ESC system is comprised of a detonation sensor and an ESC module.
As long as the ESC module is sending a voltage signal (8 to 10 volts) to the ECM (no detonation detected by the ESC sensor) the calculated spark advance (EST) remains unaffected by the ESC input.
When the sensor detects detonation, the module turns "OFF" the circuit to the ECM and the voltage at ECM terminal"B7" drops to 0 volts. The ECM then retards EST as much as 20 in one (1) degree increments, to reduce detonation. This happens fast and frequently enough that if looking at this signal with a DVM, you won't see 0 volts, but an average voltage somewhat less than what is normal with no detonation.
A loss of the Detonation sensor signal or a loss of ground at ESC module would cause the signal at the ECM to remain high. This condition would result in the ECM controlling EST as if no detonation were occuring. The EST would not be retarded, and detonation could become severe enough under heavy engine load conditions to result in pre-ignition and potential engine damage.
Loss of the ESC signal to the ECM would cause the ECM to constantly retard the EST to its max retard of 20 from the spark table. This could result in sluggish performance and cause a Code EO43 to set.
Code E043 will set when:
o Engine Running. o ESC input signal has been low more than 2.2 seconds.
Test Description: The following numbered steps correspond with the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. If the ECM Data ED17 (Knock Signal) display is fluctuating widely, the ECM is monitoring a low voltage signal on circuit (457) at ECM terminal "B792.
2. Probing ESC harness terminal "C" with a test light connected to 12 volts should result in the "OLD PA3" (knock signal) display holding a steady reading due to over 8 volts having been applied to ECM terminal "B7" through CKT 457.
3. If over 6 volts is measured at ECM terminal "B7", CKT 457 is OK and the fault is due to a poor connection at the ECM or the ECM is faulty.
General Motors bulletins are intended for use by professional technicians, not a "do-it-yourselfer". They are written to inform those technicians of conditions that may occur on some vehicles, or to provide information that could assist in the proper service of a vehicle. Properly trained technicians have the equipment, tools, safety instructions and know-how to do a job properly and safely. If a condition is described, do not assume that the bulletin applies to your vehicle, or that your vehicle will have that condition. See a General Motors dealer servicing your brand of General Motors vehicle for information on whether your vehicle may benefit from the information.
