Circuit Description
In order to control emissions, a catalytic converter converts any harmful exhaust emissions into harmless water vapor and carbon dioxide.
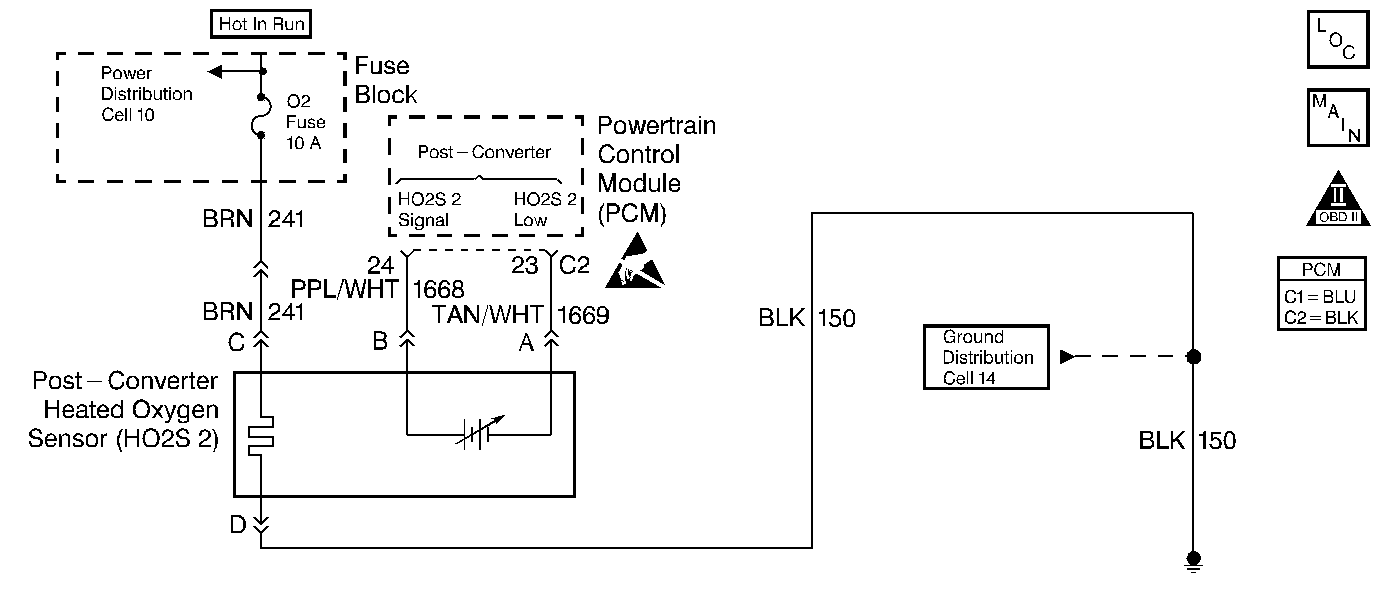
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) has the capability to monitor this process by using a rear heated oxygen sensor (HO2S 2). The HO2S 2 , located in the exhaust stream past the catalytic converter, produces an output signal which indicates the storage capacity of the catalyst. This in turn indicates the catalyst's ability to convert the exhaust emissions effectively. If the catalyst is functioning properly, the HO2S 2 signal will be far less active than the signal produced by the front oxygen sensor (O2S 1).
Replace the entire HO2S 2 assembly. Do not attempt to repair the HO2S 2 if the following conditions exist:
| • | Damaged wiring |
| • | Damaged electrical connectors |
| • | Damaged terminals |
Obstruction of the air reference and degraded HO2S 2 performance could result from any attempt to repair the above conditions.
The HO2S 2 must have a clean air reference in order for the HO2S 2 to function properly. This clean air reference is obtained by way of the HO2S 2 wires.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is less than 45°C (113°F). |
| • | The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) is less than 45°C (113°F). |
| • | The difference between the ECT and the IAT is less than 7°C (45°F). |
| • | The Throttle Position (TP) is less than 20 percent. |
| • | The HO2S 2 voltage increases, decreases, or is less than 150 mV in 100 to 190 seconds (based on start up coolant temperature). |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will illuminate after two consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the malfunction present. |
| • | The PCM will record the operating conditions at the time that the diagnostic fails. This information will store in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers. |
| • | A history DTC stores. |
| • | The coolant fan turns ON. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | The MIL/DTCs can be cleared by using the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent could be the result of the following conditions:
| • | A poor electrical connection |
| • | Moisture in the connector/wiring |
| • | Rubbed-through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Check for a poor electrical connection or a damaged harness. Inspect the harness electrical connectors for the following conditions:
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly-formed electrical connectors |
| • | Damaged terminals |
| • | A poor terminal-to-wire connection |
| • | A damaged harness |
Replace the entire HO2S 2 assembly. Do not attempt to repair the HO2S 2 if the following conditions exist:
| • | Damaged wiring |
| • | Damaged electrical connectors |
| • | Damaged terminals |
Obstruction of the air reference and degraded HO2S 2 performance could result from any attempt to repair the above conditions.
The HO2S 2 must have a clean air reference in order for the HO2S 2 to function properly. This clean air reference is obtained by way of the HO2S 2 wires.
Test Description
An example test description follows:
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored on the scan tool for later reference.
-
This step determines if DTC P0141 is the result of a hard malfunction or an intermittent condition. With the ignition switch ON, engine OFF, the HO2S 2 voltage displayed on the scan tool should change within several minutes towards 0 or 1 volt, indicating that the heater is working properly.
-
Probing terminal D of the HO2S 2 electrical connector verifies if voltage is available to the HO2S 2 heater.
-
If voltage is available at the electrical connector, then it becomes a good voltage source to check for a ground at terminal C.
-
Determines if voltage is not available at the HO2S 2 due to an open O2 fuse or open ignition feed circuit. If the fuse is open, determine if it was due to a short in the ignition feed circuit before replacing the fuse.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | |||
Important: If the engine has just been operating, allow the engine to cool for about one half hour before proceeding. Does the HO2S 2 voltage gradually change towards the specified voltage? | 0V or 1V | |||
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | |||
Connect a test light between the ignition feed and ground circuits (PCM side) of the electrical connector. Does the test light illuminate? | -- | |||
Inspect the fuse in the fuse block. Is the fuse open? | -- | |||
6 | Check the electrical connections at the HO2S 2 electrical connector and repair as necessary. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
7 | Check the electrical connections at the HO2S 2 electrical connector and repair as necessary. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
8 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
9 | Check the electrical connections at the HO2S 2 connector and repair as necessary. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
10 | Replace the HO2S 2 sensor. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
11 | Repair the open in the ground circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
12 | Repair the open in the ignition feed circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
13 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has and passed? | -- | ||
14 | Check if any additional DTCs are set. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to applicable DTC table | System OK |
