Removing the Flat Tire and Installing the Spare Tire CTS Only
- Do a safety check before proceeding. See Changing a Flat Tire for more information.
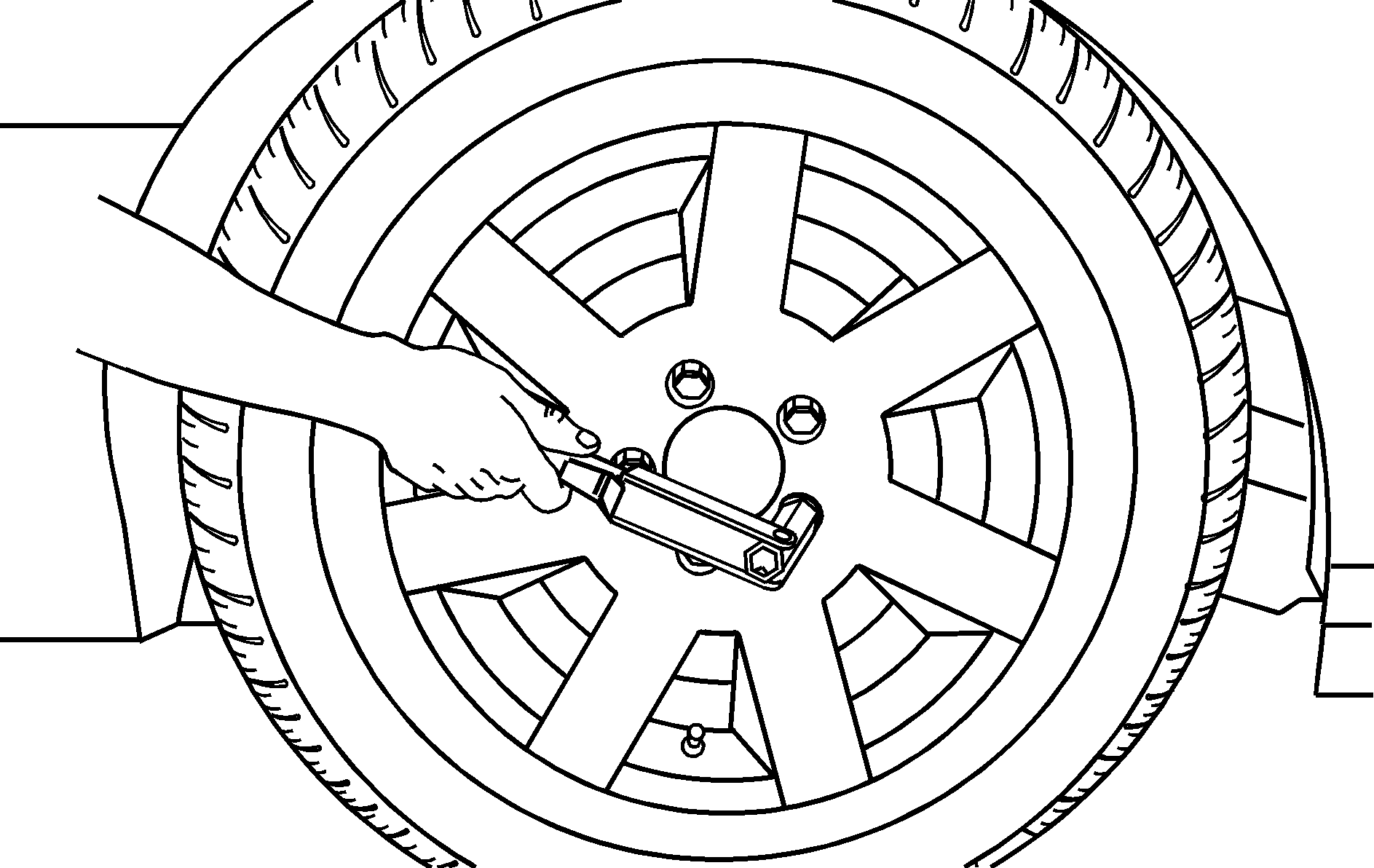
- Loosen the wheel nuts, but do not remove them yet, using the wheel wrench. Turn the handle about 180 degrees, then return the handle back to the starting position. This avoids taking the wrench off the lug nut for each turn.
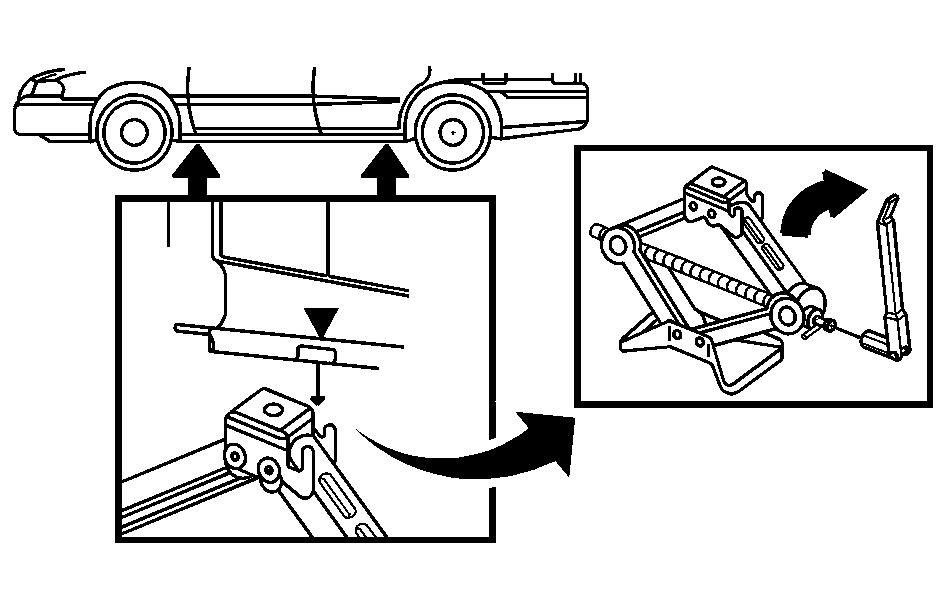
- Find the jacking location using the diagram above and corresponding triangular-shaped hoisting notches located in the plastic molding.
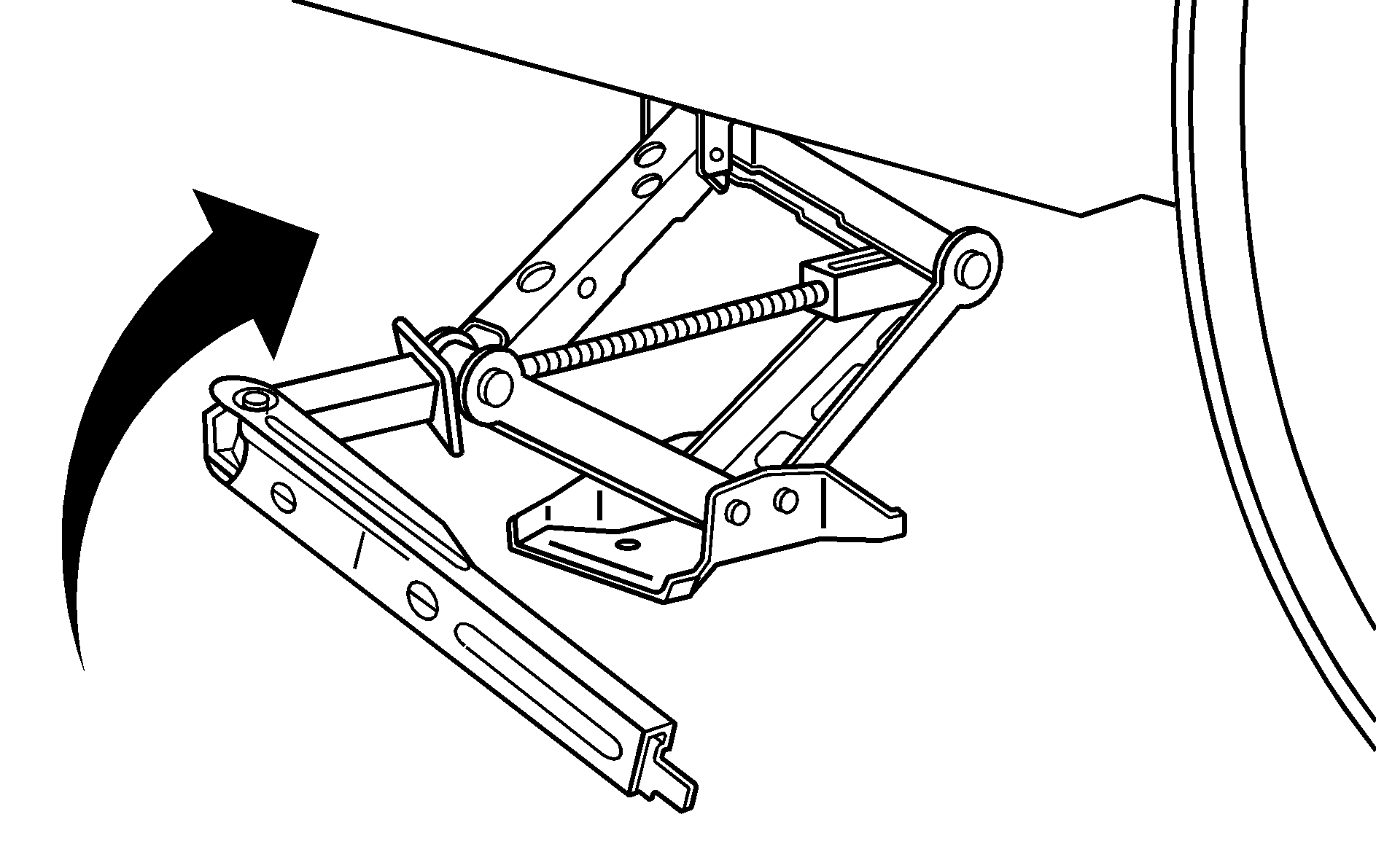
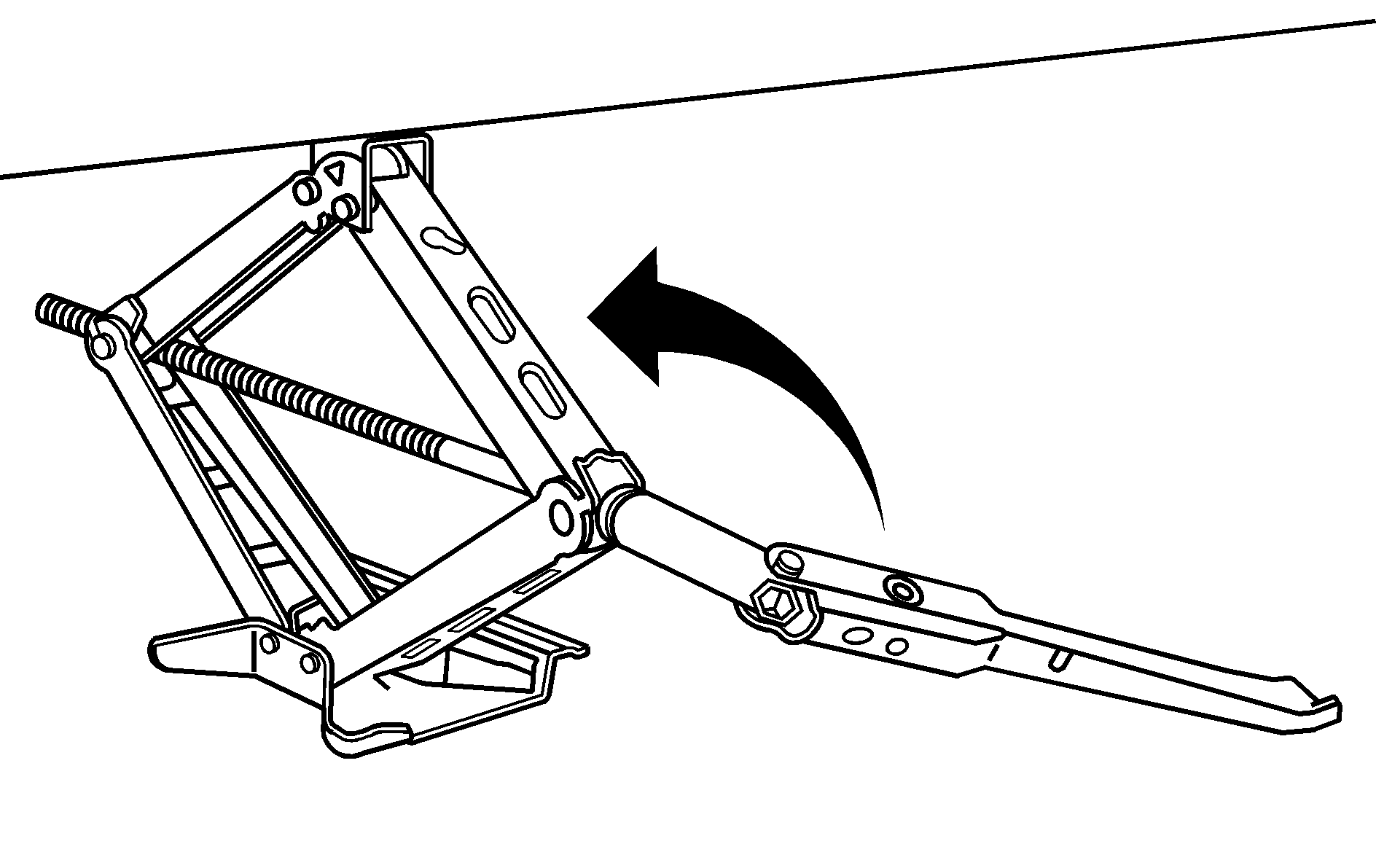
- Attach the wheel wrench to the jack.
- Turn the wheel wrench counterclockwise to lower the jack lift head until the jack fits under the vehicle.
- Raise the jack by turning the wheel wrench clockwise until the slots in the jack head fit into the metal flange located behind the triangle on the plastic molding as shown.
- Put the compact spare tire near you.
- Raise the vehicle by turning the wheel wrench clockwise. Raise the vehicle far enough off the ground for the compact spare tire to fit under the vehicle.
- Remove all the wheel nuts and the flat tire.
- Install the spare tire.
- Put the wheel nuts back on with the rounded end of the nuts toward the wheel.
- Tighten each wheel nut by turning it clockwise with your hand until the wheel is held against the hub.
- Lower the vehicle by turning the wheel wrench counterclockwise. Lower the jack completely.
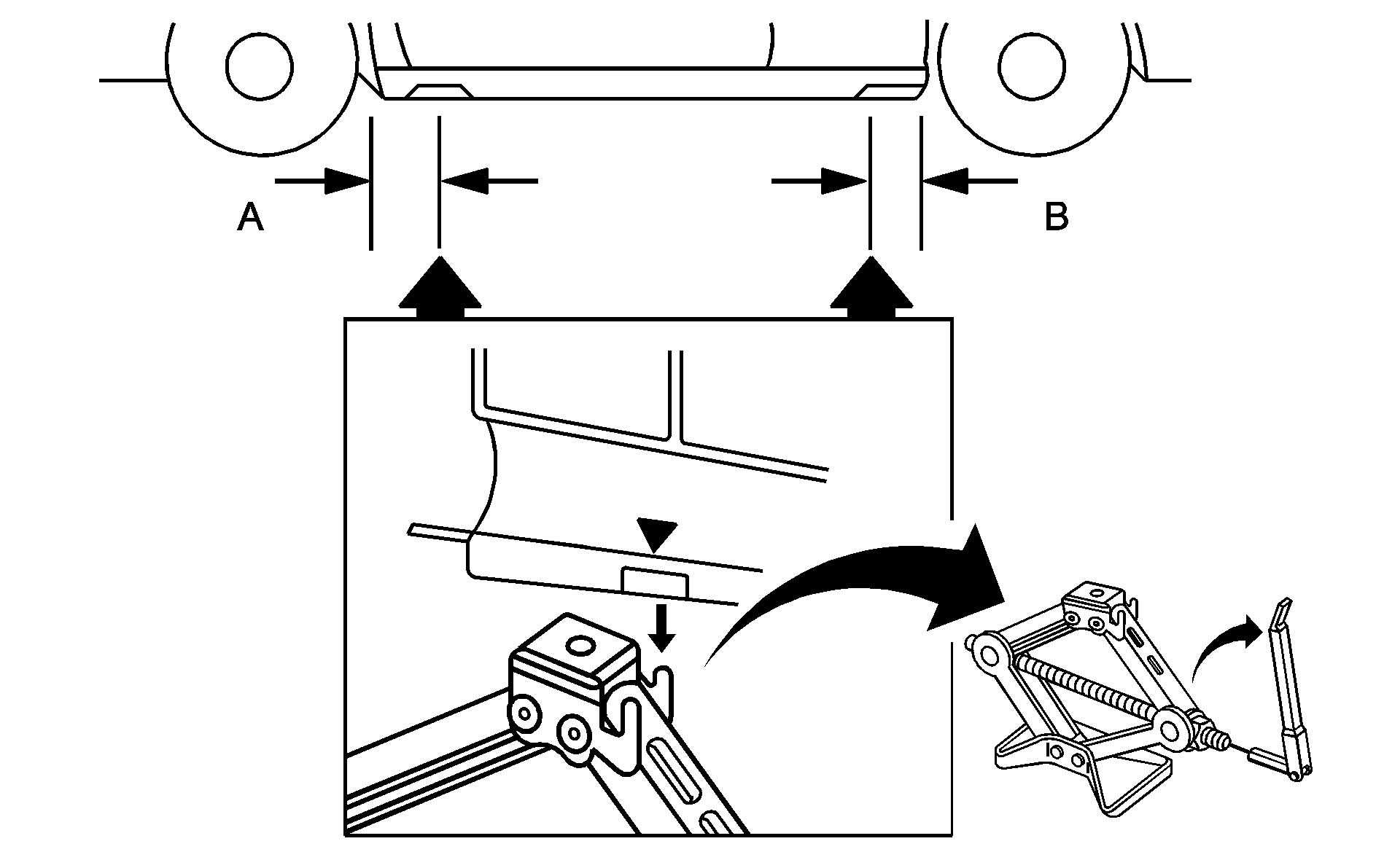
The front location (A) is about 14 inches (35.6 cm) from the rear edge of the front wheel well, and the rear location (B) is about 7 inches (17.8 cm) from the front edge of the rear wheel well.
Caution: Getting under a vehicle when it is jacked up is dangerous. If the vehicle slips off the jack you could be badly injured or killed. Never get under a vehicle when it is supported only by a jack.
Caution: Lifting a vehicle and getting under it to do maintenance or repairs is dangerous without the appropriate safety equipment and training. If a jack is provided with the vehicle, it is designed only for changing a flat tire. If it is used for anything else, you or others could be badly injured or killed if the vehicle slips off the jack. If a jack is provided with the vehicle, only use it for changing a flat tire.
Caution: Raising your vehicle with the jack improperly positioned can damage the vehicle and even make the vehicle fall. To help avoid personal injury and vehicle damage, be sure to fit the jack lift head into the proper location before raising the vehicle.
Notice: If you position the jack under the rocker molding and attempt to raise the vehicle, you could break the molding and/or cause other damage to your vehicle. Always position the jack so that when the jack head is raised, it will fit firmly in the notch located inboard from the rocker molding.
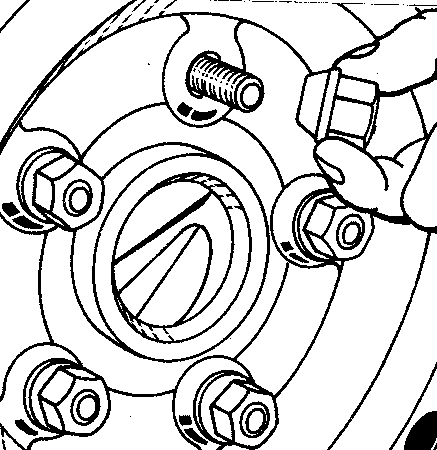
Caution: Rust or dirt on a wheel or other parts to which it is fastened, can make the wheel nuts become loose and eventually the wheel could come off and cause a crash. Always remove all rust and dirt from wheels and other parts.
Caution: Never use oil or grease on bolts or nuts because the nuts might come loose. The vehicle's wheel could fall off, causing a crash.
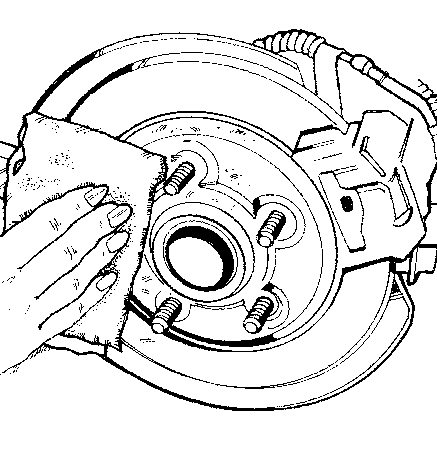
Remove any rust or dirt from the wheel bolts, mounting surfaces, and spare wheel.
Caution: Incorrect or improperly tightened wheel nuts can cause the wheel to come loose and even come off. This could lead to a crash. If you have to replace them, be sure to get new original equipment wheel nuts. Stop somewhere as soon as you can and have the nuts tightened with a torque wrench to the proper torque specification. See Capacities and Specifications for wheel nut torque specification.
Notice: Improperly tightened wheel nuts can lead to brake pulsation and rotor damage. To avoid expensive brake repairs, evenly tighten the wheel nuts in the proper sequence and to the proper torque specification. See Capacities and Specifications for the wheel nut torque specification.
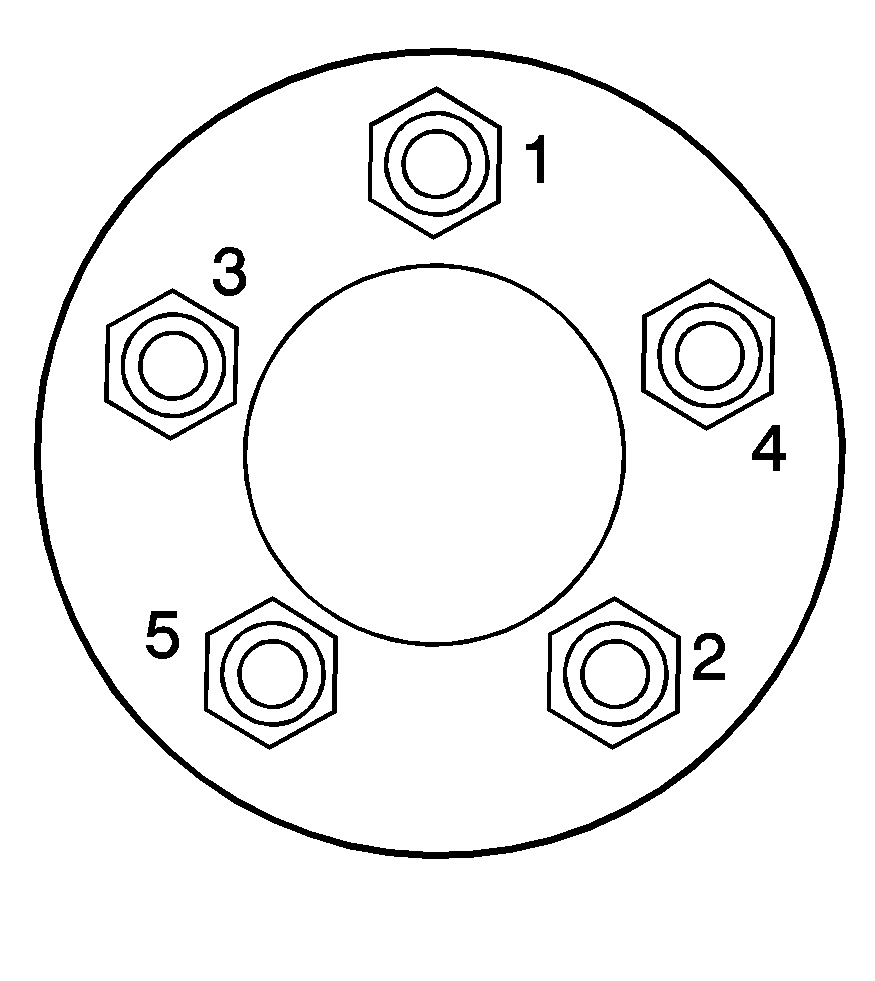
Tighten the wheel nuts firmly in a crisscross sequence as shown.
