Intake Manifold/Supercharger Assembly
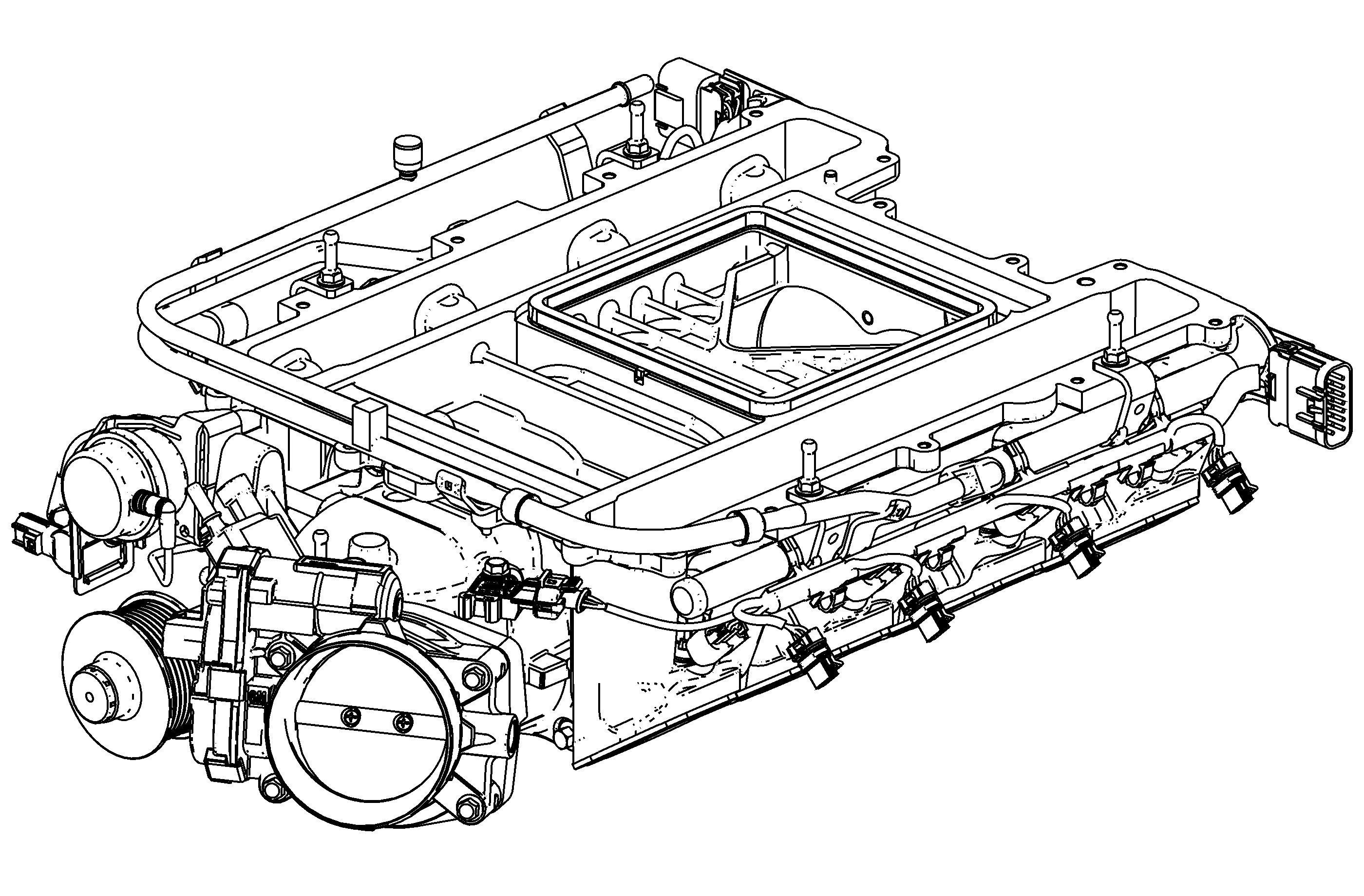
Intake Manifold/Supercharger Assembly
The LSA Roots-type supercharger is a positive displacement pump that consists of 2 counter-rotating rotors installed into the lower intake manifold housing. The rotors are designed with 4 lobes and a helical twist. The rotors of the supercharger
are designed to run at a minimal clearance, not in contact with each other or the housing and are timed to each other by a pair of precision spur gears which are pressed onto the rotor shafts. The rotors are supported at each end by self-lubricating non-serviceable
bearings. The drive belt pulley is pressed onto the input shaft. The input shaft is coupled to the rotor shaft. Both the belt pulley and torsional isolator are also non-serviceable.
The lower supercharger assembly consists of the following components:
| • | Lower Intake Manifold Housing, to include rotors, gears, bearings, torsional isolator, and drive belt pulley |
| • | Charged Air Bypass Valve |
| • | Fuel Rail with Injectors |
| • | Evaporative Emission Canister Purge Valve |
| • | Inlet Air Pressure Sensor |
Cover/Intercooler
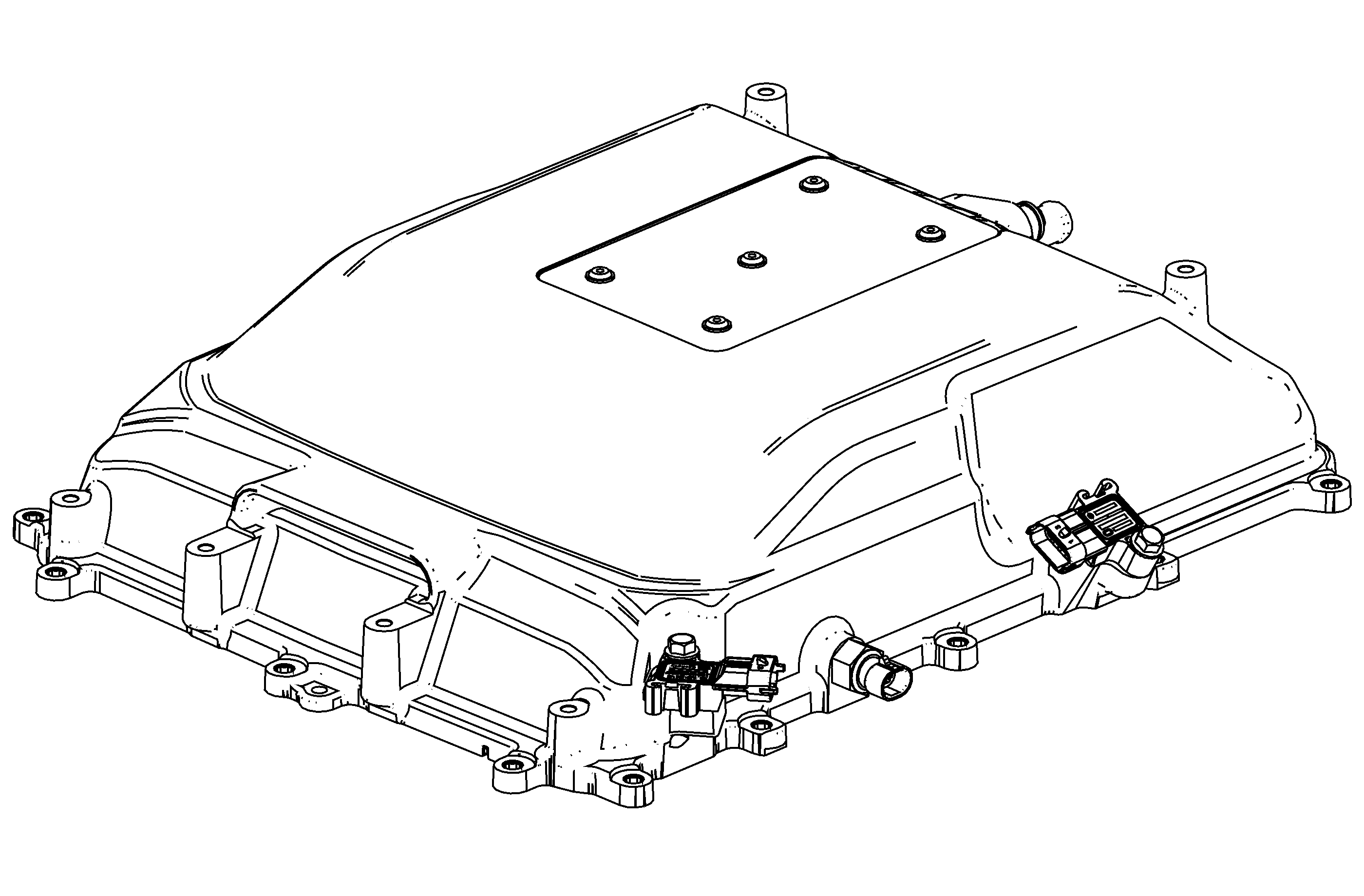
Cover/Intercooler
The cover assembly has an integrated intercooler. Cooling the air enhances the effectiveness of the supercharger. The intercooler uses conventional coolant in a system that is separate from the engine cooling system. The intercooler assembly includes the
cover, a charge air cooler/heat exchanger and a variety of sensors to monitor air temperature and pressure. The charge air cooler pipe assembly, located at the rear of cover transfers coolant to the intercooler cooling system via vehicle coolant hoses. The charge
air cooler pipe assembly is sealed to the charge air cooler with O-rings and a press-in-place seal. Coolant enters the inlet port of the assembly, is directed into and through the charge air cooler/heat exchanger, and exits returning to the separate cooling
system.
The cover/intercooler consists of the following components:
| • | Charge Air Cooler Pipe Assembly |
| • | Charge Air Cooler Cover |
| • | Charge Air Cooler/Heat Exchanger |
| • | Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor |
| • | Barometric Pressure Sensor |
| • | Air Outlet Pressure Sensor |
Operation
The supercharger is designed to increase the air pressure and density in the intake manifold. When this air is mixed with the correct amount of fuel the result is more power from the engine. This excess air creates a boost pressure in the intake manifold
with a maximum engine boost of 69.6 kPa (10.1 psi). Because the supercharger is a positive displacement pump and is directly driven from the engine drive belt system, boost pressure is available at all driving conditions.
When boost is not required in situations such as idle or light throttle cruising, the excess air is routed through an internal bypass passage located between the intake manifold and the supercharger inlet. The bypass circuit is regulated by a bypass valve
which is similar to a throttle plate. Spring force holds the bypass valve in a normally closed position to create boost.
The bypass actuator is a vacuum operated valve that is connected to the vacuum signal between the throttle and the supercharger inlet. Vacuum to the actuator pulls the bypass valve open during idle and light load conditions to decrease boost.
The charge air bypass valve is a vacuum/electrically operated solenoid valve that is attached to the supercharger housing. The three-way valve is controlled by the engine control module (ECM). The ECM determines when pressure from the manifold is
routed to the bypass actuator. The charge air bypass valve allows pressure from the manifold to open the bypass valve and lower boost pressure during specific driving conditions. The open bypass valve reduces the pumping effort of the supercharger, thereby increasing
the fuel efficiency in light load operations.


